Summaries
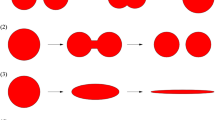
The deformation and breakup of a droplet in two-phase shear flow were simulated by the finite difference lattice Boltzmann method (FDLBM). The fine droplets formation process was investigated in a beadless disperser using ultrathin film and high shear (ultrathin film high-shear disperser, UFHD). As a result, the critical capillary number,C ac,was found at a constant Reynolds number,R e.The necessary condition for the creation of fine droplets in the disperser was that the capillary numberC a>C ac.The atomisation ability of the disperser was discussed based onC ac.The simulation results demonstrated that the disperser can be used to prepare nanometre-size droplets.
Résumé
On a simulé la déformation et la désintégration d’une gouttelette dans un écoulement de cisaillement à deux phases, grâce à la méthode de Boltzmann de treillis de différence finie (FDLBM). Le procédé de formation de gouttelettes fines a été investigué dans un disperseur beadless, en utilisant un film ultra mince et un [taux de] cisaillernent élevé (disperseur à film ultra mince et à taux de cisaillement élevé, UFHD). Comme résultat, le nombre capillaire critique,C ac,a été trouvé à un nombre de Reynolds constant,R e.La formation de gouttelettes fines dans le disperseur dépendait du fait que le nombre capillaireC a>C ac.Une discussion de la capacité d’atomisation du disperseur était basée surC ac.Les résultats de la simulation ont montré que le disperseur peut être utilisé pour la préparation de gouttelettes de taille nanométrique.
Zusammenfassung
Die Verformung und Zerstörung eines Tropfens in Zwei-Phasen Scherfluss wurde mittels der Endlich-Differenz Lattice-Boltzmann Methode (finite difference lattice Boltzmann method, FDLBM) untersucht. Wir verwendeten einen kugellosen Disersator mit ultra-dünnem Film und großen Scherkräften (ultrathin film high-shear disperser, UFHD) um den Prozess der Tropfenbildung zu studieren und fanden, daß die kritische Kapillarnummer,C ac,einer konstanten ReynoldsnummerR e,entsprach. Für die Bildung feiner Tropfen im Dispersator war es nötig, daßC a>C ac.Wir diskutieren die Atomisierungsleistung des Dispersators auf der Basis vonC ac.Die Ergebnisse unserer Simulation demonstrieren, daß der Dispersator zur Herstellung von Tropfen im Nanometerbereich verwendet werden kann.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koishi M,Fine Particles Design, Kogyo Chosakai Publishing Co Ltd, Tokyo, Japan, 1987, ISBN 4 7693 4050 8
Kitahara A,Elucidation of Dispersion — Cohesion and its Application Technology, Techno System Publishing Co Ltd Tokyo, Japan, 1996, ISBN 4 924728 23 3
Komoto M,Stability of Pigment Dispersion and Surface Treatment Technology, Technology and Information Association Publishing Co Ltd, Tokyo, Japan, 2002, ISBN 4 906317 56 1
Koizumi M, Y Sakka, K Chojo and K Niihara,Advanced Technology of Nano-materials, CMC Publishing Co Ltd, Tokyo, Japan, 2001, ISBN 4 88231 303 0
Enomura M, JP Patent 207533, ‘A new dispersion — emulsification device and a new dispersion emulsification method’, 2002
Enomura M, K Araki, M Yokosuka, K Takebayashi, M Yuasa and M Abe, ‘Development and applicability of a new beadless disperser’,Journal of Japan Society of Colour Material,75, (12), 586–91, December 2002
Enomura M, X F Zhang, K Araki, M Yokosuka, K Takebayashi, M Yuasa and M Abe, ‘Performance improvement of the new beadless disperser’,Journal of Japan Society of Colour Material,77, (3), 116–20, March 2004
Taylor G I, ‘The viscosity of a fluid containing small drops of another fluid’,Proceedings of the Royal Society (London) Part A,138, 41–8, 1932
Tsutahara M, N Takata and T Kataoka,Lattice Gas and Lattice Boltzmann Methods — New Methods of Computational Fluid Dynamics, Corona Publishing Co Ltd, Tokyo, Japan, 1999, ISBN 4 339 04343 5
Inamuro T, ‘Lattice Boltzmann method — New simulation method of computational fluid dynamics’,Bussei Kenkyu,77, 193–232, 2001
Nourgaliev R R, T N Dinh, T G Theofanous and D Joseph, ‘The Lattice Boltzmann equation method: Theoretical interpretation, numerics and implications’,Int J Multiphase Flow,29, 117–69, 2003
Tsutahara M, M Kurita and T Iwakami, ‘A new model of finite difference Lattice Boltzmann method’,JSME B,68, 15–21, 2002
Bhatnagar P L, E P Gross and M Krook, ‘A model for collision processes in gases. I: Small amplitude processes in charged and neutral one-component systems’,Phys Rev A,94, 511–25, 1954
Ferziger JH and M Peric,Computational Methods for Fluid Dynamics, Springer, Tokyo, Japan, 1999, ISBN 3 540 65373 2
Enomura M, X F Zhang, M Tsutahara, K Takebayashi and M Abe, ‘Numerical simulation on the flow in a beadless disperser by finite difference Lattice Boltzmann method’,Journal of Japan Society of Colour Material,78, (8), 347–52, August 2005
Taylor G I, ‘The formation of emulsions in definable fields of flow’,Proceedings of the Royal Society (London) Part A,146, 501–23, 1934
Rumscheidt F D and S G Mason, ‘Practice motions in sheared suspensions: Deformation and burst of fluid drops in shear and hyperbolic flow’,Journal of Colloid Science,16, 238–61, 1961
Bruijn R A, ‘Deformation and break up of drops in simple shear flows’, PhD thesis, Technical University of Eindhoven, 1989
Stone H A, ‘Dynamics of drop deformation and break up in viscous fluid’,Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics,26, 65–102, 1994
Enomura M, ‘Development and applicability of a new beadless disperser’, Doctoral dissertation, Tokyo University of Science, March 2006
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X.F., Enomura, M., Tsutahara, M. et al. Numerical simulation of fine droplets formation process in beadless disperser. Surface Coatings International Part B: Coatings Transactions 89, 269–274 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02765578
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02765578