Abstract
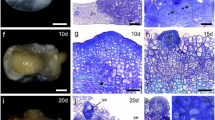
The relationship between the callus formation and intracellular Ca2+ at the early stage of development of graft unions inGinkgo biloba L. was investigated. On the second day after grafting, part of the undamaged living cells at the graft interface of the stock and scion in the regions of the cortex and pith began to dedifferentiate or divide. 8 d after grafting, a great number of callus cells were produced from the cortex and phloem, while callus bridges linking the stock with scion formed between the callus cells of the graft partners from the cortex. A membrane Ca2+ probe, chlortetracycline (CTC), was used to locate the intracellular Ca2+ distribution and it was found that the cortical and pith parenchyma cells were the first to show remarkably increased CTC-Ca2+ fluorescence, suggesting that the cortical and other parenchyma cells play a leading role at the early stage of development of graft unions by earlier dedifferentiation and more rapid production of callus cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kollmann, R., Glockmann, C., Study on graft unions III. On the mechanism of secondary formation plasmodesmata at the graft interface,Protoplasma. 1991, 165: 71.
Miller, H., Barnett, J. R., The formation of callus at the graft interface in Sitka spruce,IAWA J., 1993, 14: 13.
Yang, X., Li, Z., Shen, X.et al., Callus formation at graft interface inGinkgo biloba L.,Acta Botanica Sinica (in Chinese), 1995, 37: 909.
Das, R., Bagga, S., Sopory, S. K., Involvement of phosphoinosilides, calmodulin and glyoxalase-I in cell proliferation in callus cultures of Amaranthus-Panioclatus,Plant Science, 1987, 33: 45.
Yu, F., Zuo, D. H., Sun, D. Y., Relationship between Ca2+ and hormone effect in callus formation,Acta Biologiae Experimentalis Sinica (in Chinese), 1991, 24: 385.
Youqun, W., Kollmann, R., Vascular differentiation in the graft union ofin vitro grafts with different compatibility— Structural and functional aspects,J. Plant Physiol., 1996, 147: 521.
Tanimonto, S., Harada, H., Involvement of calcium in adventitious bud initiation in Torenia stem segments,Plant Cell Physiol., 1986, 27: 1.
Balamani, V., Veluthambi, K., Poovaiah, B. W., Effect of calcium on tuberization in potato,Plant Physiol., 1986, 80: 856.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Li, Z. Callus formation in relation to changes of the membrane Ca2+ in the graft unions ofGinkgo biloba L.. Chin. Sci. Bull. 43, 1732–1736 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02883975
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02883975