Abstract
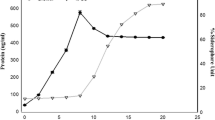
In iron-limited medium, a siderophore producing soil isolate ofAzotobacter chroococcum showed a high level of hydroxamate with relatively low level of nitrogen fixation. Inclusion of iron in the medium resulted in increased nitrogen fixation with decreased hydroxamate production. Under shake culture conditions, the level of both hydroxamate and catechol type of siderophores decreased after 2 d of incubation in iron-deficient medium. However, under iron-sufficient conditions, both siderophore production and nitrogen fixation increased with time although the level of siderophore was quite low. A number of soil isolates and mutants ofA. chrococcum were tested for nitrogen fixation, hydroxamate and catechol type of siderophore production. Wide variation was observed in the siderophore level and nitrogen fixation in the cultures tested. Nitrogen fixation was higher in the iron-sufficient medium than in iron-limited one while hydroxamate yield was higher in iron-limited medium than in the iron-sufficient one in all the cultures. Inclusion of ammonium acetate in the medium induced catechol synthesis in more than 60% of the cultures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnow L.E.: Colorimetric determination of the components of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine-tyrosine mixtures.J. Biol. Chem.118, 531–537 (1937).
Balajee S., Mahadevan A.: Dissimilation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid byAzotobacter chroococcum.Xenobiotica20, 607–617 (1990).
Bothe H., de Bruijn F.J., Newton W.E.: Nitrogen fixation hundred years after.Proc. 7th Internat. Congr. Nitrogen Fixation, Koln (Cologne), Germany. Fischer, Stuttgart-New York 1988.
Brill W.J.: Biochemical genetics of nitrogen fixation.Microbiol. Rev.44, 449–467 (1980).
Collinson S.K., Doran J.I., Page W.J.: Production of 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid byAzomonas macrocytogenes andAzotobacter paspali.Can. J. Microbiol.33, 169–175 (1987).
Csaky T.Z.: On the estimation of bound hydroxylamine in biological materials.Acta Chem. Scand.2, 450–454 (1948).
Dalton H., Postgate J.R.: Growth and physiology ofAzotobacter chroococcum in continuous culture.J. Gen. Microbiol.56, 307–319 (1969).
Expert D., Gill P.R.: Iron: A modulator in bacterial virulence and symbiotic nitrogen fixation, pp. 229–245 inMolecular Signals in Plant Microbe Communications (D.A.S. Verma, Ed.). CRC Press, Boca Raton 1991.
Fekete F.A., Lanzi R.A., Beaulieu J.B., Longcope D.C., Sulya A.W., Hayes R.N., Mabbott G.A.: Isolation and preliminary characterization of hydroxamic acids formed by nitrogen fixingAzotobacter chrococcum B 8.Appl. Environ. Microbiol.55, 298–305 (1989).
James E.: Strain variation inAzotobacter chroococum. MSc Thesis. Post-gradiate School, Indian Agriculture Research Institute, New Delhi (India) 1970.
Knosp O., Von Tigerstrom M., Page W.J.: Siderophore mediated uptake of iron byAzotobacter vinelandii.J. Bacteriol.159, 341–347 (1984).
Lakshminarayana K.: Influence ofAzotobacter on nitrogen nutrition of plants and crop productivity.Proc. Indian Nat. Sci. Acad.B59, 303–308 (1993).
Markham R.: A steam distillation apparatus for micro-Kjeldahl analysis.Biochem. J.36, 790–791 (1942).
Neilands J.B.: Microbial iron compounds.Ann. Rev. Biochem.50, 715–731 (1981).
Page W.J.: Iron dependent production of hydroxamte by sodium dependentAzotobacter chroococcum.Appl. Environ. Microbiol.53, 1418–1424 (1987).
Page W.J., Huyer M.: Derepression ofAzotobacter vinelandii siderophore system using iron containing minerals to limit iron repletion.J. Bacteriol.158, 496–502 (1984).
Page W.J., Sadoff H.L.: Physiological factors affecting transformation ofAzotobacter vinelandii.J. Bacteriol.125, 1080–1087 (1976).
Purushothaman D., Sadasivan S., Dhanpal N.: Nitrogen fixation and ammonia assimilation inAzotobacter chroococcum isolates from C3 and C4 plants.Curr. Sci.48, 174–176 (1979).
Sayed M.L., Rafel A.H., Mohmad T.A.: Nitrogen fixation by some cultures ofAzotobacter.Pakistan J. Microbiol.4, 67–69 (1971).
Shivprasad S., Page W.J.: Catechol formation and melanization by Na+-dependentAzotobacter chroococcum: A protective mechanism for aeroadaptation.Appl. Environ. Microbiol.55, 1811–1817 (1989).
Suneja S., Lakshminarayana K.: Production of hydroxamate and catechol siderophores byAzotobacter chroococcum.Indian J. Exp. Biol.31, 878–881 (1993).
Suneja S., Lakshminarayana K., Gupta P.P.: Role ofAzotobacter chroococcum siderophores in control of bacterial rot andSclerotinia rot of mustard.Indian J. Mycol. Plant Pathol.24, 202–205 (1994a).
Suneja S., Lakshminarayana K., Narula N.: Optimization of cultural conditions for hydroxamate type of siderophore production byAzotobacter chroococum.Microbiol. Res.149, 385–390 (1994b).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suneja, S., Narula, N., Anand, R.C. et al. Relationship ofAzotobacter chrooccum siderophores with nitrogen fixation. Folia Microbiol 41, 154–158 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02814692
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02814692