Summary
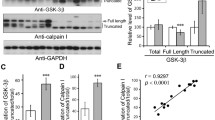
In this study, we studied the effect of glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) overactivation on neurofilament phosphorylation in cultured cells. After N2a cells were treated with the specific inhibitor (wortmannin) of phosphoinositol-3 kinase (PI-3K) or treated with wortmannin and the specific inhibitor (LiCl) of glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3), GSK-3 activity and neurofilament phosphorylation were detected by using GSK-3 activity assay, Western blots and immunofluoresence. Our results showed that after treatment of N2a cells with wortmannin for 1 h, overactivation of GSK-3 caused a reduced staining with antibody SMI32 and an enhanced staining with antibody SMI31. When N2a cells were treated with wortmannin and LiCl, the activity of GSK-3 was reduced substantially. At the same time, the phosphorylation of neurofilament was also reduced. The study demonstrated that overactivation of GSK-3 induced hyperphosphorylation of neurofilament and suggested thatin vitro overactivation of GSK-3 resulted in neurofilament hyperphosphorylation and this may be the underlying mechanism for Alzheimer's disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Drewes G, Lichtenberg-Kraag B, Doring Fet al. Mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinase transforms tau protein into an Alzheimer-like state. EMBO J, 1992, 11(6):2131
Mandelkow E M, Drewes G, Biernat Jet al. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 and the Alzheimer-like state of microtubule-associated protein tau. FEBS Lett, 1992,314(3):315
Yang S D, Song J S, Yu J Set al. Protein kinase FA/GSK-3 phosphorylates tau on Ser235-Pro and Ser404-Pro that are abnormally phosphorylated in Alzheimer's disease brain. J Neurochem, 1993,61(5):1742
Ishiguro K. Involvement of tau protein kinase in amyloid-beta-induced neurodegeneration. Rinsho Byori, 1998,46(10):1003
Delcommenne M, Tan C, Gray Vet al. Phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase-dependent regulation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 and protein kinase B/AKT by the integrin-linked kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1998,95 (19):11211
Billingsley M L, Kincaid R L. Regulated phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of tau protein: effects on microtubule interaction, intracellular trafficking and neurodegeneration. Biochem J, 1997,1:323:577
Pei J J, Tananka T, Tung YCet al. Distribution, levels, and activity of glycogen synthase-3 in the Alzheimer disease brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol, 1997, 56:70
Wang J, Tung Y C, Wang Yet al. Hyperphosphorylation and accumulation of neurofilament proteins in Alzheimer disease brain and in okadaic acid-treated SY5Y cells. FEBS Lett, 2001,507(1):81
Betts J C, Blackstock W P, Ward M Aet al. Identifi cation of phosphorylation sites on neurofilament proteins by nanoelectrospray mass spectrometry. J Biol Chem, 1997,272(20):12922
Hu Y Y, He S S, Wang X Cet al. Elevated levels of phosphorylated neurofilament proteins in cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer disease patients. Neurosci Lett, 2002, 320(3):156
Straube-West K, Loomis P A, Opal Pet al. Alterations in neural intermediate filament organization: functional implications and the induction of pathological changes related to motor neuron disease. J Cell Sci, 1996, 109:2319
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
CHEN Juan, female, born in 1969, Lecturer
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Juan, C., Jie, Z., Youmei, F. et al. Effect of GSK-3 overactivation on neurofilament phosphorylation. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 25, 375–377 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02828200
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02828200