Summary
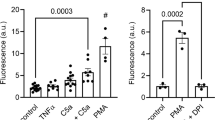
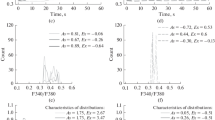
The past few years have seen a significant refinement in our understanding of the mechanism of activation of granulocytes. The involvement of surface receptors and the role of calcium as second messenger have been further supported by recent data. However, with the exception of the unexamined potential role of ITP, all the previous hypotheses attempting to provide a biochemical basis for the transduction mechanisms involved in calcium mobilization have either been dismissed or at the least been seriously weakened by lack of experimental support. A particularly glaring example of the work that still needs to be done is the near total lack of knowledge about stimuli-induced changes in the physical properties of the plasma membrane of these cells and of the biochemical targets of the raised levels of cytoplasmic calcium (e.g. protein kinases). Glimpses into the nature of the calcium-independent pathway of neutrophil activation have been provided by phorbol esters. The modulatory nature of the role of cyclic mucleotides appears to have been established, its biochemical basis, however, is unknown. The description of the dynamic nature of the neutrophils’ cytoskeletal structures should lay the foundation of the understanding of the regulation of the neutrophils’ force generating system, the structure(s) ultimately responsible for the expression of the critical granulocyte functions of locomotion, phagocytosis, and granule fusion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bareis, D.L.; Hirata, F.; Schiffmann, E.; Axelrod, J.: Phospholipid metabolism, calcium flux, and the receptor mediated induction of chemotaxis in rabbit neutrophils. J. Cell Biol.93: 690–697 (1982).
Bormann, B.J.; Huang, C.-K.; Mackin, W.M.; Becker, E.L.: Receptor-mediated activation of a phospholipase A2 in rabbit neutrophil plasma membrane. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. USA (in press, 1984).
Chandler, D.; Meusel, G.; Schumaker, E.; Stapleton, D.: FMLP-induced enzyme release from neutrophils: a role for intracellular calcium. Am. J. Physiol.245: C196-C202 (1983).
Chenoweth, D.E.; Goodman, M.G.: The C5a receptor of neutrophils and macrophages; in Keller, Till, Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis, pp. 252–269 (Birkhäuser, Basel 1983).
Coates, T.D.; Torres, M.; Williams, L.V.; Sisken, J.E.; Baehner, R.L.: Localization of the chlorotetracycline labelled pool of trigger calcium in human neutrophils by quantitative video intensification microscopy. J. Cell Biol.97: 420a (1983).
Cockcroft, S.: Phosphatidylinositol metabolism in mast cells and neutrophils. Cell Calcium3: 337–349 (1982).
Downs, P.; Michell, R.H.: Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-bisphosphate: lipids in search of a function. Cell Calcium3: 467–502 (1982).
Fletcher, M.P.; Gallin, J.I.: Human neutrophils contain an intracellular pool of putative receptors for the chemoattractant N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine. Blood62: 792–799 (1983).
Garcia-Castro, I.; Mato, J.M.; Vasanthakuman, G.; Wiesmann, W.P.; Schiffmann, E.; Chiang, P.K.: Paradoxical effects of adenosine on neutrophil chemotaxis. J. biol. Chem.255: 4345–4549 (1983).
Goldman, D.W.; Goetzl, E.J.: Specific binding of leukotriene B4 to receptors on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J. Immun.129: 1600–1604 (1982).
Gomperts, B.: Involvement of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the gating of Ca2+ by receptors. Nature, Lond.306: 64–66 (1983).
Holmes, R.P.; Yoss, N.L.: Failure of phosphatidic acid to translocate Ca2+ across phosphatidylcholine membranes. Nature, Lond.305: 637–638 (1983).
Huang, C.-K.; Hill, J.M.; Bormann, B.-J.; Mackin, W.M.; Becker, E.L.: Endogenous substrates for cyclic AMP-dependent and calcium-dependent protein phosphorylation in rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. Biochim. biophys. Acta.760: 126–135 (1983).
Jackowski, S.; Sha’afi, R.I.: Response of adenosine cyclic 3′, 5′-monophosphate level in rabbit neutrophils to the chemotactic peptide formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine. Molec. Pharmacol.16: 473–481 (1979).
Jesaitis, A.J.; Naemura, J.R.; Painter, R.G.; Sklar, L.A.; Cochrane, C.G.: The fate of an N-formylated chemotactic peptide in stimulated human granulocytes. J. biol. Chem.258: 1969–1977 (1983).
Koo, C.; Lefkowitz, R.I.; Snyderman, R.: The oligopeptide chemotactic factor receptor on human polymorphonuclear leukocyte membranes exists in two affinity states. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun.106: 442–449 (1982).
Mackin, W.M.; Huang, C.-K.; Becker, E.L.: The formyl peptide chemotactic receptor on rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. J. Immun.129: 1608–1611 (1982).
Michell, R.H.: Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim. biophys. Acta415: 81–147 (1975).
Naccache, P.H.; Sha’afi, R.I.: Arachidonic acid, leukotriene B4 and neutrophil activation. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. (in press, 1984).
Niedel, J.E.; Cuatrecasas, P.: Formyl peptide chemotactic receptors of leukocytes and macrophages. Curr. Top. cell. Regul.17: 137–170 (1980).
Palmer, R.J.J.; Salmon, J.A.: Release of leukotriene B4 from human neutrophils and its relationship to degranulation induced by N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine, serum treated zymosan and the ionophore A23187. Immunology.50: 65–73 (1983).
Pozzan, T.; Lew, D.P.; Wollheim, C.B.; Tsien, R.Y.: Is cytosolic ionized calcium regulating neutrophil activation? Science221: 1413–1415 (1983).
Schiffmann, E.; Corcoran, B.A.; Wahl, S.A.: N-for-mylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. USA72: 1059–1062 (1975).
Schmitt, M.; Painter, R.C.; Jesaitis, A.J.; Preissner, K.; Sklar, L.A.; Cochrane, C.G.: Photoaffinity labelling of the N-formyl peptide receptor binding site of intact human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J. biol. Chem.258: 649–654 (1983).
Schneider, C; Zanetti, M.; Romeo, D.: Surface reactive stimuli selectively increase protein phosphorylation in human neutrophils. FEBS Lett.127: 4–8 (1981).
Serhan, C; Anderson, P.; Goodman, E.; Dunham, P.; Weissmann, G.: Phosphatidate and oxidized fatty acids are calcium ?onophores J. biol. Chem.256: 2736–2741 (1982).
Sha’afi, R.I.; Naccache, P.H.: Ionic events in neutrophil chemotaxis and secretion. Adv. Inflammation Res., vol. 2, pp. 115–148 (Raven Press, New York 1981).
Sha’afi, R.I.; White, J.R.; Molski, T.F.P.; Shefcyk, J.; Volpi, M.; Naccache, P.H.; Feinstein, M.B.: Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate activates rabbit neutrophils without an apparent rise in the level of intracellular calcium. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun.114: 638–645 (1983).
Simchowitz, L.; Spilberg, I.; Atkinson, J.P.: Evidence that the functional responses of human neutrophils occur independently of transient elevations in cAMP levels. J. cyclic Nucleotide Prot. Phosphoryl. Res.9: 35–47 (1983).
Sirois, P.; Borgeat, P.: Mediators of immediate hypersensitivity. Immunopharmacology4: 201–222 (1982).
Snyderman, R.; Edge, S.; Pike, M.C.: Macrophage chemotactic factor receptor exists in two interconvertible affinities modulated by guanine nucleotides. Clin. Res.30: 521A (1982).
Snyderman, R.; Goetzl, E.J.: Molecular and cellular mechanisms of leukocyte chemotaxis. Science213: 830–837 (1981).
Streb, H.; Irvine, R.F.; Berridge, M.J.; Shulz, I.: Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature, Lond.306: 67–69 (1983).
Tsien, R.Y.: A non-disruptive technique for loading calcium buffers and indicators into cells. Nature Lond.290: 527–528 (1981).
Volpi, M.; Yassin, R.; Naccache, P.H.; Sha’afi, R.I.: Chemotactic factor causes rapid decrease in phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-bis-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4-monophosphate in rabbit neutrophils. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun.112: 951–964 (1983).
White, J.R.; Huang, C.-K.; Hill, J.; Naccache, P.H.; Becker, E.L.; Sha’afi, R.I.: Effect of PMA and its analogue 4-α-PDD on protein phosphorylation, actin association with cytoskeleton, lysozomal enzyme release and cell aggregation in rabbit neutrophils (submitted for publication 1984).
White, J.R.; Naccache, P.H.; Molski, T.F.P.; Borgeat, P.; Sha’afi, R.I.: Direct demonstration of increased intracellular concentration of free calcium in rabbit and human neutrophils following stimulation by chemotactic factor. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun.113: 44–50 (1983a).
White, J.R.; Naccache, P.H.; Sha’afi, R.I.: Stimulation by chemotactic factor of actin association with the cytoskeleton in rabbit neutrophils. Effects of calcium and cytochalasin B. J. biol. Chem.258: 14041–14047 (1983b).
Young, J.D.-E.; Unkeless, J.C.; Young, T.M.; Mauro, A.; Cohn, Z.A.: Role for mouse macrophage IgG Fc receptor as ligand-dependent ion channel. Nature, Lond.306: 186–189 (1983).
Zigmond, S.H.; Sullivan, S.T.; Lauffenburger, D.A.: Kinetic analysis of chemotactic peptide receptor modulation. J. Cell Biol.92: 34–43 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by NIH grants AM-31000, AI-09648, and AI-13734.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naccache, P.H., Sha’afi, R.I. Granulocyte activation. Surv. immunol. Res. 3, 288–294 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02919046
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02919046