Abstract
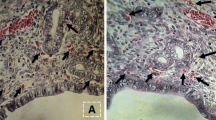
The first distinct mark of rodent implantation is the increased vascular permeability and significant angiogenesis at the sites of blastocyst implantation, but its mechanism is not clearly defined. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is the key mediator for angiogenesis during embryogenesis and adult span and also serves as a vascular permeability factor. The aim of this study is to explore VEGF regulation mechanism and the possible role that VEGF plays in implantation by studying the VEGF expression and angiogenesis in the rat uterus during estrous cycle, ovarioectomized and peri-implantation stages usingin situ message RNA hybridization and confocal laser scanning techniques. The results indicated that VEGF was regulated by ovarian steroid hormones. VEGF expression before implantation was localized at luminal epithelium, shifted to stroma as implantation initiated and extensively located at the decidualizing stroma region after implantation. Bandeiraea simplicifolia-1 (BS-1) agglutinin and antibody against von Willebrand factor (vWF) were used to mark the endothelial cells and blood vessels. The results showed that the active angiogenesis occurred during the implantation process and this effect was probably mediated by VEGF. The results suggest that under the regulation of ovarian steroid hormones, VEGF plays an essential role in angiogenesis and increasing vascular permeability in endometrium, which are necessary for successful implantation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Enders, A. C., Schlafke, S. A., Morphological analysis of the early implantation stages in the rat, Am. J. Anat., 1967, 120: 185.
Parr, E. L., Tung, H. N., Parr, M. B., Apoptosis as the mode of uterine epithelial cell death during embryo implantation in mice and rats, Biol. Reprod., 1987, 36: 211.
Thomas, K. A., Hewelman, D. M., Kuang, W. J. et al., Vascular endothelial growth factor, a potent and selective angiogenic agent, J. Biol. Chem., 1996, 271(2): 603.
Shalaby, F., Rossant, J., Yamaguchi, T. P. et al., Failure of blood-island formation and vasculogenesis in FLK-1-deficient mice, Nature, 1995, 376: 62.
Ferrara, N., Oshea, K. S., Carvermoore, K. et al., Heterozygous embryonic lethality induced by targeted inactivation of the VEGF gene, Nature, 1996, 380: 339.
Schaeren-Wilemers, N., Gerfin-Moser, A., A single protocol to detect transcripts of various types and expression levels in neural tissue and cultured cells:in situ hybridization using digoxigenin-labelled cRNA probes, Histochemistry, 1993, 100: 431.
Luo, W. X., Zhu, C., Expression and regulation of mRNAs for insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and LH receptor in corpora lutea, Science in China, Ser. C, 2000, 43(2): 183.
Karuri, A. R., Kumar, A. M., Mukhopadhyay, D., Differential expression and selective localization of vascular permeability factor/ vascular endothelial growth factor in the rat uterus during the estrous cycle, J. Endocrinol., 1998, 159: 489.
Knobil, E., Neill, J. D., The Physiology of Reproduction, Vol. 2, New York: Raven Press, 1988, 1898.
Bausero, P., Cavaille, F., Meduri, G. et al., Paracrine action of vascular endothelial growth factor in the human endometrium: production and target sites, and hormonal regulation, Angiogenesis, 1998, 2: 167.
Cullinan-Bove, K., Kathleen, C. D., Koos, R. D., Vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor expression in the rat uterus: rapid stimulation by estrogen correlates with estrogen-induced increases in uterine capillary permeability and growth, Endocrinology, 1993, 133: 829.
Psychoys, A., Endocrine control of egg implantation, in Handbook of Physiology (eds. Greep, R. O., Astwood, E. G., Geiger, S. R.), Washington DC: American Physiology Society, 1973a, 187.
Chakraborty, I., Das, S. K., Dey, S.K., Differential expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor mRNA in the mouse uterus around the time of implantation, J. Endocrinol., 1995, 147: 339.
Hansen-Smith, F. M., Joswiak, G. R., Baustert, J. L., Regional differences in spontaneously occurring angiogenesis in the adult rat mesentery, Microvasc. Res., 1994, 47: 369.
Halder, J. B., Zhao, X., Soker, S. et al., Differential expression of VEGF isoforms and VEGF(164)-specific receptor neuropilin-1 in the mouse uterus suggests a role for VEGF(164) in vascular permeability and angiogenesis during implantation, Genesis, 2000, 26(3): 213.
Zhang, J., Wang, L., Cai, L. Q. et al., The expression and function of VEGF at embryo implantation “window” in the mouse, Chinese Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(5): 409.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, L., Wang, H., Duan, E. et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in rat uterus during peri-implantation. Chin.Sci.Bull. 46, 1178–1181 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02900597
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02900597