Abstract
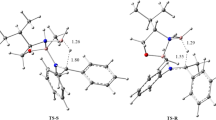
The whole catalytic cycle of the carbonylation of methanol to acetic acid catalyzed by Rh complex is theoretically studied. All structural geometries of reactant, intermediates, transition states and product are optimized at HF/LANL2DZ level under the ECP approximation. The potential energy profiles for elementary reactions of carbonylation are calculated respectively. The transition states are further confirmed by having one and only one imaginary vibrational frequency. The results indicate that the activation energy values of CHin3I oxidative addition, carbonyl insertion and CH3COI reductive elimination fundamental steps are 216.03, 128.10 and 126.55 kJ/mol, respectively; and that the CH3I oxidative addition step is predicted to be the rate-determining one.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thomas, R., Cundari, T. R., Computational studies of transition metal-main group multiple bonding, Chem. Rev., 2000, 100:807.
Maricel Torrent, Miquel Sola, Gernot Frenking, Theoretical studies of some transition-metal-mediated reactions of industrial and synthetic importance, Chem. Rev., 2000, 100: 439.
Paulik, F. E., Roth, J. F., Catalysts for the low-pressure carbonylation of menthanol to acetic acid, Chem. Commun., 1968, 24:1578.
Jiang Hua, Diao Kaisheng, Pan Pinglai et al., Anew class of rhodium complexes containing free donor atoms and their intramolecular substitution reaction, Chin. J. Chem., 2000, 18: 752.
Jiang Dazhi, Li Xiaobao, Wang Enlai, Synthesis Chemistry of Carbonylation, Beijing: Chemical Technology Press, 1996.
Adamson, G. W., Daly, J. J., Forster, D., Reduction of iolocarbonyl rhodium ions with methyl iodide, structure of the rhodium acetyl complex: [Me3PhN+], [Rh2I6-(Me(O)2(CO)2)]2-, J. Organomet. Chem., 1974, 71: C17.
Forster, D., On the mechanism of a rhodium-complex-catalyzed carbonylation of methanol to acetic acid, J. Am. Chem. Soc, 1976, 98: 846.
Hjortkjaer, J., Jensen, O. R., Rhodium complexes catalyzed methanol carbonylation, Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Dev, 1976, 15: 46.
Jeffrey, P., Wadt, W. R.,Ab initio effective core potentials for molecular calculations, Potentials for the transition metal atoms Sc to Hg, J. Chem. Phys., 1995, 82: 270.
Frisch, M. J., Trunks, G W., Schlegel, H. B. et al., Gaussian 94, Pittsburgh PA: Gaussian, Inc., 1995.
Lei Ming, Feng Wenlin, Xu Zhenfeng et al., A theoretical study on the key reactions of hydroformylation cycle by modified carbonyl cobalt, Chemical Journal of Chinese University, 2001, 22: 455.
Lei Ming, Feng Wenlin, Xu Zhenfeng,Ab initio MO study on the reaction mechanism for carbonyl insertion catalyzed by the carbonyl cobalt complex, Chemical Research in Chinese University, 2000, 19: 31.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, M., Feng, W., Hao, M. et al. Ab initio study on the mechanism of rhodium-complexcatalyzed carbonylation of methanol to acetic acid. Sc. China Ser. B-Chem. 44, 465–472 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02880675
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02880675