Abstract
The growth hormone-insulin like growth factor (GH-IGF) axis plays a crucial role in the regulation of growth. Initially considered to be a mediator of growth hormone actions, IGF axis has been established as an independent endocrine system with wide array of actions. Recent advances have led to tremendous increase in the clinical utility of the IGF axis. IGF-based investigations (IGF1 and IGF binding protein 3) are now replacing GH-based investigations for evaluation and monitoring of disorders of the GH-IGF axis. IGF therapy has been successfully utilized in growth hormone insensitivity syndrome and GHD type 1B. The possibility of IGF axis as therapeutic options is being explored in wide variety of disorders like hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, Alzheimer's disease and psoriasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosenfield GR, Cohen P. Disorders of growth hormone/ insulin like growth factor and action. In Sperling MA, ed.Pediatric Endocrinology. 2nd edn. Philadelphia; WB Saunders, 2002; 211–288.
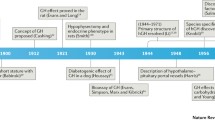
Le Roith D, Bondy C, Yakar Set al. The somatomedin hypothesis: 2001.Endocr Rev 2001; 22: 53–74.
Salmon WD, Daughaday WH. A hormonally controlled serum factor which stimulates sulfate incorporation by cartilage in vitro.J Lab Clin Med 1957; 49: 825–836.
Zapf J, Rinderknecht E, Humbel REet al. Nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) from human serum: recent accomplishments and their physiologic implications.Metabolism 1978; 27: 1803–1828.
Rinderknecht E, Humbel RE. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin.J Biol Chem 1978; 25: 2769–2776.
Monzavi R, Cohen P. IGFs and IGFBPs: role in health and disease.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002; 16: 433–447.
Sizonenko PC, Clayton PE, Cohen Pet al. Diagnosis and management of growth hormone deficiency in childhood and adolescence. Part 1: diagnosis of growth hormone deficiency.Growth Horm IGF Res 2001; 11: 137–165.
Wetterau LA, Moore MG, Lee KWet al. Novel aspects of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Mol Genet Metab 1999; 68: 161–181.
Lupu F, Terwilliger JD, Lee Ket al. Roles of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor 1 in mouse postnatal growth.Dev Biol 2001; 229: 141–162.
Woods KA, Camacho-Hubner C, Barter Det al. Insulin-like growth factor I gene deletion causing intrauterine growth retardation and severe short stature. Acta Paediatr Suppl 1997; 423: 39–45.
Rosenfeld RG, Wilson DM, Lee PD,et al. Insulin-like growth factors I and II in evaluation of growth retardation.J Pediatr 1986; 109: 428–433.
Blum WF, Ranke MB. Use of insulin-like growth factorbinding protein 3 for the evaluation of growth disorders.Horm Res 1990; 33 Suppl 4: 31–37.
Blum WF, Cotterill AM, Postel-Vinay MCet al. Improvement of diagnostic criteria in growth hormone insensitivity syndrome: solutions and pitfalls. Pharmacia Study Group on Insulin-like Growth Factor I Treatment in Grwoth Hormone Insensitivity Syndromes.Acta Paediatr Suppl 1994; 399: 117–124.
Lee KW, Cohen P. Individualized growth hormone therapy in children: advances beyond weight-based dosing.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2003; 16 Suppl 3: 625–630.
Park P, Cohen P. The role of insulin-like growth factor I monitoring in growth hormone-treated children.Horm Res 2004; 62 Suppl 1: 59–65.
Shim M, Cohen P. IGFs and human cancer: implications regarding the risk of growth hormone therapy.Horm Res 1999; 51 Suppl 3: 42–51.
Laron Z, Klinger B, Erster Bet al. Effect of acute administration of insulin-like growth factor I in patients with Laron-type dwarfism.Lancet 1988; 19: 1170–1172.
Guevara-Aguirre J, Rosenbloom AL, Vasconez Oet al. Two-year treatment of growth hormone (GH) receptor deficiency with recombinant insulin-like growth factor I in 22 children: comparison of two dosage levels and to GH-treated GH deficiency.J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997; 82: 629–633.
Azcona C, Preece MA, Rose SJet al. Growth response to rhIGF-I 80 microg/kg twice daily in children with growth hormone insensitivity syndrome: relationship to severity of clinical phenotype.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1999; 51: 787–792.
Backeljauw PF, Underwood LE, GHIS Collaborative Group. Growth hormone insensitivity syndrome. Therapy for 6.5–7.5 years with recombinant insulin-like growth factor I in children with growth hormone insensitivity syndrome: a clinical research center study.J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 1504–1510.
Ranke MB, Savage MO, Chatelain PGet al. Long-term treatment of growth hormone insensitivity syndrome with IGF-I. Results of the European Multicentre Study. The Working Group on Growth Hormone Insensitivity Syndromes.Horm Res 1999; 51: 128–134.
Shaw NJ, Fraser NC, Rose Set al. Bone density and body composition in children with growth hormone insensitivity syndrome receiving recombinant IGF-I.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2003; 59: 487–491.
Underwood LE, Backeljauw P, Duncan V, GHIS Collaborative Group. Effects of insulin-like grwoth factor I treatment on statural growth, body composition and phenotype of children with growth hormone insensitivity syndrome.Acta Paediatr Suppl 1999; 88: 182–184.
Brain CE, Hubbard M, Preece MAet al. Metabolic status of children with growth hormone insensitivity syndrome and responses to treatment with IGF-I.Horm Res 1998; 50: 61–70.
Guan J, Waldvogel HJ, Faull RLet al. The effects of the N-terminal tripeptide of insulin-like growth factor-1, glycineproline-glutamate in different regions following hypoxicischemic brain injury in adult rats.Neuroscience 1999; 89: 649–659.
Wraight CJ, White PJ, McKean SCet al. Reversal of epidermal hyperproliferation in psoriasis by insulin-like growth factor I receptor antisense oligonucleotides.Nat Biotechnol 2000; 18: 521–526.
Carro E, Trejo JL, Gomez-Isla Tet al. Serum insulin-like growth factor I regulates brain amyloid-beta levels.Nat Med 2002; 8: 1390–1397.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bajpai, A., Menon, P.S.N. Insulin like growth factors axis and growth disorders. Indian J Pediatr 73, 67–71 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02758264
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02758264