Abstract
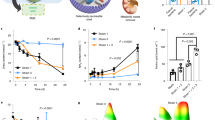
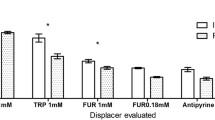
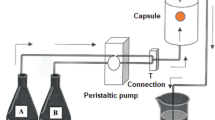
Ingestible adsorbents for the removal of uremic metabolites are being investigated as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of chronic uremia. In particular, a microcapsule product containing urease and zirconium phosphate (UZP) has been investigated for removing urea. A dog model, simulating chronic uremia, was developed to investigate: (1) the concentration of various nitrogenous metabolites (urea, creatinine, and uric acid) in the GI tract, (2) flux rates of H2O and various nitrogenous metabolites in the GI tract, and (3) the efficacy of the microcapsule product. The results of these perfusion studies suggest that urea and creatinine can be removed from the GI tract via ingestible adsorbents. In addition, the model may be useful in investigating suspect uremic toxins, e.g., guanidinosuccinic acid (GSA). The reduction of blood urea nitrogen levels in the dog model when the animal was fed the microcapsule product was limited by the capacity of the zirconium phosphate to bind ammonium ion. Preliminary clinical studies with the microcapsule product indicate that it may be of potential adjunctive therapy in patients suffering from chronic renal failure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pendleton, W. R., and West, F. E. (1932),Amer. J. Physiol. 101, 391.
Twiss, E. E., and Kolff, W. J. (1951),JAMA 146, 1019.
Yatzidis, H. (1964),Nephron 1, 310.
Denti, E., Luboz, M. P., Tessore, V. A., Castino, F., and Gaglia, P. F. (1975),Kidney Int. 7, S-401.
Zeig, S. and Friedman, E. A. (1980), inSorbents and Their Clinical Applications, Giordano, C., ed., Academic Press, New York, pp. 275–294.
Dunea, G., and Kolff, W. J. (1965),Trans. Amer. Soc. Artif. Int. Organs 11, 178.
Hagstam, K. E., Larsson, L. E., and Thysell, H. (1966),Acta. Med. Scand. 180, 593.
Chang, T. M. S., and Malave, N. (1970),Trans. Amer. Soc. Artif. Int. Organs 16, 141.
Chang, T. M. S., Gonda, A., Dirks, J. H., and Malave, N. (1971),Trans. Amer. Soc. Artif. Int. Organs 17, 246.
Chang, T. M. S. (1966),Trans. Amer. Soc. Artif. Int. Organs 12, 13.
Chang, T. M. S., and Loa, S. K. (1970),Physiologist 13, 70.
Sparks, R. E., Salemme, R. M., Meier, P. M., Litt, M. H., and Lindan, O. (1969),Trans. Amer. Soc. Artif. Int. Organs 15, 353.
Gardner, D. L., Falb, R. D., Kim, B. C., and Emmerling, D.C. (1971),Trans. Amer. Soc. Artif. Int. Organs 17, 239.
Giordano, C., Esposito, R., and Randazzo, C. (1971), in Workshop on Gastrointestinal Sorbents in Uremia, DHEW Publ. No. (NIH) 72-78, pp. 121–138.
Giordano, C., ed. (1980),Sorbents and Their Clinical Applications, Academic Press, New York, pp. 1–503.
Friedman, E. A., and Manis, T. (1981),Proceedings of the 8th International Congress on Nephrology, p. 385.
Gardner, D. L., Emmerling, D. C., Williamson, K. D., Baytos, W. C., and Hassler, C. R. (1975),Kidney Int. 7, S-393.
Kjellstrand, C., Borges, H., Pru, C., Gardner, D., and Fink, D. (1981),Trans. Amer. Soc. Artif. Int. Organs 27, 24.
Bricker, N. S. (1964),J. Clin. Invest. 43, 1915.
Hyden, S. (1956),Lantbrhogak Ann. 22, 139.
Cooper, H., Levitan, R., Fordtran, J. S., and Ingelfinger, F. J. (1966),Gastroenterology 50, (1), 1.
Gardner, D. L., and Emmerling, D. C. (1977), inBiomedical Applications of Immobilized Enzymes and Proetins, Vol. 1, Chang, T. M. S., ed., Plenum Press, New York, pp. 163–170.
Stein, I. M. (1969),New Eng. J. Med. 280, 926.
Knapowski, J. (1963),Acta Medica Polonia 4, 201.
Duker, H. H. (1955),The Physiology of Domestic Animals, Comstock, Ithica, NY, 75th ed., p. 300
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gardner, D.L., Kjellstrand, C.M., Hassler, C.R. et al. An orally administered microcapsule system for treating chronic renal failure patients. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 10, 27–40 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02783733
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02783733