Abstract
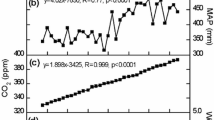
The areal extent of cold freshwater wetlands on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (QTP) is estimated at 0.133 × 106 km2, suggesting a significant methane potential. Methane fluxes from wet alpine meadows, peatlands,Hippuris vulgaris mires and secondary marshes were 43.18, 12.96, −0.28 and 45.90 mg · m−2 · d−1, respectively based on the transect flux studies at the Huashixia Permafrost Station (HPS) from July to August 1996. Average CH4 fluxes in the thaw season were extrapolated at 5.68 g · m−2 according to the areal percentage of wetland areas in the Huashixia region. The CH4 fluxes at four fixed sites, representative of similar ecosystems, ranged from −19.384–347.15 mg · m−2 · d−1, and the average CH4 fluxes varied from 6.54 to 71.97 mg · m−2 · d−1 at each site during the observation period from April to September 1997. The CH4 emissions at each site during the entire thaw season was estimated from 1.21 to 10.65 g · m−2, displaying strong spatial variations. Seasonal variations of CH4 fluxes also were observed at four sites: CH4 outbursts occurred upon the spring thaw in May and June, CH4 fluxes increased afterwards with rising soil temperatures. Episodic fluxes were observed in summer, which influenced the average CH4 fluxes considerably. Annual CH4 emissions from cold wetlands on the QTP were estimated at about 0.7–0.9 Tg based on the distribution of wetlands, representative CH4 fluxes, and number of thaw days. The centers of CH4 releasing were located in the sources of the Yangtze and Yellow rivers, and Zoigê Peatlands.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khalil, M. A. K., Shearer, M. J., Rasmussen, R. A., Methane sources in China: historical and current emissions,Chemosphere, 1993, 26: 127.
Zheng Du, Wang Xiuhong, Shen Yuancun, Preliminary discussion on wetlands on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau,Study on Wetlands in China (in Chinese) Changchun: Jilin Science and Technology Press, 1995, 236–240.
Zhao Kuiyi, Liu Xingtu, Status qua and prospert of studies in wetlands,Study on Wetlands in China (in Chinese), Changchun: Jilin Science and Technology Press, 1995, 1–9.
Xu Qi, Cai Li, Dong Yuanhua, Chararteristics, types and management of the wetlands in China,Study on Wetlands in China (in Chinese), Changchun: Jilin Science and Technology Press, 1995, 24–33.
Wang Minging, Dai Aiguo, Huang Jun. Estimation of methane emission from rice paddies in China,Atmospheric Sciences (in Chinese), 1993, 17(1): 52.
Cai Zucun, Methane emission fmm Chinese rice paddies,Study on Wetlands in China (in Chinese), Changchun: Jilin Science and Technology Press, 1995, 79–85.
Chen Weilie. Vegetation types, distribution and protection of wetlands in China,Study on Wetlands in China (in Chinese), Changchun: Jilin Science and Technology Press, 1995, 55–62.
Liu Xingtu, Wetlands in Sanjiang Plain, their logical exploitation and protection,Study on Wetlands in China (in Chinese), Changchun: Jilin Science and Technology Press, 1995, 108–117.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, H., Wu, J., Cheng, G. et al. Methane emissions from wetlands on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chin.Sci.Bull. 44, 2282–2286 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02885940
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02885940