Abstract
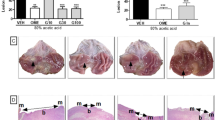
Manda, a natural product made by yeast fermentation of many fruits and black sugar, has antioxidant activity. In the present study, manda prevented stomach ulcers caused by immobilization-induced emotional stress. Manda [5% manda solution (w/v)] and saline as control, were administered by a canula into the stomach of each experimental animal subsequently after 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 hours from the start of the emotional stress. We classified the severity of gastric lesion formation induced by immobilization with each rat lying on its back for 6 hours at room temperature on a five-grade scale. The control rats all showed congestion and some degree of bleeding in the mucosa of the stomach. However, of the experimental rats, one showed no hemorrhagic lesions only congestion in four cases, and slight or moderate bleeding in eight cases with no massive bleeding cases. The distribution of these data significantly differ from that of the control rats, which suffered the greater damage (X2=10.589,p<0.05). In light microscopic examinations, the control rats showed necrosis in the gastric mucous membranes, desquamation, and bleeding of gastric mucosa. However, the rats treated with manda showed only congestion and did not show erosion or hemorrhage. These results suggest that manda or manda metabolite(s) was absorbed from the stomach and may have produced these action. In the meantime, we are analyzing manda components to try to isolate the active ingredient(s)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Granger, D. N., Rutiki, G., & McCord, J. M. (1981). Superoxide radicals in ferine intestinal ischemia.Gastroenterology, 81, 22–29.
Henrotte, J. G., Franck, G., Santarromana, M., Nakib, S., Dauchy, F., & Boulu, R. G. (1992). Effect of pyridoxine on mice gastric ulcer and brain catecholamines after an immobilization stress.Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism, 36, 313–317.
Kawai, M., Matsuura, S., & Mori, A. (1994). Free radical scavenging action of Manda.The Clinical Report, 28, 393–397.
Kawai, M., & Matsuura, S. (1997). Manda scavenges free radicals and inhibits lipid peroxidation in iron-induced epileptic focus in rats. In M. Hiramatsu, T. Yoshikawa, & M. Inoue, (Eds.),Foods and free radical (pp. 141–145). New York: Plenum Press.
Kurose, I., & Suematsu, M. (1991). Involvement of superoxide anion and platelet-activating factor increased tissue-type plasminogen activator during rat gastric microvascular damages.Thrombosis Research, 62, 241–248.
Kurose, I., Suematsu, M., Miura, S., Fukumura, D., Sekizuka, E., Nagata, H., Oshio, C., & Tsuchiya, M. (1993). Oxyradical generation from leukocytes during endotoxin-induced micro-circulatory disturbance in rat mesentery—Attenuating effect of cetraxate.Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 120, 37–44.
Lewis, M. S., & Whatley, R. E. (1988). Hydrogen peroxide stimulates the synthesis of platelet activating factor by endothelium and induces endothelial cell-dependent neutrophil adhesion.Journal of Clinical Investion, 82, 2045–2055.
Liu, J., & Mori, A. (1994). Involvement of reactive oxygen species in emotional stress: A hypothesis based on the immobilization stress-induced oxidative damage and antioxidant defense changes in rat brain, and the effect of antioxidant treatment with reduced glutathione.International Journal of Management, 1, 249–263.
Liu, J., Wang, X., & Mori, A. (1994). Immobilization stress induced antioxidant defense changes in rat plasma: effect of treatment with reduced glutathione.International Journal of Biochemistry, 26, 511–517.
Obispo, M. J. M. (1993). Gastric ulcers caused by post-burning stress: contribution of free radical.Revista Espanola de Enfermedades Digestivas, 84, 287–289.
Ray, A., & Henke, P. G. (1990). Enkephalin-dopamine interactions in the central amygdalar nucleus during gastric stress ulcer formation in rats.Behavioural Brain Research, 36, 179–183.
Salim, A. S. (1989). Scavening free radicals to stress-induced gastric mucosal injury.Lancet, 2, 1390.
Sato, N., & Kameda, T. (1979). Measurement of hemoperfusion and oxygen sufficiency in gastric mucosa in vivo.Gastroenterology, 76, 814–819.
Suematsu, M., & Kurose, I. (1989). In vivo visualization of oxyradical-dependent photoemission during endothelium-granulocyte interaction in microvascular beds treated with platelet-activating factor.Journal of Biochemistry, 106, 355–360.
Weininger, O. (1956). The effects of experiment of behavior and growth characteristics.Journal of Comparative Physiolosy & Psychology, 49, 1–9.
Yoshikawa, T., Miyagawa, H., Yoshida, N., Sugino, S., & Kondo, M. (1986). Increase in lipid peroxidation in rat gastric mucosal lesions induced by water-immersion restraint stress.Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition, 1, 271–277.
Yoshikawa, T., Yoshida, N., Miyagawa, H., Takemura, T., Sugino, S., & Kondo, M. (1987). Role of lipid peroxidation in gastric mucosal lesions induced by burn shock in rats.Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition, 2, 163–170.
Yoshikawa, T., Ueda, S., Naito, Y., Takahashi, S., Oyamada, H., Morita, Y., Yoneta, T., & Kondo, M. (1989). Role of oxygen-derived free radicals in gastic mucosal injury induced by ischemia or ischemia-reperfusion in rats.Free Radical Research Communications, 7, 285–291.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawai, M., Matsuura, S. Manda suppresses emotional stress-induced stomach ulcers in rats. Int J Stress Manage 4, 63–69 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02766073
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02766073