Summary
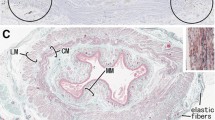
We tried to make a clear three-dimensional picture of the autonomic nerves in the wall of the human colon, using a Golgi method rarely applied to human materials. At autopsy, sigmoid colon without mucosal lesions were collected from 16 males after sudden death from apoplexy, head injury, or myocardial infarction. These materials were fixed in 10% formalin, impregnated with a modified Golgi method and embedded in celloidin. Then three-dimensional serial sections were made and observed with a light microscope. Many fine nerve fibers formed a plexus in the subserosa, muscular layer, submucosa, and mucosa. The myenteric plexus was made up of rectangular meshes of nerve fiber bundles. However, unlike myenteric plexus, no regular mesh was found in the submucosal plexus. Further, nerve fibers connecting myenteric and submucosal plexus were observed. It may be concluded from these findings that there exist nerve pathways regulating intestinal motility between myenteric and submucosal plexus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fukuhara T, et al: On the intestinal intrinsic reflexes. Jpn J Physiol 8: 9, 1958
Schofield GC: Anatomy of muscular and neural tissues in the alimentary canal, in “Handbook of Physiology” Sec 6, Alimentary Canal, 4, Motility, by Code CF, Am Physiol Soc, Washington DC 1968, p 1579
Baumgarten HG, et al: Auerbach’s plexus of mammals and man: Electron microscopic identification of three different types of neuronal processes in myenteric ganglia of the large intestine from rhesus monkeys, guinea-pigs and man. Z Zellforsch 106: 376, 1970
Gershon MD: The enteric nervous system: Multiplicity of neurotransmitters outside of the brain, in “Smooth Muscle” by Bülbring E, Brading AF, Jones AW, Tomita T. Arnold, London 1981, p 263
Truelove SC: Movements of the large intestine. Physiol Rev 46: 457, 1966
Parks TG: Colonic motility in man. Postgraduate Med J 49:90, 1973
Christensen J: Myoelectric control of the colon. Gastroenterology 68: 601, 1975
Snape WJ, et al: Colonic myoelectric activity in the irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 70: 326, 1976
Sasaki D, et al: Antispasmodic effect of prifinium bromide on the proximal and distal colon in patients with diverticular disease. Gastroenterologia Jpn 16: 344, 1981
Golgi C: Sulla structura della sostanza grigia del cervello. Gazzetta Medica Italiana 33: 244, 1873
Braitenberg V, et al: Morphological observations on the cerebellar cortex. J Comparative Neurol 109: 1, 1958
Braitenberg V, et al: Correlation of crystal growth with the staining of axons by the Golgi procedure. Stain Techn 42: 277, 1967
Narita N, et al: Formalin fixed material and modified Golgi staining. Hirosaki Med J 32: 191, 1980 (Jpn)
Koya G, et al: Rapid method of embedding with celloidin. Hirosaki MedJ 32: 156, 1980 (Jpn)
Hirst GDS, et al: Two descending nerve pathways activated by distension of guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol 244: 113, 1975
Hirst GDS, et al: Synaptic potentials recorded from neurones of the submucous plexus of guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol 249: 369, 1975
Ohkubo K: Studies on the intrinsic nervous system of the digestive tract. I. The submucous plexus of guinea-pig. Jpn J Med Sci, 1 Anatomy 6: 1, 1936
Fehèr E: Ultrastructural study of nerve terminals in the submucous plexus and mucous membrane after extirpation of the myenteric plexus. Acta Anat 94: 78, 1976
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narita, N., Kawakami, K., Yoshida, Y. et al. Morphological study on the motility of the human colon. Gastroenterol Jpn 18, 310–313 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02774947
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02774947