Summary
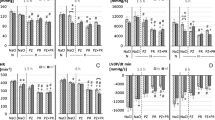
To investigate the effects of prostaglandins (PGs) and leukotrienes (LTs) on hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction (HPV),in vivo rats experiment andin vitro perfused lung experiment were conducted. The effect of hypoxia on hemodynamics, concentrations of TXB2 and 6-keto-PGF14 in serum and lung tissue during hypoxia and effects of PGs and LTs on HPV were observed. The results showed that pulmonary arterial pressure (Ppa) and pulmonary vascular resistance were increased during hypoxia, but cardiac output and systemic arterial pressure were decreased. There were increases of the concentrations of TXB2 and 6-keto-PGF14 and their ratio in serum and lung tissue during hypoxia. After use of cyclooxygenase inhibitor (indomethacin)in vivo andin vitro, HPV was augmented respectively, but after use of lipoxygenase inhibitor (diethylcorbamazine) or leukotriene receptor blocker (LY-171883), HPV was attenuated. It was suggested that LTs mediated pulmonary vasoconstriction, PGs inhibited pulmonary vasoconstriction and they played a modulating role during hypoxia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
1997, 49(6):671
Ishibe Y, Shiokawa Y, Umeda Tet al. Prostaglandin E1 antagonizes hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction but reduces systemic blood pressure in dogs. Crit Care Med, 1998, 26(1):126
Dumas M, Dumas J P, Rochette Let al. Role of potassium channels and nitric oxide in the effects of iloprost and prostaglandin E1 on hypoxic vasoconstriction in the isolated perfused lung of the rat. Br J Pharmacol, 1997, 120(3):405
Max M, Kuhlen R, Dembinski Ret al. Effect of aerosolized prostacyclin and inhaled nitric oxide on experimental hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Intensive Care Med, 1999, 25(10):1147
Shirai M. Vasomotor control of the pulmonary circulation. Nippon Yakurigaku Zasshi, 1999, 113(4):235
Gordon J B, Moreira G A, O’Donnell DCet al. Relative effects of cyclooxygenase and nitric oxide synthase inhibition on vascular resistances in neonatal lambs lung. Pediatr Res, 1997, 42(6):738
Mayers I, Johnson D, Wobeser W. Relative roles of prostaglandins and leukotrienes in canine hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. Clin Invest Med, 1991, 14 (1): 44
Weissmann N, Seeger W, Conzen Jet al. Effects of arachidonic acid metabolism on hypoxic vasoconstriction in rabbit lung. Eur J Pharmacol, 1998, 356(2–3):231
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guangtian, Y., Gang, C. & Dixun, W. Effects of prostaglandins and leukotrienes on hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction in rats. Current Medical Science 20, 197–199 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02886987
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02886987