Abstract
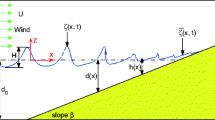
This paper introduces a numerical model for studying the evolution of a periodic wave train, shoaling, and breaking in surf zone. The model can solve the Reynolds averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) equations for a mean flow, and thek-ε equations for turbulence kinetic energyk and turbulence dissipation rate ε. To track a free surface, the volume of fluid (VOF) function, satisfying the advection equation was introduced. In the numerical treatment, third-order upwind difference scheme was applied to the convection terms of the RANS equations in order to reduce the effect of numerical viscosity. The shoaling and breaking processes of a periodic wave train on gently sloping beaches were modeled. The computed wave heights of a sloping beach and the distribution of breaking wave pressure on a vertical wall were compared with laboratory data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basco, D. R., 1985. A qualitative description of wave breaking.J. Wtrwy. Port Coast. Ocean. Engrg. ASCE111(2): 171–188.
Battjes, J. A., 1988. Surf-zone dynamics.Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 20: 257–293.
Hirt, C. W. and B. D. Nichols, 1981. Volume of fluid (VOF) method for the dynamics of free boundaries.J. Comp. Phys. 39(1): 201–225.
Kodama, Y., 1992. Computation of ship's resistance using a N-S solver with global conservation.J. Soc. Naval Architects Japan. 172: 147–155.
Lin, P. and P. L. F. Liu, 1998. A numerical study of breaking waves in the surf zone.J. Fluid Mech. 359: 239–264.
Madsen, P. A., O. R. Sorensen and H. A. Schaffer, 1997a. Surf zone dynamics simulated by a Boussinesq type model, Part I: Model description and cross-shore motion of regular waves.Coast. Engrg. 32: 255–287.
Madsen, P. A., O. R. Sorensen and H. A. Schaffer, 1997b. Surf zone dynamics simulated by a Boussinesq type model, Part II: Surf beat and swash zone oscillations for wave groups and irregular waves.Coast. Engrg. 32: 288–319.
Rodi, W., 1980. Turbulence Models and Their Application in Hydraulics-A State-of-the-Art Review. IAHR Publication.
Shih, T. H., J. Zhu and J. L. Lumley, 1996. Calculation of wall-bounded complex flows and free shear flows.Intl. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 23: 1133–1144.
Sorensen, R. M., 1993. Basic Wave Mechanics. Wiley, New York.
Svendsen, I. A., 1984. Mass flux and undertow in a surf zone.Coast. Engrg. 8: 347–365.
Wang, Y., 1994. A study on periodic wave breaking by absorbed numerical wave channel. Proc. 4th Intl. Offshore and Polar Engrg. Conf., Japan, Vol. III: 32–36.
Wang, Y., 1995. Numerical Wave Channel with Absorbed Wave Maker.China Ocean Engrg. 9(2): 149–160.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the High-Tech Research and Development Program of China (863 Program. No. 2001AA633070; 2003AA604040), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40476015).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, Q., Yijun, H. A VOF-based numerical model for breaking waves in surf zone. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 24, 57–64 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02842775
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02842775