Abstract
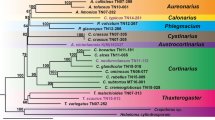
In nineteen pathogenic and saprophytic isolates denoted asAspergillus terreus the presence and restriction pattern of the genepksM (6-methylsalicylic acid synthase) was determined. Five patterns (A−E) were found and in three isolates the gene was missing. The RAPD (random amplified polymorphic DNA) patterns with three primers were analyzed. The strains withpksM pattern possibly derived from the most common pattern A by single mutation (patterns B−D) were also related by RAPD. Among them, three clades were found. The first one contained saprophytes from Asia, the other two clades contained both European and American pathogens and each of them one saprophyte. The sequences of rDNA region containing 5.8S rDNA and spacers ITS1 and ITS2 were established for representatives of each group and the strains missing thepksM gene. The isolates possessingpksM (although with different restriction patterns) grouped asA. terreus group, whereas the isolates lacking this gene were close toFennellia flavipes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aufauvre-Brown A., Cohen J., Holden D.W.: Use of randomly amplified polymorphic DNA markers to distinguish isolates ofAspergillus fumigatus.J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992 (11) 2991–2993 (1992).
Beck J., Ripka S., Siegner A., Schiltz E., Schweizer E.: The multifunctional 6-methylsalicylic acid synthase gene ofP. patulum.Eur. J. Biochem. 192, 487–498 (1990).
Crowhurst R.N., Hawthorne B.T., Rikkerin E.H., Templeton M.D.: Differentiation ofFusarium solani f.sp.cucurbitae races 1 and 2 by random amplification of polymorphic DNA.Curr. Genet. 20, 391–396 (1991).
Felsenstein J.: PHYLIP—Phylogeny Inference Package (Version 3.2).Cladistics 5, 164–166 (1989).
Fujll I., Ono Y., Tada H., Gomi K., Ebizuka Y., Sankawa U.: Cloning of the polyketide synthase geneatX fromAspergillus terreus and its identification as the 6-methylsalicylic acid synthase gene by heterologous expression.Mol. Gen. Genet 253, 1–10 (1996).
Geiser D.M., Timberlake W.E., Arnold M.L.: Loss of meiosis inaspergillus.Mol. Biol. Evol. 13, 809–817 (1996).
Chang P.K., Bhatnagar D., Cleveland T.E., Bennett J.W.: Sequence variability in homologues of the aflatoxin pathway geneaflR distinguishes species inAspergillus sectionFlavi.Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61, 40–43 (1995).
Jukes T.H., Cantor C.R.: Evolution of protein molecules, pp. 21–132 in H.N. Munro (Ed.):Mammalian Protein Metabolism. Academic Press, New York 1969.
Kumar S., Tamura K., Nei M. MEGA: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis software for microcomputers.CABIOS 10, 189–191 (1994).
Kusumoto K.-I., Yabe K., Nogata Y., Ohta H.:Aspergillus oryzae with and without a homologue of aflatoxin biosynthetic genever-l.Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 50, 98–104 (1998).
Link W., Dixkens C., Singh M., Schwall M., Melchinger A.E.: Genetic diversity in European and Mediterranean faba bean germ plasm revealed by RAPD markers.Theor. Appl. Genet. 90, 27–32 (1995).
Loudon K.W., Burnie J.P., Coke A.P., Matthews R.C.: Application of polymerase chain reaction to fingerprintingAspergillus fumigatus by random amplification of polymorphic DNA.J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993 (5), 1117–1121 (1993).
Nemec P., Barth Z., Betina V., Kutkov M.: Antibiotic activity of fungi isolated from soil samples from Indonesia.Folia Microbiol. 9, 383–386 (1964).
Pażoutová S., Linka M., Štorková S., Schwab H.: Polyketide synthase genepksM fromAspergillus terreus expressed during growth phase.Folia Microbiol. 42, 419–430 (1997).
Raper K.B., Fennel D.I.:The Genus Aspergillus, pp. 558–577. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore 1965.
Saitou N., Nei M.: The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees.Mol. Biol. Evol. 4, 406–425 (1987).
Van de Peer Y., De Wachter R.: TREECON for Windows: a software package for the construction and drawing of evolutionary trees for the Microsoft Windows environment.CABIOS 10, 569–570 (1994).
White T.J., Bruns T., Lee S., Taylor J.W.: Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics, pp. 315–322 in M.A. Innis, D.H. Gelfand, J.J. Sninsky, T.J. White (Eds):PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications. Academic Press, San Diego 1990.
Wiley B.J., Fennell D.I.: Ascocarps ofAspergillus stromatoides, A. niveus andA. flavipes.Mycologia 65, 752–760 (1973).
Wiley B.J., Simmons E.G.: New species and a new genus ofPlectomycetes withAspergillus states.Mycologia 65, 936–938 (1973).
Woloshuk C.P., Foutz K.R., Brewer J.F., Bhatnagar D., Cleveland T.E., Payne G.A.: Molecular characterization ofaflR, a regulatory locus for aflatoxin biosynthesis.Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60, 2408–2414 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pažoutová, S., Hamplová, I., Anderson, M. et al. Use of the 6-methylsalicylic-acid-synthase gene as a discriminating marker betweenaspergillus terreus andAspergillus flavipes . Folia Microbiol 44, 503–509 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02816250
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02816250