Abstract
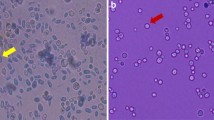
Patients with malignancies are at high risk to develop infections byCandida albicans. We have compared the adherence ofC. albicans isolated from urine cultures to bladder epithelial cells obtained from healthy volunteers and patients with cancer of the bladder. The mean number ofC. albicans adhering per epithelial cell from areas infiltrated from cancer was significantly higher as compared to cells obtained from intact areas of cancerous bladders bladders and from normal bladders. The increased adherence ofC. albicans to cancerous epithelial cell suggests that malignancies are associated with alterations of the epithelial cell surface which render the cells more susceptible to colonization byC. albicans. The increased colonization may predispose these patients toC. albicans infections.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Louria, D. B., Stiff, D. P., Bennett, B.: Disseminated moniliasis in the adult.Medicine, 41, 307 (1968).
Odds, F. C., Evans, E. G.: Distribution of pathogenic yeasts and humoral antibodies toCandida among hospital inpatients.J. Clin. Pathol. 33, 750 (1980).
Gibbons, R. J., Van Houte, J.: Bacterial adherence in oral microbial ecology.Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 29, 19 (1975).
Smith, H.: Microbial surfaces in relation to pathogenicity.Bacteriol. Rev. 41, 475 (1977).
Douglas, L. J.: Adhesion ofCandida species to epithelial surfaces.Crit. Rev. Microbiol., 15, 27 (1987).
Ellen, R. P., Gibbons, R. S.: M-protein associated adherence ofStreptococcus pyogenes to epithelial surfaces.Infect. Immun. 5, 826 (1972).
Critchley, I. A., Douglas, L. J.: Isolation and partial characterization of an adhesion fromCandida albicans.J. Gen. Microbiol. 133, 629 (1987).
Calderone, R. A., Braun, P. C.: Adherence and receptor relationships ofCandida albicans.Microbiol. Rev. 55, 1 (1991).
Kalo, A., Segal, E., Sahar, E., Dayan, D.: Interaction ofCandida albicans with genital mucosal surfaces: Involvement of fibronectin in adherence.J. Infect. Dis. 157, 1253 (1988).
Ahern, D. G.: Medically important yeasts.Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 32, 59 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skoutelis, A.T., Lianou, P.E., Votta, E. et al. Adherence ofCandida albicans to epithelial cells from normal and cancerous urinary bladders. International Urology and Nephrology 26, 519–522 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02767652
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02767652