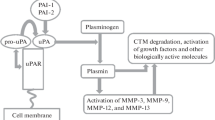
Abstract
We measured the antigen levels of urokinasetype plasminogen activator (u-PA) and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) in tissue extracts from nasopharyngeal carcinomas. An increase in u-PA antigen was observed with the advanced stages of disease. However, the levels of PAI-1 antigen decreased with each advanced stage. These results suggest that local administration of antiplasminic agents may be effective in suppressing tumor invasion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carrell RW, Boswell DR (1986) Serpins: the superfamily of plasma proteinase inhibitors. In: Barrett A, Salvesen S, (eds) Proteinase inhibitors. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 403–420
Danø K, Andreasen PA, Grondahl-Hansen J, Kristensen P, Nielsen LS, Skriver L (1985) Plasminogen activators tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res 44: 139–266
Kosugi T, Huang G-W, Nakamura M, Koja S, Nong H-T (1990) Identification of a plasminogen activator derived from nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 247: 374–378
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall JR (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193: 265–295
Markus G, Camiolo SM, Kohga S, Madeja JM, Mittelman A (1983) Plasminogen activator secretion of human tumor in short-term organ culture, including a comparison of primary and metastatic colon tumors. Cancer Res 43: 5517–5525
Nagayama M, Sato A, Hayakawa H, Urano T, Takada Y, Takada A (1994) Plasminogen activators and their inhibitors nonsmall cell lung cancer: low content of type 2 palsminogen activator inhibitors associated with tumor dissemination. Cancer 73: 1398–1405
Nishino N, Aoki K, Tokura Y, Sakaguchi S, Takada Y, Takada A (1988) The urokinase type of plasminogen activator in cancer of digestive tract. Thromb Res 50: 527–535
Pappot H, Gårdsvoll H, Rømer J, Pedersen AN, Grøndahl-Hansen J, Pyke J, Brünner N (1995) Plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 in cancer: therapeutic and prognostic implications. Biol Chem Hoppe-Seyler 376: 259–267
Saksela O, Rifkin DB (1988) Cell-associated plasminogen activator: regulation and physiological function. Annu Rev Cell Biol 4: 93–126
Schwab W, Clasen B, Steinhoff H-J (1987) Neue und geänderte Richtlinien zum TNM-System im Kopf-Hals-Bereich. HNO 35: 112–118
Sumiyoshi K, Baba S, Sakaguchi S, Urano T, Takada Y, Takada A (1991) Increase in levels of plasminogen activator and type-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor in human breast cancer: possible roles in tumor progression and metastasis. Thromb Res 63: 59–71
Vassalli J-D, Sapppino A-P, Belin D (1991) The plasminogen activator/plasmin system. J Clin Invest 88: 1067–1072
Wiman B, Almquist Å, Sigurdardottir O, Lindahl T (1988) Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1) is bound to vitronectin in plasma. FEBS Lett 242: 125–128
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sunagawa, M., Huang, G.W., Nakamura, M. et al. The concentration of u-PA and PAI-1 antigen in tissue extracts of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 254, 277–280 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02905987
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02905987