Summary
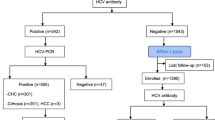
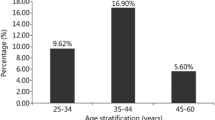
The authors examined the contribution of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) to the morbidity of chronic liver diseases (CLD) in selected districts of Saga, Japan, one group with low (L) and the other with a high (H) mortality rate of CLD. Age and sex-matched epidemiological studies showed an extremely high morbidity of CLD in the H-districts (5.3%) and a low one in the L-districts (2.1%). Randomized selected studies of anti-HCV antibodies showed an extremely high frequency of 10.8% in the H-district and a frequency of 4.6% in the L-district. In addition, the number of subjects with both CLD and positive anti-HCV antibodies was significantly higher in subjects older than the fifth decade, in the H-district. The high prevalence of HCV may be related to the high morbidity and mortality rate of CLD in these districts of Japan.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. of Health and welfare statistics, Health and Welfare Statistics Association, Tokyo 1985; 32:50–65 (in Japanese)
Sigematsu I: Major disease mortalities for cities, towns and villages in Japan. The Research Committee on Geographical Distribution of Diseases, ed. Japan Health Promotion Foundation Press, Tokyo, 1982; 243–244, 543–544 (in Japanese)
Choo QL, Kuo G, Weiner AJ, et al: Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood borne non A nonB hepatitis genome, Science 1989;244:359–364
Furuta S: Anti HCV antibody in nonA nonB hepatitis in Japan. Abstracts of the Tenth Joint Meeting of US-Japan Hepatitis Panel 1989;31
Yano M, Koga M, Inoue C: Hepatitis type C in post transfusion and sporadic hepatitis. Kan Tan Sui 1990;20:21–23 (in Japanese)
Kuhnl P, Seidl S, Stangel W, et al: Antibody to hepatitis C virus in German Blood donors. Lancet 1989;ii:324
Esteban JI, Esteban R Vilodomiu L, et al: Hepatitis C virus antibodies among risk groups in Spain. Lancet 1989;ii:294–297
Fujisawa K: An epidemic outbreak of nonA nonB hepatitis in Japan. International Committee of JSGE, ed. New trends in peptic ulcer and chronic hepatitis Part II Excepta Medica, Tokyo. 1987;196–203
Fujisawa K, Yamauchi M, Shikata T: Epidemic outbreak of type C hepatitis. Kan Tan Sui 1990;20:25–33 (in Japanese)
Kiyosawa K, Sodeyama T, Akahara Y, et al: Infection of nonA nonB acute viral hepatitis in hospital employees, Jpn J Gastroenterol 1989;86:32–38 (in Japanese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Setoguchi, Y., Yamamoto, K., Ozaki, I. et al. Prevalence of chronic liver diseases and anti-HCV antibodies in different districts of Saga, Japan. Gastroenterol Jpn 26, 157–161 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02811074
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02811074