Abstract
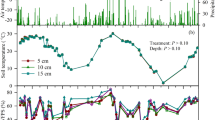
To understand influence of litters on the emission/absorption of CO2, N2O and CH4 in broadleaved/Korean pine forest in Changbai Mountain, fluxes of soil CO2, N2O and CH4 were measured by closed static chamber technique, from Sept 3, 2002 to Oct 30, 2003 in two types of soil ecosystems, of which one was covered with litters on the surface soil, and the other had no litters. The results showed that litters had significant influences on CO2, N2O and CH4 fluxes (p<0.05). Their diurnal change patterns of plot with litters and litter-free plot were similar, and they all showed emission/absorption peak at 18:00. The diurnal change fluxes of CO2 and N2O of plot with litters were significantly higher than those of the litter-free plot, while the diurnal flux of CH4 of plot with litters was lower than that of litter-free plot. The fluxes of CO2, N2O, and CH4 showed the similar seasonal patternsfor both plots. The fluxes of CO2, CH4 showed their peak fluxes in June, but the fluxes of N2O showed its peak emissions in August. The annual fluxes of CO2 and N2O of plot with litters were significantly higher than those of the litter-free plot, while the annual flux of CH4 of plot with litters was lower than that of litter-free plot.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouwnan, A.F. 1990. Soils and greenhouse effct [M]. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Cheng Borong, Xu Guangshan, Ding Guifang. 1981. The main soil groups and their properties of the Natural Reserve on Northern Slope [C]. In: Forest Ecosystem Research. (2). Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, p196–206.
Daubenmire, R. and Prusso, D.C. 1963. Studies of the decomposition rate of tree litter [J]. Ecology,44(3): 589–592.
Du Rui, Wang Gengchen, Lu Daren,et al. 2001. The variation characters of N2O and CH4 fluxes in Stipa grandis grassland in Inner, Mongolia [J]. China Environmental Science,21(4): 289–292. (in Chinese)
Goodroad, L.L. and Keeney, D.R. 1984. Nitrous oxide emissions from soils during thawing [J]. Soil Sci.,64: 187–194.
Guo Jixun. 1994. The decomposer subsystem in Leymus chinensis grassland [M]. Changchun: Jidh University Press.
Hili, O.W. 1983. Decomposition principle and study methods of organic matter-forest ecology system [M]. Beijing, China forestry Press, p286–288. (in Chinese)
Houghton, J.T., Meira Filho, L.G. and Gallander, B.A.et al. 1996. Climate Change 1995: The science of Climate Change [R]. Cambridge, Great Britain: Cambridge University Press, p351–371.
Huang Guohong, Chen Guanxiong, Wu Jie,et al. 1995. N2O and CH4 fluxes from typical upland fields in northeat China [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol.,6 (4): 383–386. (in Chinese)
Klemedtsson, A.K., Klemedtsson, L. 1997. Methane uptake in Swedish forest soil in relation to liming and extra N-deposition [J]. Biol. Fert. Soils,25: 296–301.
Lashof, D.A. and Ahuja, D.R. 1990. Relative contributions of greenhouse gas emissions to global Warming [J]. Nature,344: 529–531.
Li Wenhua, Deng Kunmei, Li Fei. 1981. Study on Biomass and Primary Production of the main ecosystems in Changbai Mountain [C]. In: Foret Ecosystem Research (2). Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, p34–50. (in Chinese)
Liu Xiaodong, Hou Ping. 1998. Relationship between the climatic warming over the QingHai-Xizang plateau and its surrounding areas in recent 30 years and the elevation [J]. Plateau metaorology,17(3): 245–249.
Nebsit, S.P. and Breitenbeck, G.A. 1992. A laboratory study of factors influencing methane uptake by soils [J]. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ.,41: 39–54.
Priemer, A. and Christensen, S. 1997. Seasonal and spatial variation of methane emission oxidation in a Danish spruce forest [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem.,29: 1165–1172.
Robert, E. Schlentner and Keith Van Cleve. 1985. Relationships between CO2 evolution from soil, substrate temperature, and substrate moisture in four mature forest types in interior Alaska [J]. Can. J. For. Res.,15: 97–106.
Rodhe, H. 1990. A comparison of the contribution of various gases to greenhouse effect [J]. Science,248: 1217–1219.
Wakesman, S.A. and Gerretsen, F.C. 1931. Influence of temperature and moisture upon the nature and extent of decomposition of plant residues by microorganisms [J]. Ecology,12: 33–60.
Wang Mingxing, zhang Renjian, Zheng Xunhua. 2000. Sources and sinks of greenhouse gases [J]. Climate and Environment Research,5(1): 75–79.
Wang Wei, Guo Jixun, Zhang Baotian. 2003. Seasonal dynamics of environmental factors and decomposition rate of litter in leymus chinensis community in Songnen grassland in Northeast China [J]. Acta Pratacult Sin.,12(1): 47–52.
Wang Yuesi, Ji Baoming, Wang Yanfen,et al. 2000. A method of measurement the exchange rate of greenhouse gases between field and atmosphere in semiarid grassland [J]. Environmental Sciences.21(3): 6–10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The study was supported by innovation research project of Institute of Appiied Ecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (SCXZD0101-02) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (30271068)
Bigraphy: XIAO Dong-mei (1979-), female, master of Institute of Applied Ecology. Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016. P. R. China.
Responsible editor: Song Funan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong-mei, X., Miao, W., Yue-si, W. et al. Fluxes of soil carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide and firedamp in broadleaved/Korean pine forest. Journal of Forestry Research 15, 107–112 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02856743
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02856743