Summary
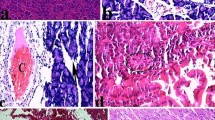
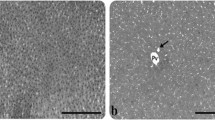
Rats develop acute pancreatitis when infused iv for 3 h with cerulein (10 μg/kg/h). Autopsies of the pancreas seen by light microscope show interstitial edema, acinar cells vacuolization, and leukocyte margination in pancreatic capillaries; under electron microscope, severe damage concerning mitochondrial and zymogen granules structures are apparent. Particularly, swelling of the mitochondria and disruption of mitochondrial cristae was observed as well as formation of large vacuoles arising from zymogen granules and liposome fusion. A significant increase of lipid hydroperoxide level in the pancreatic tissue was observed. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of 4-hydroxy-TEMPO—a low-mol-wt superoxide dismutase mimic—in a rat cerulein model of acute pancreatitis, with the expectation that free radical mediated hydroperoxide formation and tissue damage may be reduced significantly. Twenty-one male Wistar rats were divided into three groups: Group 1 (n=5) served as a control and was infused iv for 3 h with physiologic saline; Group 2 (n=8) was infused iv for 3 h with cerulein 10 μg/kg/h; and Group 3 (n=8) infused iv both with cerulein and 4-hydroxy-TEMPO 22.6 mg/kg/h. Pancreatic tissue damage was quantified by measuring lipid hydroperoxide (LOOH) level, the weight of the organ, and by light and electron microscopic examination. 4-hydroxy-TEMPO penetration across cellular membrane barriers was quantified by ESR spectrometric measuremts of 4-hydroxy-TEMPO concentration in pancreatic tissue samples and pancreatic juice as well. Administering 4-hydroxy-TEMPO to rats resulted in preventing both lipid hydroperoxide formation and severe morphological damage. 4-hydroxy-TEMPO crossed cellular membrane barriers and was excreted to pancreatic juice. Infusion of 4-hydroxy-TEMPO appears to prevent pancreatic injury caused by free radicals in experimental cerulein pancreatitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dabrowski A, Gabryelewicz A, Wereszczynska-Siemiatkowska U, et al. Oxygen-derived free radicals in cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis.Scand J Gastroenterol 1988; 23: 1245–1249.
Wisner JR, Renner JG, Green D, et al. Evidence for a role of oxygen derived free radicals in the pathogenesis of caerulein induced acute pancreatitis in rats.Gut 1988; 29: 1516–1523.
Sanfey H, Bulkey GB, Cameron JL. The pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis The source and role of oxygen-derived free radicals in three different experimental models.Ann Surg 1985; 200: 405–413.
Feher J, Csomos G, Vereckei A. Free radical reactions in medicine. Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg, 1987, pp. 3–17.
Nonaka A, Manabe T, Kyogoku T, et al. Changes in lipid peroxide and oxygen radical scavengers in cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis.Digestion 1990; 47: 130–137.
Sanfey H, Sarr M, Bulkey GB, et al. Oxygen-derived free radicals and acute pancreatitis: a review.Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 1986; 584: 109–118.
Guice KS, Miller DE, Oldham KT, et al. Failure of antioxydant therapy (polyethylene glycol-conjugated catalase) in acute pancreatitis.Am J Surg 1989; 157: 145–149.
Mitchell JB, Samuni A, Krishna MC, et al. Biologically active metal-independent dismutase mimics.Biochemistry 1990; 29: 2802–2807.
Wisner JR, Renner JG. Allopurinol attenuates caerulein induced acute pancreatitis in the rat.Gut 1988; 29: 926–929.
Sarr MG, Bulkley GB, Cameron JL. Temporal efficacy of allopurinol during the induction of pancreatitis in the ex vivo perfused canine pancreas.Surgery 1987; 101: 342–346.
Schoenberg MH, Buchler M, Gaspar M, et al. Oxygen free radicals in acute pancreatitis of the rat.Gut 1990; 31: 1138–1143.
Sledziński Z, Wożniak M, Antosiewicz J, et al. Protective effect of a mimic nitroxide of superoxide dismutase on lipid peroxidation in caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in rats.Br J Surg 1992; 79: S112.
Thomas PD, Poznansky MJ. A modyfied tetramentyl-benzidine method for measuring lipid hydroperoxides.Analytical Biochemistry 1990; 188: 228–232.
Lampel M, Kern HF. Acute interstitial pancreatitis in the rat induced by excessive doses of a pancreatic secretagogue.Virchows Arch (A) 1977; 376: 97–117.
Steer ML, Meldolesi J. The cell biology of experimental pancreatitis.N Engl J Med 1987; 316: 144–150.
Steer ML, Meldolesi J, Figerella C. Pancreatitis. The role of lisosomes.Dig Dis Sci 1984; 29: 934–938.
Sanfey H, Bulkley GB, Cameron JL. The role of oxygen derived free radicals in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis.Ann Surg 1984; 200: 405–413.
Miura Y, Utsumi H, Hamada A. Antioxidant activity of nitroxide radicals in lipid peroxydation of rat liver microsomes.Arch Biochem Biophys 1993; 300: 148–156.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Śledziński, Z., Woźniak, M., Antosiewicz, J. et al. Protective effect of 4-hydroxy-TEMPO, a low molecular weight superoxide dismutase mimic, on free radical toxicity in experimental pancreatitis. Int J Pancreatol 18, 153–160 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02785889
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02785889