Abstract
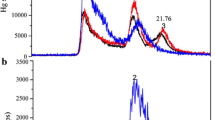
The mercury-binding capacity of seleno-DL-methionine and selenium dioxide was assessed in male Wistar rats. Mercury was supplied as fish loaves made of northern pike or rainbow trout. We used a selenium concentration of 3.4 mg/kg fish, about sixfold compared to the equivalent quantity of mercury. Seleno-DL-methionine had a tendency to increase both methyl mercury and total mercury in blood, although it also seemed to reduce the proportion of methyl mercury of total mercury. Selenium dioxide lowered mercury levels by 24–29% both in the blood and in the liver of rats that were fed with northern pike.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. C. Linder, Nutrition and metabolism of trace elements, inNutritional Biochemistry and Metabolism, 2nd ed., M. C. Linder, ed. Elsevier, New York, pp. 215–276 (1991).
International Programme on Chemical Safety (IPCS),Environmental Health Criteria 101, Methyl Mercury, World Health Organization, Geneva (1990).
R. Von Burg, F. K. Northington, and A. Shamoo, Methyl mercury inhibition of rat brain muscarinic receptors,Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 53, 285–292 (1980).
M. Verta,Mercury in Finnish Forest Lakes and Reservoirs: Anthropogenic Contribution to the Load and Accumulation in Fish, Water and Environment Research Institute, National Board of Waters and the Environment, Helsinki (1990).
T. W. Clarkson, Mercury—an element of mystery,New Engl. J. Med. 323, 1137–1139 (1990).
J. Kämäri, M. Forsius, P. Kortelainen, J. Mannio, and M. Verta, Finnish lake survey: present status of acidification,Ambio 20, 23–27 (1991).
J. Leskinen, O. V. Lindqvist, J. Lehto, and P. Koivistoinen,Selenium and Mercury Contents in Northern Pike (Esox lucius L) of Finnish Manmade and Natural Lakes, Water Research Institute, National Board of Waters, Finland, Helsinki (1986).
D. Kromhout, E. B. Bosschieter, and C. De Lezenne Coulander, The inverse relation between fish consumption and 20-year mortality from coronary heart disease,New Engl. J. Med. 312, 1205–1209 (1985).
R. B. Shekelle, L. U. Misell, O. Paul, A. M. Shryock, and J. Stamler, Fish consumption and mortality from coronary heart disease,New Engl. J. Med. 313, 820 (1985).
S. E. Norell, A. Ahlbom, M. Feychting, and N. L. Pedersen, Fish consumption and mortality from coronary heart disease,Br. Med. J. 293, 426 (1986).
T. A. Dolecek and G. Grandits, Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids and mortality in the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial (MRFIT), inHealth Effects of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Seafood, World Rev. Nutr. Diet, vol.66, A. P. Simopoulos, R. R. Kifer, R. E. Martin, and S. D. Barlow, eds., Karger, Basel, pp. 205–216 (1991).
S. E. Vollset, I. Heuch, and E. Bjelke, Fish consumption and mortality from cardiovascular disease,New Engl. J. Med. 313, 820–821 (1985).
J. D. Curb and D. M. Reed, Fish consumption and mortality from cardiovascular disease,New Engl. J. Med. 313, 821–822 (1985).
A. Ascherio, E. B. Rimm, M. J. Stampfer, E. L. Giovannucci, and W. C. Willett, Dietary intake of marine n-3 fatty acids, fish intake, and the risk of coronary disease among men,New Engl. J. Med. 332, 977–982 (1995).
P. Pietinen, A. Ascherio, P. Korhonen, A. M. Hartman, W. C. Willett, D. Albanes, et al., Intake of fatty acids and risk of coronary heart disease in a cohort of Finnish men. The alpha-tocopherol, beta-carotene cancer prevention study,Am. J. Epidemiol. 145, 876–887 (1997).
A. Keys, Seven countries. A multivariate analysis of death and coronary heart disease. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA, pp. 64–95 (1980).
M. Ihanainen, R. Salonen, R. SeppÄnen, and J. T. Salonen, Nutrition data collection in the Kuopio Ischaemic Heart Disease Risk Factor Study: nutrient intake of middleaged Eastern Finnish men,Nutr. Res. 9, 597–604 (1989).
J. T. Salonen, G. Alfthan, J. K. Huttunen, J. Pikkarainen, and P. Puska, Association between cardiovascular death and myocardial infarction and serum selenium in a matched-pair longitudinal study,Lancet 2, 175–179 (1982).
J. T. Salonen, R. Salonen, K. SeppÄnen, M. Kantola, S. Suntioinen, and H. Korpela, Interactions of serum copper, selenium, and low density lipoprotein cholesterol in atherogenesis,Br. Med. J. 302, 756–760 (1991).
J. T. Salonen, S. YlÄ-Herttuala, R. Yamamoto, S. Butler, H. Korpela, R. Salonen, et al., Autoantiobody against oxidized LDL and progression of carotid atherosclerosis,Lancet 339, 883–887 (1992).
J. T. Salonen, K. SeppÄnen, K. Nyyssönen, H. Korpela, J. Kauhanen, M. Kantola, et al. Intake of mercury from fish, lipid peroxidation, and the risk of myocardial infarction and coronary, cardiovascular, and any death in Eastern Finnish men,Circulation 91, 645–655 (1995).
T. H. Lin, Y. L. Huang, and S. F. Huang, Lipid peroxidation in liver of rats administrated with methyl mercuric chloride,Biol. Trace Element Res. 54, 33–41 (1996).
M. Kantola, M. Saaranen, and T. Vanha-Perttula, Selenium and glutathione peroxidase in seminal plasma of men and bulls,J. Reprod. Fertil. 83, 785–794 (1988).
B. Halliwell and J. M. C. Gutteridge, Oxygen toxicity, oxygen radicals, transition metal, and disease,Biochem. J. 219, 1–14 (1984).
F. W. Sunderman, Jr., Metals and lipid peroxidation,Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 5, 137–143 (1986).
G. Drasch, E. Wanghofer, G. Roider, and S. Strobach, Correlation of mercury and selenium in the human kidney,J. Trace Elements Med. Biol. 10, 251–254 (1996).
H. Kawahara, M. Nakamura, A. Jamagami, and T. Nakanisi, Cellular responses to dental amalgam in vitro,J. Dental Res. 54, 394–401 (1995).
J. E. Spallholz, On the nature of selenium toxicity and carcinostatic activity,Free Radical Biol. Med. 17, 45–64 (1994).
C. Coudray, H. Hida, F. Boucher, V. Tirard, J. De Leiris, and A. Favier, Effect of selenium supplementation on biological constants and antioxidant status in rats,J. Trace Elements Med. Biol. 10, 12–19 (1996).
A. W. Halverson, I. S. Palmer, and P. L. Guss, Toxicity of selenium to post-wealing rats,Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 9, 477–484 (1966).
N. Ballatori, Z. Gatmaitan, and A. T. Truong, Impaired biliary excretion and whole body elimination of methyl mercury in rats with congenital defect in biliary glutathione excretion,Hepatology 22, 1469–1473 (1995).
J. K. Miettinen, T. Rahola, T. Hattula, K. Rissanen, and M. Tillander, Elimination of203Hg-methyl mercury in man,Ann. Clin. Res. 3, 116–122 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seppänen, K., Laatikainen, R., Salonem, J.T. et al. Mercury-binding capacity of organic and inorganic selenium in rat blood and liver. Biol Trace Elem Res 65, 197–210 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02789096
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02789096