Abstract
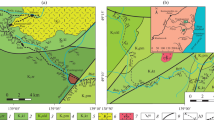
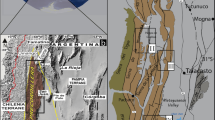
The sedimentary characteristics, grain-size distribution, geochemical composition and surface characteristics of quartz grains, together with palaeoenvironmental reconnaissance, all point to an aeolian origin for the intercalated siltstone beds in the Plio-Pleistocene Artux and Xiyu Formations along the southern margins of the Tarim Basin, indicating that loess deposition in the region started, at least, in the Early Pliocene. Loess deposition in the southern Tarim Basin was a response to the global deterioration, which might be attributed to the uplift of the Tibetan Plateau.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, T., Loess Deposits in China (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 1965, 1–115.
Zheng, H., An, Z., Shaw, J., New contribution to Chinese Plio-Pleistocene magnetostratigraphy, Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interior, 1992, 70: 146.
Ding, Z., Xiong, S., Sun, J. et al., Pedostratigraphy and paleomagnetism of an approximately 7.0 Ma eolian loess-red clay sequence at Lingtai, Loess Plateau, north-central China, Palaeogeogr., Palaeoclimatol., Palaeoecol., 1999, 152: 49.
Sun, D., Shaw, J., An, Z. et al., Magnetostratigraphy and paleoclimatic interpretation of a continuous 7.2 Ma late Cenozoic Elias sediments from the Chinese Loess Plateau, Geophysical Research Letters, 1998, 25(1): 85.
Qiang, X., An, Z., Li, Z. et al., Magnetostratigraphic record of the late Miocene onset of the East Asian monsoon, and Pliocene uplift of Northern Tibet, Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2001, 187: 83–93.
Liu, T., Loess and the Environment (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 1985, 1–481.
Dong, G., Chen, H., Jing, J. et al., Cenozoic paleo-eolian sands in the south marginal area of Taklimakan Desert (ed. Dong, G.), Proceedings of Study on the Formation and Palaeoclimatic Changes of the Deserts in China, Lanzhou Institute of Desert Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese), 1996, 42–48.
Li, B., Dong, G., Zhang, J. et al., Aeolian facies distribution in and to the south of the Taklimakan Desert, Acta Geologica Sinica (in Chinese), 1995, 69(1): 55.
Zheng, H., Powell, C., An, Z. et al., Pliocene uplift of the northern Tibetan Plateau, Geology, 2000, 28(8): 715.
Cande, S., Kent, D., Revirsed calibration of the geomagnetic polarity timescale for the Late Cretaceous and Cenozoic, Journal of Geophysical Research, 1995, 100: 6093.
Li, Y. T. (ed.), Stratigraphy of China, 13: Tertiary (in Chinese), Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1984, 1–325.
Zhu, Z., The Aeolian Landforms of the Taklimakan Desert, Beijing: Science Press, 1981, 1–350.
Wen, Q., Qiao, Y., Palaeoclimatic records of late Pleistocene sediments in the northern Kunlun (ed. Tibetan Plateau Research Association), Proceedings of the Tibetan Plateau and Global Change (in Chinese), Beijing: Meteorology Press, 1995, 96–104.
Li, B., Li, S., Wang, Y. et al., Geological age of the sand and dust deposits of the Aqiang section in the extremely arid region of China, Acta Geological Sinica, 1998, 72(1): 83.
Ruddiman, W. F., Kutzbach, J. E., Forcing of late Cenozoic Northern Hemisphere climate by plateau uplift in southern Asia and the American west, Journal of Geophysical Research (in Chinese), 1989, 94(D15): 18409.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, H., Chen, H. & Cao, J. Palaeoenvironmental implication of the Plio-Pleistocene loess deposits in southern Tarim Basin. Chin.Sci.Bull. 47, 700–704 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02902833
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02902833