Abstract
Purpose: Using different micropipettes for zona drilling and blastomere aspiration for embryo biopsy is prevalent at centers of preimplantation genetic diagnosis. The purpose of our study was to simplify the technique by using only one micropipette.
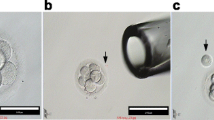
Methods: In this animal model, ICR mouse embryos at the four-cell stage (n=446) were randomly allocated into two groups: a biopsied group (n=224) for blastomere aspiration and a control group (n=222) without micromanipulation. We used a drilling/biopsy micropipette to drill a hole in the zona by expulsion of acidified Tyrode’s solution and to aspirate the blastomere by gentle suction with the same micropipette and pull it out of the zona. One blastomere was biopsied from each embryo.
Results: In all, 222 (99.1%) intact blastomeres were successfully biopsied from 224 embryos. Only two blastomeres were damaged during aspiration. The capacity for blastocyst development (92.4 vs 93.7%) was not different between the two groups, but the percentages of embryos hatching (51.8 vs 18.0%) and hatched (29.9 vs 8.1%) were significantly higher in the biopsied group than in the control group.
Conclusions: This simplified technique of embryo biopsy is safe and highly efficient for obtaining blastomeres for preimplantation genetic diagnosis and may also facilitate hatching of the blastocysts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edwards RG, Gardner RL: Sexing of live rabbit blastocysts. Nature 1967;214:576–577
Handyside AH, Kontogianni EH, Hardy K, Winston RML: Pregnancies from biopsied human preimplantation embryos sex by Y-specific DNA amplification. Nature 1990;344: 768–770
Cui KH, Matthews CD: Preimplantation diagnosis. Lancet 1994;343:972–973
Liu J, Lissens W, Van Broeckhoven C, Lofgren A, Camus M, Liebaers I, Van Steirteghem A: Normal pregnancy after preimplantation DNA diagnosis of a dystrophin gene deletion. Prenat Diagn 1995;15:351–358
Wilton LJ, Trounson AO: Biopsy of preimplantation mouse embryos: Development of micromanipulated embryos and proliferation of single blastomeres in vitro. Biol Reprod 1989;40:145–152
Krzyminska UB, Lutjen J, O’Neill C: Assessment of the viability and pregnancy potential of mouse embryos biopsied at different preimplantation stages of development. Hum Reprod 1990;5:203–208
Roudebush WE, Kim JG, Minhas BS, Dodson MG: Survival and cell acquisition rates after preimplantation embryo biopsy: Use of two mechanical techniques and two mouse strains. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1990;162:1084–1090
Grifo JA, Boyle A, Fischer E, Lavy G, DeCherney AH, Ward DC, Sanyal MK: Preembryo biopsy and analysis of blastomeres by in situ hybridization. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1990;163:2013–2019
Han YM, Yoo OJ, Lee KK: Sex determination in single mouse blastomeres by polymerase chain reaction. J Assist Reprod Genet 1993;10:151–156
Gordon JW, Gang I: Use of zona drilling for safe and effective biopsy of murine oocytes and embryos. Biol Reprod 1990;42:869–876
Tarin JJ, Conaghan J, Winston RM, Handyside AH: Human embryo biopsy on the 2nd day after insemination for preimplantation diagnosis: Removal of a quarter of embryo retards cleavage. Fertil Steril 1992;58:970–976
Santalo J, Veiga A, Calafell JM, Calderon G, Vidal F, Barri PN, Gimenes C, Egozcue J: Evaluation of cytogenetic analysis for clinical preimplantation diagnosis. Fertil Steril 1995;64:44–50
Handyside AH: Preimplantation diagnosis: Strategies for embryo biopsy and genetic analysis.In Gamete and Embryo Micromanipulation in Human Reproduction, SB Fishel, EM Symonds (eds). Boston, Little, Brown, 1992, p 175
Munne S, Sultan KM, Weier HU, Grifo JA, Cohen J, Rosenwaks Z: Assessment of numeric abnormalities of X, Y, 18, and 16 chromosomes in preimplantation human embryos before transfer. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:1191–1199
Gibbons WE, Gitlin SA, Lanzendorf SE, Kaufmann RA, Slotnick RN, Hodgen GD: Preimplantation genetic diagnosis for Tay-Sachs disease: Successful pregnancy after pre-embryo biopsy and gene amplification by polymerase chain reaction. Fertil Steril 1995;63:723–728
Takeuchi K, Sandow BA, Morsy M, Kaufmann RA, Beebe SJ, Hodgen GD: Preclinical models for human pre-embryo biopsy and genetic diagnosis. I. Efficiency and normalcy of mouse pre-embryo development after different biopsy techniques. Fertil Steril 1992;57:425–430
Cui KH, Verma PJ, Matthews CD: Hatching rate: An optimal discriminator for the assessment of single-blastomere biopsy. J Assist Reprod Genet 1993;10:157–162
Quinn P, Kerin JF, Warness GM: Improved pregnancy rate in human in vitro fertilization with the use of a medium based on the position of human tubal fluid. Fertil Steril 1985;44:493–498
Chen SU, Yang YS, Ho HN, Hwang JL, Hong TS, Lin HR, Huang SC, Lee TY: Microinjection of human spermatozoa into the perivitelline space of hamster eggs: Comparison with the zona-free hamster egg penetration of human spermatozoa. Arch Androl 1993;30:201–207
Chen SU, Ho HN, Chen HF, Chao KH, Huang SC, Lee TY, Yang YS: Effect of assisted hatching by partial zona pellucida dissection on mouse embryos in vitro. J Formos Med Assoc 1995;94:463–468
Cohen J, Alikani M, Trowbridge J, Rosenwaks Z: Implantation enhancement by selective assisted hatching using zona drilling of human embryos with poor prognosis. Hum Reprod 1992;7:685–691
Grifo JA, Tang YX, Munne S, Alikani M, Cohen J, Rosenwaks Z: Healthy deliveries from biopsied human embryos. Hum Reprod 1994;9:912–916
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, SU., Ho, HN., Chen, HF. et al. A simplified technique for embryo biopsy: Use of the same micropipette for zona drilling and blastomere aspiration. J Assist Reprod Genet 14, 157–161 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02766133
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02766133