Summary
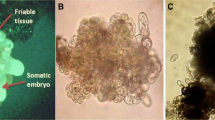
A cell suspension of French Sombre plantain banana (Musa spp. AAB genome) was initiated from callus obtained from young male flowers. Histological examination enabled us to describe and follow the evolution of the suspension consisting of: embryogenic aggregates, proembryos, nodules, and isolated cells. It demonstrated the unicellular origin of somatic embryos, either during maintenance of the suspension or after plating on a semisolid medium. The cells from which the embryos originated had no starch but only protein reserves. Plating 1 ml of packed cells from the suspension led to the formation of 105 embryos of which 10 to 40% could be converted into plantlets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Touchet, B.; Duval, Y.; Pannetier, C. Plant regeneration from embryogenic suspension cultures of oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.). Plant Cell Rep. 10:529–532; 1991.
Dhed'a, D.; Dumortier, F.; Panis, B., et al. Plant regeneration in cell suspension cultures of cooking banana cv. “Bluggoe” (Musa spp. ABB group). Fruits 46:125–135; 1991.
Durham, R. E.; Parrott, W. A. Repetitive somatic embryogenesis from peanut cultures in liquid medium. Plant Cell Rep. 11:122–125; 1992.
Emons, A. M. C. Somatic embryogenesis: cell biological aspects. Acta Bot. Neerl. 43:1–14; 1994.
Emons, A. M. C.; Kieft, H. Histological comparison of single somatic embryos of maize from suspension culture with somatic embryos attached to callus cells. Plant Cell Rep. 10:485–488; 1991.
Escalant, J. V.; Teisson, C.; Côte, F. X. Amplified somatic embryogenesis from male flowers of triploid banana and plantain cultivars (Musa sp.). In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 30:181–186; 1994.
Finer, J. J.; Nagasawa, A. Development of an embryogenic suspension culture of soybean (Glycine max Merrill.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 15:125–136; 1988.
Fisher, D. B. Protein staining of ribboned epon sections for light microscopy. Histochemie 16:92–96; 1968.
Fujimura, T.; Komamine, A. Synchronization of somatic embryogenesis in a carrot cell suspension culture. Plant Physiol. 64:162–164; 1979.
Gavish, H.; Vardi, A.; Fluhr, R. Extracellular proteins and early embryo development inCitrus nucellar cell cultures. Physiol. Plant. 82:606–616; 1991.
Halperin, W.; Jensen, W. A. Ultrastructural changes during growth and embryogenesis in carrot cell cultures. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 18:428–443; 1967.
Ma, S. S. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from cell suspension culture of banana. Proceedings of symposium on tissue culture of horticultural crops. Taipei, Taiwan 1988 March 8–9. Published by Department of Horticulture, National Taiwan University. June 1991:181–188.
Marroquin, C. G.; Paduscheck, C.; Escalant, J. V., et al. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration through cell suspensions inMusa acuminata. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 29:43–46; 1993.
McGahan, M. W. Studies on the seed of banana. I. Anatomy of the seed and embryo ofMusa balbisiana. Am. J. Bot. 48:230–238; 1961.
Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15:473–497; 1962.
Novak, F. J.; Afza, R.; Van Duren, M., et al. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in suspension cultures of dessert (AA and AAA) and cooking (ABB) bananas (Musa spp.). Bio/Technology 7:154–159; 1989.
Schenk, R. U.; Hildebrandt, A. C. Medium and techniques for induction and growth of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plant cell cultures. Can. J. Bot. 50:199–204; 1972.
Street, H. E.; Withers, L. A. The anatomy of embryogenesis in culture. In: Street, H. E., ed. Tissue culture and plant science. London: Academic Press; 1974:71–100.
Tabaeizadeh, Z.; Campeau, N. Embryogenic cell suspensions ofTriticum aestivum × Leymus angustus F1 hybrids: characterization and plant regeneration. Plant Cell Rep. 11:81–85; 1992.
Vasil, V.; Vasil, I. K. Characterization of an embryogenic cell suspension culture derived from cultured inflorescences ofPennisetum americanum (Pearl Millet, Gramineae). Am. J. Bot. 69:1441–1449; 1982.
Williams, E. G.; Maheswaran, G. Somatic embryogenesis: factors influencing coordinated behaviour of cells as an embryogenic group. Ann. Bot. 57:443–462; 1986.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grapin, A., Schwendiman, J. & Teisson, C. Somatic embryogenesis in plantain banana. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 32, 66–71 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02823133
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02823133