Abstract
A series of chlorinated phenols, derivatives of pentachlorophenol and chlorinated benzene derivatives were prepared and their toxicity to the brown-rot fungiGloeophyllum trabeum was determined in a standard ASTM 12-wk soil-block test. 2,3,5,6-Tetrachlorophenyl isocyanate and pentachlorophenyl isocyanate were synthesized, reacted with southern pine sapwood, and the extracted wood placed in the 12-wk soil-block test.
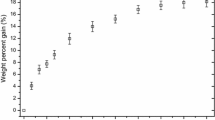
Pentachlorophenol was found to be the most toxic chemical tested toGloeophyllum trabeum in the soil-block test. Pentachlorophenol is effective in eliminating attack at 0.16 lb/ft3. Acetylation of pentachlorophenol does not reduce its toxicity. Methylation of the phenol produces a methyl ether derivative that has little observed toxicity even at 1 lb/ft3. Tetrachlorophenol eliminates attack at 0.33 lb/ft3. All other partially chlorinated phenols showed little toxicity toGloeophyllum trabeum even at 1 lb/ft3. Phenol and polychlorinated benzene derivatives showed little toxicity in the soil-block tests. The bonded tetra- and pentachlorophenyl isocyanates reduced attack compared to controls, but the mechanism of effectiveness of the mechanism probably results from substrate modification and enzyme blocking rather than toxicity. The level of treatment (12 wt% gain) corresponds to 4.5 lb/ft3, or four times higher than the highest treatment for the non-bonded chemicals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blackman, G. E., Parke, M. H., and Garton, G.,Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 54, 45 (1955).
Byrde, R. J. W., and Woodcock, D.,Ann. Appl. Biol. 44(1), 138 (1956).
Barral, E.,Bull. Soc. Chim. 13(3), 341 (1895).
Weber, A., and Wolff, N.,Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 18, 335 (1885).
American Society for Testing and Materials. ASTM Stand. Desig. D 1413, Philadelphia, Pa., 1976.
Holtschmidt, H. O., Bayer, O., and Degener, E., US Patent 3,277,138, Oct. 4, 1966.
Rowell, R. M., and Ellis, W. D.,Wood Sci. 12(1), 52 (1979).
Rowell, R. M., and Ellis, W. D.,ACS Symp. Ser. 172, 263 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rowell, R.M. Bonding of toxic chemicals to wood. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 9, 447–453 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02798399
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02798399
Index Entries
- Bonding, of toxic chemicals to wood
- phenols, bonding of chlorinated to wood
- chlorinated phenols, bonding to wood
- wood, bonding of chlorinated phenols to
- toxicity, of phenols to wood brown-rot fungi
- fungi, wood brown-rot and toxic phenols
- brown-rot fungi, effect of phenols on wood
- Gloeophyllum trabeum, toxicity of wood brown-rot to