Summary
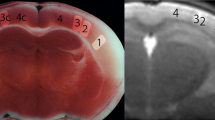
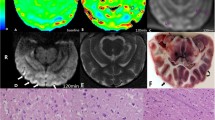
To study the dynamic changes of CT perfusion parameters during the first 12 h in the embolic cerebral ischemia models. Local cerebral ischemia model were established in 7 New Zealand white rabbits. All CT scans were performed with a GE Lightspeed 16 multislice CT. Following the baseline scan, further CT perfusion scans were performed at the same locations 20 min, 1–6 h and 8, 10 and 12 h after the embolus delivery. Maps of all parameters were obtained by CT perfusion software at each time point. The brains, taken 12 h after the scan, were sliced corresponding to the positions of the CT slices and stained by 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC). On the basis of the TTC results, the ischemic sides were divided into 3 regions: core, penumbra and the relatively normal region. The changes of all parameters were then divided into 3 stages. In the first two hours (the first stage), the CBV dropped more remarkably in the core than in the penumbra but rose slightly in the relatively normal region while the CBF decreased and MTT, TTP extended in all regions to varying degrees. In the 2nd–5th h (the second stage), all the parameters fluctuated slightly around a certain level. In the 5th–12th h (the third stage), the CBV and CBF dropped, and MTT and TTP were prolonged or shortened slightly in the core and penumbra though much notably in the former while the CBV, CBF rose and MTT, TTP were shortened remarkably in the relatively normal region. We experimentally demonstrated that the location and extent of cerebral ischemia could be accurately assessed by CT perfusion imaging. The pathophysiology of the ischemia could be reflected by the CT perfusion to varying degrees.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deborah F, Patrick L, Paul A Let al. Comparison of TNK with wild-type tissue plasminogen activator in a rabbit embolic stroke model. Stroke, 2001, 32: 748
Darius G N, Aleksa C, Sarah Het al. Perfusion mapping using computed tomography allows accurate prediction of cerebral infarction in experimental brain ischemia. Stroke, 2001, 32: 175
Cheung R T, Cheng P W, Lui W Met al. Visualization of ischaemic penumbra using a computed tomography perfusion method. Cerebrovasc Dis, 2003, 15: 182
Barnett H J, Mohr J P, Stein B Met al. Stroke: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management, 3rd ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone Press, 1998. 103
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
CHEN Weiwei, female, born in 1977, Doctoral Student
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weiwei, C., Jianpin, Q., Jinhua, Z. et al. Dynamic changes of the CT perfusion parameters in the embolic model of cerebral ischemia. Current Medical Science 24, 615–617 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02911372
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02911372