Abstract
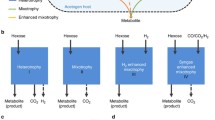
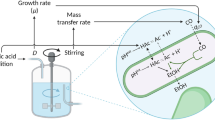
Continuous, steady-state fermentations using carbon monoxide gas as the sole carbon and energy source have been achieved with the CO strain ofButyribacterium methylotrophicum. Fermentation pH was found to regulate carbon monoxide metabolism over the pH range of 6.8 to 5.0. Cell growth diminished at low pH, with washout occurring at pH 5.0. As observed previously in batch culture, lower pH values favored production of butyrate over acetate. The mechanism responsible for this trend is currently being investigated by quantification of key intracellular enzyme activities.
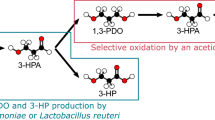
At low pH values, direct, steady-state fermentation of carbon monoxide to alcohols has been verified. Of major significance is the production of butanol from carbon monoxide in pure culture. This newly identified pathway provides a potential mechanism for direct bioconversion of synthesis gas to butanol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zeikus, J. G. (1981),Anaerobic Digestion, Elsevier, Oxford, p. 23.
Zeikus, J. G. (1983),Adv. Microbiol. Phys. 24, 218.
Zeikus, J. G. (1983),Organic Chemicals From Biomass, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, p. 359.
Zeikus, J. G., Kerby, R., and Krzycki, J. A. (1985),Science 227, 1167.
Kerby, R. and Zeikus, J. G. (1983),Curr. Microbiol. 8, 27.
Lorowitz, W. H., and Bryant, M. P. (1984),Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 47, 961.
Sharak-Genthner, B. P., Davis, C. L., and Bryant, M. P. (1981),Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 42, 12.
Sharak-Genthner, B. P. and Bryant, M. P. (1982),Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 43, 70.
Zeikus, J. G., Lynd, L. H., Thompson, T. E., Krzycki, J. A., Weimer, P. J., and Hegge, P. W. (1980),Curr. Microbiol. 3, 381.
Lynd, L. H., Kerby, R., and Zeikus, J. G. (1982),J. Bacteriol. 149, 225.
Worden, R. M., Grethlein, A. J., Zeikus, J. G., and Datta, R. (1989),Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 20/21, 687.
Erickson, L. E., Minkevich, I. G., and Eroshin, V. K. (1978),Biotech. Bioeng. 20, 1595.
Erickson, L. E. and Oner, M. D. (1983),Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 413, 99.
Erickson, L. E., Selga, S. E., and Viesturs, U. E. (1978),Biotech. Bioeng. 20, 1623.
Grethlein, A. J., Worden, R. M., Jain, M. K., and Datta, R. (1990),Appl. Environ. Microbiol., submitted.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grethlein, A.J., Worden, R.M., Jain, M.K. et al. Continuous production of mixed alcohols and acids from carbon monoxide. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 24, 875–884 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02920301
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02920301