Abstract
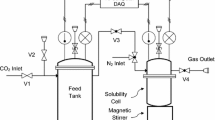
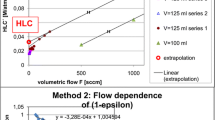
Many nonvolatile organic compounds, e.g., polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), are readily stripped during aerobic biodegradation. This is because of the high infinite dilution activity coefficient resulting from forces generated by the water-organic interactions at the molecular level. Several models have been proposed for air-stripping based on the Henry’s law constant. By definition, the Henry’s law constant is the infinite dilution activity coefficient multiplied by the pure component vapor pressure. In this article, a gas saturation technique was used to measure the very low vapor pressures exhibited by these nonvolatile compounds. Literature values of other PAHs have been tabulated and are presented. For determining infinite dilution activity coefficients, a differential ebulliometery apparatus has been constructed. In this technique, the boiling point difference between pure water and a water-organic solution is measured very precisely. Thermodynamics is then used to calculate the infinite dilution activity coefficient. The method’s accuracy has been tested using the phenol-water system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbuckle, W. B. (1983),Environ. Sci. Tech. 17(9), 537.
Blackburn, J. W., Troxler, W. L., Truong, N. K., Zink, R. P., Meckstroth, S.C., Florance, J. R., Groen, A., Sayler, G. S., Beck, R. W., Minear, R. A., Breen, A., and Yagi, O. (1985), EPA Project Report 600/S2-85/102.
DiGrazia, P. M., Blackburn, J. W., Bienkowski, P. R., Hilton, B., Reed, G. D., King, J. M., and Sayler, G. S. (1990),Applied Biochem. Biotech. 24/25, 1.
Macknick, A. B. and Prausnitz, J. M. (1979),J. Chem. Eng. Data. 24(3), 175.
Reid, R. Prausnitz, and Poling, E. (1986),The Properties of Gases and Liquids., Sun, B. and Fleck, G. H., ed., McGraw-Hill, New York.
Murphy, T. J., Mullin, M. D., and Meyer, J. A. (1987),Environ. Sci. Tech. 21(2), 155.
Karickhoff, S. W. and Morris, K. R. (1985),Environ. Toxic. Chem. 4, 469.
Dilling, W. L. (1977),Environ. Sci. Tech. 11(4), 405.
Blackburn, J. W., Troxler, W. L., and Sayler, G. S. (1984),Environ. Prog. 3(3), 163.
Barton, D. A. (1987),Environ. Prog. 6(40), 246.
Smith, J. H., Bomberger, D. C., and Haynes, D. L. (1980),Environ. Sci. Tech. 14(11), 1332.
Prausnitz, J. M., Lichtenthaler, R. N., and deAzevedo, E. G. (1986),Molecular Thermodynamics of Fluid-Phase Equilibria, Amundson, N. R., ed., Prentice-Hall, New Jersey.
Carruth, G. F. and Kobaysahi, R. (1973),J. Chem. Eng. Data 18(2), 115.
Sonnefeld, W. J. and Zoller, W. H. (1983),Anal. Chem. 55, 275.
Westcott, J. W. Simon, G., and Bidleman, T. F. (1981),Environ. Sci. Tech. 15(11), 1375.
Hansen, P. and Eckert, A. (1986),J. Chem. Eng. Data. 31(1), 1.
Osborne, A. G. and Douslin, D. R. (1975),J. Chem. Eng. Data 20(3), 229.
Murray, J. J., Pottie, R. F., and Pupp, C. (1974),Can. J. Chem. 52, 557.
Dunbar, P. D. (1989), Master’s Thesis, University of Tennessee.
Thomas, E. R. (1977) Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Illinois.
Olson, J. D. (1981),J. Chem. Eng. Data. 26(1), 58.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moore, R.C., Bienkowski, P.R. Henry’s law constant for environmentally significant compounds. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 34, 671–680 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02920588
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02920588