Summary
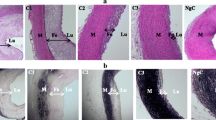
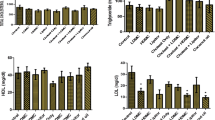
In order to search for effective drugs to reduce restenosis incidence after coronary angioplasty, we studied the effects of a Chinese herb, extract of Andrographis Paniculata Nees (APN), and Fish Oil (FO) on atherosclerotic stenosis and restenosis after experimental angioplasty. Preliminary results showed that APN can significantly alleviate atherosclerotic iliac artery stenosis induced by both deendothelialization and high cholesterol diet (control group, stenosis incidence 100 %, stenotic severe degree 60. 53±31. 03 %, of which 30 % arteries (6) are total occlusion; FO group: stenotic incidence and severe degree are 77 % and 53. 00±21.17 %, respectively, and in APN group they are 70 % and 25.39±10. 52 %, respectively,P<0. 01), and follow-up angiography 4 weeks after angioplasty showed that dilated iliac arteries in contrpol group all had severe restenosis, but in APN group no or only mild restenosis occurs, and in FO group restenosis is as severe as stenotic degree prior to angioplasty. These preliminary results suggest that APN and FO can significantly alleviate stenosis induced by deendothelialization and high cholesterol diet and restenosis after angioplasty, while the former has a more marked effect. The above findings lead the authors to conclude that APN may play an important role in preventing restenosis after coronary angioplasty, but FO may be useful in reducing the extent of of restenosis after coronary angioplasty.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Serruy P Wet al. Restenosis following coronary angioplasty. In: Meier B (ed); Interventional Cardiology. New York: Hangs Huber Publishers, 1990; P79–115
Califf R Met al. Restenosis after coronary angioplasty: an overview. J Am Coll Cardiol, 1991; 17:2B
Robertson G Cet al. Directional coronary atherectomy. In: Meier B (ed): Intervintional Cardiology. New York: Hans Huber Publishers, 1990:P225–242
Serruy P Wet al. Angiographic follow-up after placement of a self-expanding coronary artery stent. N Engl J Med, 1991;324:13
Faxon D Pet al. Effect of antiplatelet therapy of restenosis after experimintal angioplasty. Am J Cardiol, 1984;53:720
Wilentz J Ret al. PPlatelet accumulation in experimental angioplasty: time course and relation to vasculau injury. Circulation, 1987;25: 636
Bauriedel Gel al. Migratory activity of human smooth muscle cells cultivated from coronary and peripheral primary and restenosis lesions removed by percutaneous atherectomy. Circulation, 1992;85:553
Muller W M Det al. Experimental model of coronary artery restenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol, 1992;19:418
Gal Det al. Atherosclerotic Yucatan microswine: an animal model with high grade fibrocific, nonfatty lesions suetable for testing catheter-based interventions. Am Heart J, 1990;119:291
Powell J Set al. Inhibitor of angiotensin-converting enzyme prevents myointimal proliferation after vascular injury. Science, 1989; 245: 186
1989; 9: 540
Zhao H Yet al. Antithrombotische Wirkungen eines chinesischen Heilkrauts. MMW, 1990; 10:132
Zhao H Yet al. Antithrombotic iffect of andrographis Paniculata Nees in preventing myocardial infarction. Chin Med J, 1991;104:770
Wang DWet al. Experimental studies on preventing restenosis after angioplasty with Andrographis Paniculata Nees and fish oil-effect and mechanisms. Chin Med J; 1994; (in press)
Zhu B Qet al. Modification of experimental and clinical atherosclerosis by dietary fish oil. Am Heart J, 1990;119:168
Grigg L Eet al. Determinants of restenosis and lack of effect of dietary supplementation with eicosapenaenoic acid on the incidence of coronary artery restenosis after anggioplasty. J Am Coll Cardiol, 1989;13:665
Bairati Iet al. Double-blind, randomized, controlled trial of fish oil in prevention of recurrence of stenosis after coronary angioplasty. Circulation, 1992;85:950
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dao-wen, W., Hua-yue, Z. Experimental studies on prevention of atherosclerotic arterial stenosis and restenosis after angioplasty with Andrographis Paniculata Nees and Fish Oil. Journal of Tongji Medical University 13, 193–198 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02888007
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02888007