Abstract
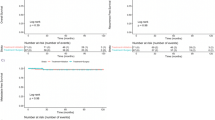
Objective: To study the importance of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (PRFA) guided by ultrasound for inoperable recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma.Methods: Forty-seven patients with inoperable recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma underwent percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (PRFA) under ultrasond between October 1999 and July 2001. Twenty-four patients had single recurrent tumor and 23 patients had multiple lesions. Twelve patients had single lesion with less than 3.5 cm in diameter. All patients were followed up to examine the value of AFP, MRI or CT after PRFA. Kaplan-Meier estimation was used to analyze the survival rate.Results: The 1-, 2- and 3-year survival rate in single lesion group was 65.2%, 37.5% and 37.5% respectively. The survival rate of 1 and 2 years was 41.7% and 19.5% in the multiple lesions group. The 1-, 2-and 3-year survival rate in single lesion groups with less than 3.5 cm in diameter was 83.3%, 51.4% and 51.4% respectively.Conclusion: PRFA is one of the important comprehensive methods for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. According to the size, number and recurrent time, PRFA can be performed separately or combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for inoperable recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. This method can control the recurrence and increase the survival rate effectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu MC. The progress of diagnosis and treatment in primary liver cancer. Chin J Surg, 1998, 36: 515–517.
Rossi S, Fornari F, Buscarini L. Percutaneous ultrasound-guided radiofrequency electrocartery for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma. J Intervent Radiol, 1993, 8: 97–103.
Rossi S, Di Stasi M, Buscarini E,et al. Percutaneous RF interstitial thermal ablation in the treatment of hepatic cancer. Am J Roentgenol, 1996, 167: 759–768.
Curley, SA, Izzo F, Delrio P,et al. Radiofrequency ablation of unresectable primary and metastatic hepatic malignancies: results in 123 patients. Ann Surg, 1999, 230: 1–8.
Zhang, ZJ, Wu MC, Chen H,et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepatic malignancies. Chin J Surg, 2001, 39: 749–752.
Zhang ZJ, Wu MC, Chen H. Percutaneous radiofrequency albation for hepatic malignancies. Chinese-German J Clin Oncol, 2002, 1: 159–162.
Zhang ZJ, Qi L, Jia H,et al. The effect of preoperative transcatheter hepatic arterial chemoembolization on disease-free survival after hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer, 2000, 89: 2606–2612.
Zhang ZJ, Wu MC, Chen H,et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Chin J Surg, 2002, 40: 826–829.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhijian, Z., Mengchao, W., Han, C. et al. Importance of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. Chin. -Ger. J. Clin. Oncol. 2, 209–212 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02835458
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02835458