Abstract
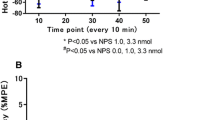
The present experiment investigated the effects of direct spinal administration of the monoaminergic receptor blockers yohimbine, phentolamine and methysergide on the expression of conditioned analgesia. Animals in the Paired group received classical conditioning trials in which one context was paired with footshock administration (1 mA shock for 15 s). Animals in the Unpaired control group were administered shock in a second, different, context. On the test day animals within each condition were administered saline (20 μl), yohimbine (30 μg), phentolamine (30 μg), or methysergide (30 μg) prior to receiving a hot plate test (50° C) in the context previously used to shock the Paired group. These ligands were administered into the spinal fluid through a chronic, indwelling spinal catheter. Animals in the Paired group which received saline displayed longer paw lick latencies than saline-treated animals in the Unpaired group. Yohimbine, but not phentolamine or methysergide, attenuated this conditioned analgesia. These results suggest that spinal cord noradrenergic substrates mediate conditioned analgesia, and that this mediation occurs specifically through the alpha-2 noradrenergic receptor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghajanian GK, Cedarbaum JM, Wand RY (1977) Evidence for norepinephrine-mediated collateral inhibition of locus coeruleus neurons. Brain Res 136: 570–577
Cedarbaum JM, Aghajanin GK (1978) Activation of locus coeruleus neurons by peripheral stimuli: modulation by a collateral inhibitory mechanism. Life Sci 23: 1383–1392
Chance WT (1980) Autoanalgesia: opiate and non-opiate mechanisms. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 4: 55–67
Chance WT (1983) Clonidine analgesia: tolerance and crosstolerance to autoanalgesia. Life Sci 33: 2241–2246
Chance WT (1986) The role of brain and spinal cord norepinephrine in autoanalgesia. Ann NY Acad Sci 467: 309–330
Chance WT, Schechter MD (1979) Autoanalgesia: blockade by yohimbine. Eur J Pharmacol 58: 89–90
Coderre TJ, Rollman GB (1984) Stress analgesia: effects of PCPA, yohimbine and naloxone. Biochem Pharmacol Behav 21: 681–686
Colpaert FC (1984) Cross generalization with LSD and yohimbine in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 102: 541–544
Dwoskin LP, Neal BS, Sparber SB (1988) Evidence for antiserotonergic properties of yohimbine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 31: 321–326
Fanselow MS (1984) Shock-induced analgesia on the formalin test: effects of shock severity, naloxone, hypophysectomy, and associative variables. Behav Neurosci 98: 79–95
Fanselow MS, Baackes MP (1982) Conditioned fear induced opiate analgesia on the formalin test: evidence for two aversive motivational systems. Learn Motiv 13: 200–221
Hagen HS, Green KF (1988) Effects of time of testing, stress level, and number of conditioning days on naloxone sensitivity of conditioned stress-induced analgesia in rats. Behav Neurosci 102: 906–914
Hayes RL, Bennett GJ, Newlon PG, Mayer DJ (1978) Behavioral and physiological studies of non-narcotic analgesia elicited in the rat by certain environmental stimuli. Brain Res 155: 69–90
Howe JR, Yaksh TL (1982) Changes in sensitivity to intrathecal norepinephrine and serotonin after 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA), 5,6-dihydroxytryptamine (5,6-DHT) or repeated monoamine administration. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 220: 311–321
Lichtman AH, Fanselow MS (1989) Yohimbine administered intrathecally reverses both opioid and nonopioid conditional antinociception. Soc Neurosci Abstr 15[1]:372
Matzel LD, Miller RR (1987) Recruitment time of conditioned opioid analgesia. Physiol Behav 39: 135–140
Oliverio A, Castellano C (1982) Classical conditioning of stress-induced analgesia. Physiol Behav 29: 171–172
Ossipov MH, Chatterjee TK, Gebhart GH (1985) Locus coeruleus lesions enhance the antinociceptive potency of centrally administered clonidine but not morphine. Brain Res 341: 320–330
Post C, Persson ML, Archer T, Minor BG, Danysz W, Sundström E (1987) Increased antinociception by alpha-adrenoreceptor drugs after spinal cord noradrenaline depletion. Eur J Pharmacol 137: 107–116
Rochford J, Henry JL (1988) Analgesia induced by continuous versus intermittent cold water swim in the rat: differential effects of intruthecal administration of phentolamine and methysergide. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 31: 27–31
Rochford J, Stewart J (1987) Morphine attenuation of conditioned analgesia: implications for theories of situation-specific tolerance to morphine analgesia. Behav Neurosci 101: 690–700
Ross RT, Randich AR (1985) Associative aspects of conditioned analgesia evoked by a discrete CS. Anim Learn Behav 13: 419–431
Ruffolo RR Jr, DeMarinis RM, Wise M, Hieble JP (1988a) Structure-activity relationships for alpha-2 adrenergic agonists and antagonists. In: Limbird LM (ed) The alpha-2 adrenergic receptors. Humana Press, Clifton, NJ, pp 115–186
Ruffolo RR Jr, Nichols AJ, Hieble JP (1988b) Functions mediated by alpha-2 adrenergic receptors. In: Limbird LM (ed) The alpha-2 adrenergic receptors. Humana Press, Clifton, NJ, pp 187–280
Sawynok J, Reid A (1986) Role of ascending and descending noradrenergic pathways in the antinociceptive effect of baclofen and clonidine. Brain Res 386: 341–350
Snow AE, Tucker SM, Dewey WL (1982) The role of neurotransmitters in stress-induced analgesia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 16: 47–50
Watkins LR, Johannessen JN, Kinscheck IB, Mayer DJ (1984) The neurochemical basis of footshock analgesia: the role of spinal cord serotonin and norepinephrine. Brain Res 290: 107–117
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rochford, J., Dubé, B. & Dawes, P. Spinal cord alpha-2 noradrenergic receptors mediate conditioned analgesia. Psychopharmacology 106, 235–238 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02801978
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02801978