Abstract
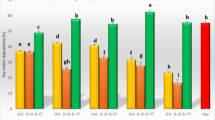
In laboratory-scale experiments, studies were made on the solid state fermentation of plant residues—rice straw and the upper soft portion of the stems of sarkanda (Saccharum munja)—by selected cultures of white-rot fungi,Pleurotus sajor-caju andPleurotus ostreatus. These cultures were selected after preliminary screening of their lignin-degrading capacities on lignin-agar medium. Their lignin degrading and (cellulose + hemicellulose) sparing, along with protein improving capacities, were studied for their potential application in animal feed production. A 100 g quantity of presoaked and sterilized residues was inoculated with wheat spawn of the two cultures and incubated at 25‡C. It was observed that, after 25 d, the crude protein contents (N × 6.25) of rice straw increased from 3 to 17.0% in the case of P.sajor-caju and to 19.2% in case of P. ostreatus. The percent removal values of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin were found to be as follows: 45.8, 16.8, and 47.1%, respectively, in the case ofP. sajor-caju and 56.5, 40.4, and 50%, respectively, in the case of P.ostreatus. After solid state fermentation of sarkanda for 25 d, its protein content increased from 3 to 12.8% in the case ofP. sajor-caju and to 14.5% in the case ofP. ostreatus. The percent removal of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin was found to be as follows: 31.2, 7.1, and 19%, respectively, in the case ofP. sajor-caju and 34.4, 7.1, and 14.3%, respectively, in the case ofP. ostreatus. The results obtained after solid state fermentation of the two residues by the mixed culture of these two basidiomycetes was also presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bisaria, V.S., Saxena, S.K., Manihar, R.B. et al. Solid state fermentation of plant residues for improved animal feed byPleurotus sp.. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 9, 341 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02798966
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02798966