Abstract
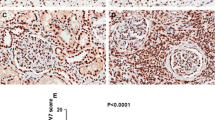
The expression ofWnt, Wntreceptor-Frizzled, and several other key components in Wnt pathway in renal cancer cell lines was studied. The result of semi-quantitative RT-PCR has shown that the expression level ofWnt5A andhFz5 mRNA were higher in renal cancer cell line (GRC-1) than in normal renal cell line (HK-2). This result has been confirmed byin situ hybridization. The expression of β-catenin protein was obviously higher in GRC-1 than in HK-2 (P< 0.01), but there were no different expressions of its mRNA between 3 lines. The reasons of the overexpression of β-catenin has been investigated by means of immunocytochemistry, SSCP and so on, no mutation ofβ-catenin gene and APC were found. That means that the overexpression ofWnt5A/hFz5 might be the reason of overexpression of β-catenin. It was concluded that the aberrant activity of Wnt pathway might play an important role in renal cell carcinoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nusse, R., Varmus, H. E., Wnt gene, Cell, 1992, 69:1073.
Iozzo, R. V., Eichstetterl, Danielson, K. G., Aberrant expression of the growth factor Wnt5A in human malignancy, Cancer Research, 1995, 55: 3495.
Ernesto, R., β-catenin-one player, two games, Nature Genetics, 1997(16): 9.
Dale, T. C., Weber-Hall, S. J., Smith, K. et al., Compartment switching of Wnt-2 expression human breast tumors, Cancer Research, 1996, 56: 4320.
Ding, Y., Yu, L. Z., Li, M. et al., Establishment and characterization of a human renal cell carcinoma cell line, Chinese Journal of Urology, 1995, 16: 3.
Hou, J. G., Cao, G. W., Li, G. H. et al., Establishment and characterization of a human renal clear cell carcinoma cell line, Chinese Journal of Experimental Surgery, 1996, 13: 352.
Wang, S. W., Gene Diagnosis Technology, Beijing: Chinese Union Medical University/Beijing Medical University Press, 1992.
Frederick, M. A., Short Protocols in Molecular Biology (3rd ed.), New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc., 1995.
Vider, B. I., Zimber, A., Evidence for the involvement of Wnt2 in human colorectal cancer, Oncogene, 1996, 12: 153.
Lejeune, S., Huguet, E. L., Hamby, A. et al., Wnt5a cloning, expression, and up-regulation in human primary breast cancers, Clin. Cancer Res., 1998, 1(2): 215.
Jackie, P., Bonnee, R., Brian, S. et al., Wnt-1 regulates free pools of catenins and stabilizes APC-catenin complexes, Mol. and Cellular Biology, 1996, 5: 2128.
Bonnee, R., Iris, A., Emilio, P. et al., Loss of beta-catenin regulation by the APC tumor suppressor protein correlates with loss of structure due to common somstic, mutations of the gene, Cancer Research, 1997, 57: 4624.
Patrice, J. M., Andrew, B. S., Vladimir, K. et al., Activation of beta-catenin-Tcf signaling in colon cancer by mutations in beta-catenin or APC, Science, 1997, 275:1787.
Jose, P., Carlos, G., Mutation in theβ-catenin gene (CTNNB1) in endometrioid ovarian carcinomas, Cancer Research, 1998, 58: 1344.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Zang, T., Zhuang, L., Zhang, Z. et al. Aberrant activity of Wnt/Frizzled signaling pathway in renal cancer cell lines. Chin.Sci.Bull. 45, 1703–1707 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02898991
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02898991