Abstract
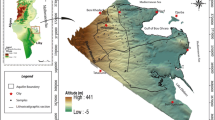
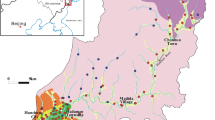
The main hydrogeochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater in the coastal area at Kimje city, Korea, have been identified in the present study. From cluster analysis, the groundwater in the study area is classified into four groups (A, B, C, and D). Groundwaters in B, C, and D groups are strongly affected by the present seawater and the trapped old seawater because the area including B, C, and D groups contacts the Yellow Sea and contains the reclaimed land. They also are governed by reduction processes. On the other hand, groundwater in group A has been largely affected by chemical fertilizers because its land has been used for the agricultural activities for a long time. As groundwater flows from group A to group D according to its path, the governing factor of the groundwater quality gradually tends to change from chemical fertilizers into reduction processes and seawater intrusion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah, M.H., Mokhtar, M.B., Tahir, S.H.J. and Awaluddin, A.B.T., 1997, Do tides affect water quality in the upper phreatic zone of a small oceanic island, Sipadan Island, Malaysia? Environmental Geology, 29, 112–117.
Aggarwal, P.K., Fuller, M.F., Gurgas, M.M., Manning, J.F. and Dillon, M.A., 1997, Use of stable oxygen and carbon isotope analyses for monitoring the pathways and rates intrinsic and enhanced in situ biodegradation. Environmental Science & Technology 31, 590–596.
Karker, A.P., Newton, R.J. and Bottrell, S.H., 1998, Processes affecting groundwater chemistry in a zone of saline intrusion into an urban sandstone aquifer, Applied Geochemistry, 13, 735–749.
Bear, J., Cheng, A.H.D., Sorek, S., Ouazar, D. and Herrera, I., 1999, Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers—Concepts, Methods and Practices, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 625 p.
Choi, S.H. and Kim, Y.K., 1989, Geochemical characteristics of groundwater in Cheju Island. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 25, 230–238 (in Korean with English abstract).
Cruz, J.V. and Silva, M.O., 2000, Groundwater salinization in Pico island (Azores, Portugal): origin and mechanisms, Environmental Geology, 39, 1181–1189.
Giménez, E. and Morell, I., 1997, Hydrogeochemical analysis of salinization processes in the coastal aquifer of Oropesa (Castellón, Spain), Environmental Geology, 29, 118–131.
Davis, S.N., Whittemore, D.O. and Fabryka-Martin, J., 1998, Uses of chloride/bromide ratios in studies of potable water. Ground Water, 36, 338–350.
Eaton, A.D., Clesceri, L.S. and Greenberg, A.E., 1995, Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 19th ed. APHA, AWWA and WPCF, Washington, D.C.
Fetter, C.W., 1994, Applied Hydrogeology. Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 572p.
Helena, B., Prardo, R., Vega, M., Barrado, E., Fernandez, J.M. and Fernandez, L., 2000, Temporal evolution of groundwater composition in an alluvial aquifer (Pisuerga River, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Research, 34, 807–816.
Kim, J.H., 2001, Hydrogeochemical study on shallow groundwater at the coastal area of Kimje. MS thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, 96p.
Kim, J.H., Kim, R.K., Lee, J. and Chang, H.W., 2003, Hydrogeochemical characterization of major factors affecting the quality of shallow groundwater in the coastal area at Kimje in South Korea. Environmental Geology, 44, 478–489.
Landmeyer, J.E., Vorblesky, D.A. and Chappele, F.H., 1996, Stable carbon isotope evidence of biodegradation zonation in a shallow jet-fuel contaminated aquifer. Environmental Science & Technology, 30, 1120–1128.
Lee, K.S., Wenner, D.B. and Lee, I., 1999, Using H- and O-isotopic data for estimating the relative contributions of rainy and dry season precipitation to groundwater: example for Cheju Island, Korea. Journal of Hydrology, 222, 65–74.
Louvat, D., Michelot, J.L. and Aranyossy, J.F., 1999, Origin and residence time of salinity in the Äspö groundwater system. Applied Geochemistry, 14, 917–925.
Morris, A.W. and Riley, J.P., 1966, The bromide/chlorinity and sulphate/ hlorinity ratios in seawater. Deep-Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 13–14, 699–705.
Park, G.S. and Oh, Y.K., 1996, A study on the chemical characteristic of ground-seawater in the coast of Cheju Island, Economic and Environmental Geology, 18, 310–315 (in Korean with English abstract)
Park, Y.S., Kim, J.K. and Kim, J., 2001, Petrochemistry of Granitoids in the Younggwang-Kimje area, Korea. Economic and Environmental Geology, 34, 55–70 (in Korean with English abstract).
Price, B.N. and Calvert, S.E., 1977, The contrasting geochemical behaviors of iodine and brominein resent sediments from the Nambian Shelf. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 41, 1769–1775.
Richter, B.C., Kreitler, C.W. and Bledsoe, B.E., 1993, Geochemical techniques of identifying sources for groundwater salinization. CRC Press, New York, 285p.
Stumm, W. and Morgan, J.J., 1996, Aquatic chemistry: chemical equilibria and rates in natural waters. 3rd edn, Wiley, New York, 1022 p.
Sukhija, B.S., Varma, V.N., Nagabhushanam, P. and Reddy, D.V., 1996, Differentiation of palaeomarine and modern seawater intruded salinities in coastal line groundwater (of Karaikal and Tanjavur, India) based on inorganic chemistry, organic biomarker fingerprints and radiocarbon dating, Journal of Hydrology, 174, 173–201.
Vega, M., Pardo, R., Barrado, E. and Deban, L., 1998, Assessment of seasonal and polluting effects on the quality of river water by exploratory data analysis. Water Research, 32, 3581–3592.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JH., Yum, BW., Kim, RH. et al. Application of cluster analysis for the hydrogeochemical factors of saline groundwater in Kimje, Korea. Geosci J 7, 313–322 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02919561
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02919561