Abstract
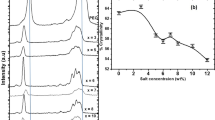
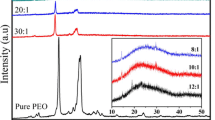
The positron lifetime spectra and ionic conductivity have been measured for polymeric electrolyte PEU-LiClO4 as a function of temperature in the range of 120≈360 K and as a function of Li-salt concentration at room temperature. From the temperature dependence of positron annihilation parameters, the glass transition and subtransition are observed, and the glass transition temperatureT g of pure PEU is determined to be 240 K. AboveT g, the free volume hole size dramatically increases with temperature. The variations of positron annihilation parameters and ionic conductivities with respect to Li-salt concentration at room temperature indicate that the Li salt mainly diffuses into the amorphous region in PEU-LiClO4. The increase of Li salt concentration brings about an increase in the number of carried ions, and a reduction of the fractional free volume.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Watanabe M, Itoh M, Sanui K,et al. Carrier transport and generation process in polymer electrolytes based on poly (ethylene oxide) network.Macromolecules, 1987,20: 569
Wieczorek W, Zalewska A, Raducha D,et al. Polyether, Poly (N, N-dimethylacrylamide) and LiClO4 Composite Polymeric Electrolytes.Macromolecules, 1996,29: 143
Jean Y C. Positron annihilation spectroscopy for chemical analysis: A novel probe for microstructural analysis of polymer.Microchem J, 1992,42: 72
Wang S J, Wang C L, Wang B. Microstructure and mechanical properties of polymers studied by positron annihilation.J Radio & Nucl Chem, 1996,210: 407
Wang C L, Wang S J. Scaling behavior of free volume in polymer probed by positron annihilation.Phys Rev B, 1995,51: 8810
Nakanishi H, Wang S J, Jean Y C.In Positron Annihilation Studies of Fluids. Singapore: World Science Press, 1988
Kirkegaard P, Eldrup M, Mogensen O E,et al. Program system for analyzing positron lifetime spectra and angular correlation curves.Comp Phys Commun, 1981,23: 307
Toyell L M, Schantz S. Structure relaxation and chain flexibility in polymeric ion conductors.J Non-Crystalline Solids, 1991,131: 981
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Wang Shaojie: born in Mar. 1942, Professor
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaojie, W., Bo, W., Shiqing, L. et al. Microstructure of polymeric electrolyte PEU-LiClO4 studied by positron spectroscopy. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 2, 171–174 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02827825
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02827825