Abstract
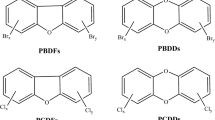
The research progress on the mechanisms of formation and degradation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs) and dibenzofurans (PCDFs) is reviewed. The primary sources of PCDD/Fs are chemical, thermal, photochemical and enzymatic reactions. Most of the thermal sources result in emissions into air. The studies on the photodegradation and biodegradation offer promise for destruction of PCDD/Fs in environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ES&T Editors, Dioxin risk,Environ. Sci. Technol., 1995, 29: 4A.
Bao, Z. C., Wang, K. O., Kang, J. X.et al., Analysis of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofuans in pentachlorophenol and sodium pentachlorophenate,Environ. Chem. (in Chinese), 1995, 14: 317.
Bao, Z. C., Wang, K. O., Kang, J. X.et al., Analysis of 2, 3, 7, 8-substituted PCDDs and PCDFs in thermolysis waste of HCH,Environ. Chem. (in Chinese), 1994, 13: 309.
Ding, X. L., Bao, Z. C., Zhang, Z.et al., Analysis of PCDDs and PCDFs in Chinese polychlorinated biphenyls,Environ. Chem. (in Chinese), 1990, 9(6): 39.
Li, L. J., Jiang, K., Determination of toxic equivalents of PCDD/Fs in two Chinese commercial PCBs by13 C isotope dilution method,Acta Scientiae Circumtantiae (in Chinese), 1995, 15: 433.
Zheng, M. H., Bao, Z. C., Wang, K. O.et al., Levels of PCDDs and PCDFs in the bleached pulp from Chinese pulp and paper industry,Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 1997, 59: 90.
Jiang, K., Li, L. J., Chen, Y. D.et al., Determination of PCDD/Fs from Chinese schistosomiasis areas and discussion of its significance for eco-environment,Chinese Sci. Bull., 1995, 40: 846.
Zheng, M. H., Bao, Z. C., Wang, K. O.et al., Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in lake sediments from Chinese schistosomiasis areas,Bull. Environ. Contam. & Toxicol., 1997, 59: 653.
Wu, W. Z., Shramm, K. W., Henklmann, B.et al., PCDD/Fs, PCBs, HCHs and HCB in sediments and soils of Ya-Er Lake area in China: Results on residual levels and correlation to the organic carbon and the particle size,Chemosphere, 1997, 34: 191.
Nestrick, T. J., Lamparski, L. L., Isomer-specific determination of chlorinated dioxins for assessment of formation and potential environmental emission for wood combustion,Anal. Chem., 1982, 54: 2292.
Sheffield, A., Sources and releases of PCDD’s and PCDF’s to the Canadian environment,Chemosphere, 1985, 14: 811.
Thomas, V.M., Spiro, T. G., The U.S, dioxin inventory: Are there missing sources?Environ. Sci. Technol., 1996, 301 82A.
Gribble, G. W., The natural production of chlorinated compounds,Environ. Sci. Technol., 1994, 28: 310A.
Svenson, A., Kjeller, L-O., Rappe, C., Enzyme-mediated formation of 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorinated dibenzodioxins and dibenzofurans,Environ. Sci. Technol., 1989, 23: 900.
Rappe, C., Dioxin patterns and source identification,Fresenius J. Anal. Chem., 1994, 348: 63.
Silk, P. J., Lonergan, G. C., Arsenault, T. L.et al., Evidence of natural organochlorine formation in peat bogs,Chemosphere, 1997, 35: 2865.
Lamparski, L. L., Stehl, R. H., Photolysis of pentachlorophenol-treated wood: Chlorinated dibenzo-dioxin formation,Environ. Sci. Technol., 1980, 14: 196.
Vollmuth, S., Zajc, A., Niessner, R., Formation of polychlorinated dihenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans during the photolysis of pentachlorophenol-containing water,Environ. Sci. Technol., 1994, 28: 1145.
Kjeller, L-O., Rappe, C., Time trends in levels, patterns and prufiles for polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans, and biphenyls in a sediment core from the Baltic Proper,Environ. Sci. Technol., 1995, 29: 346.
Kjeller, L-O., Jones, K. C., Johnston, A. E.et al., Evidence for a decline in atmospheric emission of PCDD/Fs in the U. K,Environ. Sci. Technol., 1996, 30: 1398.
Hutzinger, O., Gerg, M. V. D., Olie, K.et al., Dioxins and furans in the environment: evaluating toxicological risk from different sources by multicriteria analysis, inDioxins in the Environment (eds. Kamrin, M. A., Rodgers, P. W.), NY and London: Hemisphere Publishing Co., 1985, 9.
Zheng, M. H., Bao, Z. C., Wang, K. O.et al., Fomation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans by heating hexachlorocyclohexane in the presence of FeCl3,Environ. Chem. (in Chinese), 1995, 14: 179.
Zheng, M. H., Bao, Z. C., Xu, X. B.et al., Formation of PCDD/Fs from the pyrolysis of HCH in the presence of iron oxide,Chemosphere, 1996, 32: 595.
EHP Editors, Agent orange down under,Environ. Health Perspectiues, 1995, 103: 222.
Zheng, M. H., Bao, Z. C., Xu, X. B.et al., Discussion on the formation of polychlorinated debenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofurans in the bleaching of pulp,China Pulp & Paper, 1996, 15(3): 48.
Hanson, D.,C&EN, 1994, 30: 13.
Harnly, M., Stephens, R., Mclaughlin, C.et al., Polychlorinated dibenw-p-dioxin and dibenzofuran contamination metal recovery facilities, open bum sites, and a railroad car incineration facility,Environ. Sci. Technol., 1995, 29: 677.
Olie, K., Vermeulen, P., Hutzinger, O., Chlorodibenzo-p-dioxins and chlororodibenzofurans are trace components of fly ash and flue gas of some of municipal incinerators in Netherland,Chemospkre, 1977, 6: 455.
EPA,Environmental News, Dallas: USEPA, Sept. 13, 1994.
Luijk, R., Formation of polyhalogenated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans during thermal degradation proceeses,Universiteit van Amsterdam, 1993.
Born, J. G. P., Louw, R., Mulder, P., Fly ash mediated (oxy)chlorination of phenol and its role in PCDD/F formation,Chemosphere, 1993, 26: 2087.
Milligan, M. S., Altwicker, E. R., Chlorophenol reaction on fly wh. 1. Adsorption/desorption equilibria and conversion to polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins,Environ. Sci. Technol., 1996, 30: 225.
Cains, P. W., Mccausland, L. J., Fernandes, A. R.et al., Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans formation in incineration: Effects of fly ash and carbon source,Environ. Sci. Technol., 1997, 31: 776.
Sommeling, P. M., Mulder, P., Louw, R., Formation of PCDFs during chlorination and oxidation of chlorobenzene in chlorine/oxygen mixture arnund 340 °C.,Chemosphere, 1994, 29: 2015.
Dickson, L. C., Lenoir, D., Hutzinger, O., Quantitative comparison ofde novo and precursor formation of polychlorinated dibezo-p-dioxins under simulated municipal solid waste incineration postcombustion conditions,Environ. Sci. Technol., 1992, 26: 1822.
Froese, K. I,. Hutzinger, O., Mechanisms of formation of polychlorinated benzenes and phenols hy heterogeneous reactions of C2 aliphatics,Environ. Sci. Technol., 1997, 31: 542.
Stieglitz, L., Zwick, G., Beck, J.et al., On thede novo synthesis of PCDD/PCDF on fly ash of municipal waste incinerators.Chemosphere, 1989, 18: 1219.
Luijk, R., Akkennan, D. M., Slot, P.et al., Mechanism of formation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in the catalyzed combustion of carbon,Environ. Sci., Technol., 1994, 28: 312.
Froese, K. L., Hutzinger, O., Polychlorinated benzene, phenol, dibenzo-p-dioxin, and dibenzofuran in heterogeneous combustion reactions of acetylene,Environ. Sci. Technol., 1996, 30: 998.
Stromberg, B., Carbon dioxide—A precursor for dioxins?Chemosphere, 1991, 23: 1515.
Milligan, M. S., Altwicker, E. R., The relationship betweende novo synthesis of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans and low-temperature carbon gasification in fly ash,Environ. Sci. Technol., 1993, 27: 1595.
Milligan, M. S., Altwicker, E. R., Mechanistic aspects of thede novo synthesis of polychlorinated dibenzo-p--dioxins and furans in fly ash from experiments using isotopically labeled reagents,Environ. Sci. Technol., 1995, 29: 1353.
Crosby, D. G., Woolson, A. S., Photodecomposition of chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins,Science, 1971, 173: 748.
Buser, H. R., Preparation of qualitative standard mixtures of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans by ultraviolet and γ-inrradiation of the octachloro, compounds,J. Chromatogr., 1976, 129: 303.
Hung, H.-S., Ingram, L. L., Effect of solvents on the photodegradation rates of octachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin,Bull. Environ. Toxicol., 1990, 44: 380.
Zheng, M. H., Bao, Z. C., Xu, X. B.et al., Mechanism of photodegradation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins in carbon tetrachloride,Chemosphere, 1996, 32: 603.
Bao, Z. C., Zheng, M. H., Wang, K. O., Ultraviolet photolysis of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins in chloroform,Environ. Chem. (in Chinese), 1995, 14: 190.
Friesen, K. J., Mulr, D. C. G., Webeter, G. R. B., Evidence of Sensitized photolysis of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins in nature water under sunlight conditions,Environ. Sci. Technol., 1990, 24: 1739.
Dung, M. H., O’Keef, P. W., Comparative rates of photolyeis of polychlorinated dibenzofurans in organic solvents and in aqueous solutions,Envriron. Sci. Technol., 1994, 28: 549.
Friesen, K. J., Foga, M. M., Loewen, M. D., Aquatic photodegradation of polychlorinated dibenzofurans: Rates and photopduct analysis,Environ. Sci. Technol., 1996, 30: 2504.
Miller, G. C., Hebert, V. R., Photolysis of octachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on soil: prcduction of 2, 3, 7, 8-TCDD,Chemosphere, 1989, 18: 1265.
Zhang, Z. J., Bao, Z. C., Zheng, M. H.et al., The UV photodegradation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins on the surface of soil,Environ. Chem. (in Chinese), 1996, 15: 541.
Dougherty, E. J., Mcpeters, A. L., Overcash, M. R., Kinetics of photodegradation of 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-pdioxin: theoretical maximum rate of mil decontamination,Chemosphere, 1991, 23: 589.
Mcpeters, A. L., Overcash, M. R., Demonstration of photodegradation by sunlight of 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlrodibenzo-p-dioxin in 6 cm mil columns,Environ. Sci. Tcchnol., 1993, 27: 1221.
Hosoya, K., Kimata, K., Fukunishi, K.et al., Photodecompoeition of 1, 2, 3, 4-TCDD and 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzop-dioxin (TCDD) in water-alcohol media on a soil support,Chemphere, 1995, 31: 3687.
Yan, Q., Kappila, S., Sivils, L. D.et al., Effect of sensitizers and inhibeiton, on phototransformation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs),Chemosphere, 1995, 31: 3627.
Schuler, F., Schmid, P., Schlatter, Ch., Photodegradation of polychlorrinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in cuticular waxes of Laurel cherry,Chemosphere, 1998, 36: 21.
Zhang, Z. J., Bao, Z. C., Wang, K. O.et al., The photolysis of chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin with titanium dioxide as catalyst,Environ. Chem. (in Chinese), 1996, 15: 47.
Vollmuth, S., Niessner, R., Degradation of PCDD, PCDF, PAH, PCB and chlorinated phenols during the destruction-treatment of landfill sewagewater in laboratory model reactor (UV, ozone, and UV/ozone),Chemosphere, 1995, 30: 2317.
Smmer, S., Karmps, R., Kleinermanns, K., Photooxidation of exhaust pollutants: V Photooxidation and photoreduction of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans,Chemosphere, 1996, 33: 2221.
Orazio, C. E., Kapilla, S., Puri, P. K., Persistence of chlorinated dioxins and furans in the soil environment,Chemosphere, 1992, 25: 1467.
Du, X. Y., Zhu, N. Q., Xia, X. J.et al., A perliminary approach to biodegradation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs),Environ. Chem. (in Chinese), 1995, 14: 187.
Adriaens, P., Gribic’-Galic, D., Reductive dechlorination of PCDD/F by anaerobic cultures and sediments,Chemosphere, 1994; 29: 2253.
Disse, C., Weber, H., Hamann, R.,et al., Comparison of PCDD and PCDF concentrations after aerobic and anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge,Chemosphere, 1995, 31: 3617.
Hilarides, R. J., Gray, K. A., Guzzetta, J.et al., Feasibility system design and economic evaluation of radiolytic degradation of 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlomdibenzo-p-dioxin on soil,Water Enuiron. Res., 1996, 66: 178.
Oku, A., Tomari, K., Kamada, T.et al., Destruction of PCDDs and PCDFs: A convenient method using alkalimetal hydroxide in 1, 3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone (DMI),Chemosphere, 1995, 31: 3873.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, M., Liu, P., Bao, Z. et al. Aspects of formation and degradation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans. Chin.Sci.Bull. 44, 1249–1257 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02885839
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02885839