Abstract
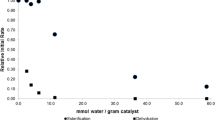
Dehydrated preparations of alcohol oxidase adsorbed on DEAEcellulose vigorously catalyze a gas-phase oxidation of ethanol vapors with molecular oxygen. The gas-phase reaction is strongly dependent on the water activity of the system. The enzymatic activity is severely inhibited by the product hydrogen peroxide. This inhibition can be alleviated, however, by an addition of catalase or peroxidase to the dry preparation. Such dehydrated, bienzymic catalysts afford a complete and selective conversion of the substrate to acetaldehyde. Dry alcohol oxidase is much more thermostable than in aqueous solution. The results of this work suggest that dehydrated enzymes have potential applications in the analysis of gaseous compounds and in the development of novel gas-solid bioreactors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guilbault, G. G., and Olivera Neto, G. (1985), inEnzymes and Immobilized Cells in Biotechnology, Laskin, A. I., ed., Benjamin/Cummins, Menlo Park, CA, pp. 227–261.
Bergmeyer, H. U., ed. (1983),Methods of Enzymatic Analysis, 3rd Ed., Verlag Chemie, Weingheim, Deerfield FL, Basel.
Takei, H., Nakashima, K., Adachi, O., Shinagawa, E., and Ameyama, M. (1985),Clin. Chem. 31, 1985.
Guilbault, G. G. (1983), inSolid Phase Biochemistry, Scouter, W. H., ed., John Wiley, NY, pp. 479–506.
Carr, P. W., and Bowers, L. D. (1980),Immobilized Enzymes in Analytical and Clinical Chemistry, Wiley, NY.
Kricka, L. J., and Thorpe, G. H. G. (1986),Trends Biotech. 4, 253.
Smith, C. H., Landt, M., Steelman, M., and Ladenson, J. H. (1983),Clin. Chem. 29, 1422.
Klibanov, A. M. (1986),Chemtech. 16, 354.
Kazandjian, R. Z., Dordick, J. S., and Klibanov, A. M. (1986),Biotech. Bioeng. 28, 417.
Clary, J. J., Gibson, J. E., and Waritz, R. S., eds. (1983),Formaldehyde: Toxicology, Epidemiology, Mechanisms, Marcel Dekker, NY.
Hanson, D. (1986),Chem. Eng. News 64, Sept. 22, p. 17.
Meyer, B., and Hermanns, K. (1985), inFormaldehyde, Turoski, V., ed., American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp. 101–116.
Barzana, E., Klibanov, A. M., and Karel, M. (1986), US Patent Application no. 895,497.
Kazandjian, R. Z., and Klibanov, A. M. (1985),J. Am. Chem. Soc. 107, 5448.
Weast, R. C., ed. (1972),Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 53rd Ed., The Chemical Rubber Co., Cleveland, OH, p. E40.
Laitinen, H. A., and Harris, W. E. (1975),Chemical Analysis, 2nd Ed., McGraw Hill, NY, pp. 361–363.
Hildebrandt, A. G., Roots, M., and Heinemeyer, G. (1978),Meth. Enzymol. 52, 342.
Tani, Y., Miya, T., and Ogata, K. (1972),Agr. Biol. Chem. 36, 76.
Kato, N., Omori, Y., Tani, Y., and Ogata, K. (1976),Eur. J. Biochem. 64, 341.
Guilbault, G. G., and Lubrano, G. L. (1984),Anal. Chem. Acta 69, 189.
Hopkins, T. R. (1985),Am. Biotech. Lab. 3, 32.
Yagi, T., Tsuda, M., Mori, Y., and Inokuchi, H. (1969),J. Am. Chem. Soc. 91, 2801.
Kimura, K., Suzuki A., Inokichi, H., and Yagi, T. (1979),Biochim. Biophys. Acta 567, 96.
Hou, C. T. (1984),Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 19, 1.
De Bont, J. A. M., van Ginkel, C. G., Tramper, J., and Luyben, K. C. A. M. (1983),Enzyme Microb. Technol. 5, 55.
Cedeno, M., and Waissbluth, M. (1978), inEnzyme Engineering, vol. 4, Brown, G. B., Maneckee, G., and Wingard, L. B., eds., Plenum, NY, pp. 405–407.
Ngeh-Ngwainbi, J., Foleym P. H., Kuan, S. S., and Guilbault, G. G. (1986),J. Am. Chem. Soc. 108, 5444.
Klibanov, A. M. (1983),Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 29, 1.
Barzana, E., Klibanov, A. M., and Karel, M. (1986), inDrying 86, Mujumdar, A. S., ed., vol. 1, Hemisphere, NY, pp. 428–431.
Silver, M., and Karel, M. (1981),J. Food Biochem. 5, 283.
Kundu, A. B., Ghosh, B. L., and Ghosh, S. N. (1982),Carbohydr. Res. 105, 288.
Saunders, B. C., Holmes-Siedle, A. G. and Stark, B. P. (1964),Peroxidase, Butterworth, London.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barzana, E., Klibanov, A.M. & Karel, M. Enzyme-catalyzed, gas-phase reactions. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 15, 25–34 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02798504
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02798504