Abstract
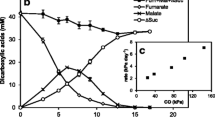
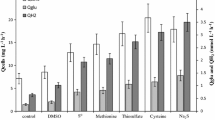
The activities of carbon metabolism enzymes were determined in cellular extracts of the moderately thermophilic, chemolithotrophic, acidophilic bacteriumSulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans subsp.asporogenes, strain 41, grown either at an atmospheric content of CO2 in the gas phase (autotrophically, heterotrophically, or mixotrophically) or autotrophically at a CO2 content increased to 5–10%. Regardless of the growth conditions, all TCA cycle enzymes (except for 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase), one glyoxylate bypass enzyme (malate synthase), and some carboxylases (ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase, pyruvate carboxylase, and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase) were detected in the cell-free extracts of strain 411. During autotrophic cultivation of strains 41 and 1269, the increase in the CO2 content of the supplied air to 5–10% resulted in the activation of growth and iron oxidation, a 20–30% increase in the cellular content of protein, enhanced activity of the key TCA enzymes (citrate synthase and aconitase), and, in strain 41, a decrease in the activity of carboxylases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karavaiko, G.I., Golovacheva, R.S., Pivovarova, T.A., Tsaplina, I. A., and Vartanyan, N.S., Thermophilic Bacteria of the GenusSulfobacillus, Biohydrometallurgy: Proc. Int. Symp., Norris, P.R. and Kelly, D.P., Eds., Kew: Science and Technology Letters, 1988, pp. 29–41.
Norris, P.R., Clark, D.A., Owen, J.P., and Waterhouse, S., Characteristics ofSulfobacillus acidophilus sp. nov. and Other Moderately Thermophilic Mineral-Sulfide-oxidizing Bacteria,Microbiology (Reading, UK), 1996, vol. 142, pp. 775–783.
Dufresne, S., Bouquet, J., Boissinot, M., and Guay, R.,Sulfobacillus disulfidooxidans sp. nov., a New Acidophilic, Disulfide-oxidizing, Gram-Positive, Spore-forming Bacterium,Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol., 1996, vol. 46, no. 4, pp. 1056–1064.
Wood, A.P. and Kelly, D.P., Autotrophic and Mixotrophic Growth of Three Thermoacidophilic Iron-oxidizing Bacteria,FEMS Microbiol. Lett, 1983, vol. 20, pp. 107–112.
Wood, A.P. and Kelly, D.P., Growth and Sugar Metabolism of a Thermoacidophilic Iron-oxidizing Mixotrophic Bacterium,J. Gen. Microbiol., 1984, vol. 130,pp. 1337–1349.
Zakharchuk, L.M., Tsaplina, LA., Krasil’nikova, E.N., Bogdanova, T.I., and Karavaiko, G.I., Carbon Metabolism inSulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans, Mikrobiologiya, 1994, vol. 63, no. 4, pp. 573–580.
Vartanyan, N.S., Pivovarova, T.A., Tsaplina, I.A., Lysenko, A.M., and Karavaiko, G.I., A New Thermoacidophilic Bacterium of the GenusSulfobacillus, Mikrobiologiya, 1988, vol. 57, no. 2, pp. 268–274.
Severina, L.O., Senyushkin, A.A., and Karavaiko, G.I., The Structure and Chemical Composition of the S-Layer in Representatives of the GenusSulfobacillus, Mikrobiologiya, 1995, vol. 64, pp. 336–340.
Krasil’nikova, E.N., Bogdanova, T.I., Zakharchuk, L.M., Tsaplina, I.A., and Karavaiko, G.I., Metabolism of Reduced Sulfur Compounds inSulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans, Strain 1269,Mikrobiologiya, 1998, vol. 67, no. 2, pp. 156–164.
Vartanyan, N.S., Karavaiko, G.I., and Pivovarova, T.A., Effect of Organic Compounds on the Growth and Oxidation of Inorganic Substrates bySulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans subsp.asporogenes, Mikrobiologiya, 1990, vol. 59, pp. 411–417.
Srere, P.A., Citrate Synthase,Methods Enzymol., 1969, vol. 13, pp. 3–11.
Miernyk, J.A., Trelease, R.N., and Choinsky, G.S. Malate Synthase Activity in Cotton and Other Ungerminated Oilseeds,Plant Physiol., 1979, vol. 63, no. 6, pp. 1068–1071.
Dixon, G.H. and Kornberg, H.L., Assay Methods for Key Enzymes of the Glyoxylate Cycle,Biochem. J., 1959, vol. 72, no. l,p. 3P.
Krasil’nikova, E.N., Pedan, L.V., Firsov, N.N., and Kondrat’eva, E.N., Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Enzymes in Various Species of Phototrophic Bacteria,Mikrobiologiya, 1973, vol. 42, no. 6, pp. 995–1000.
Romanova, A.K.,Biokhimicheskie metody izucheniya avtotrofii u mikroorganizmov (Biochemical Methods for Studying Autotrophy in Microorganisms), Moscow: Nauka, 1980, pp. 51–133.
Tabita, F.R., Molecular and Cellular Regulation of Autotrophic Carbon Dioxide Fixation in Microorganisms,MicrobioL Rev., 1988, vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 155–189.
Marsh, R.M. and Norris, P.R., The Isolation of Some Thermophilic, Autotrophic, Iron- and Sulfur-oxidizing Bacteria,FEMS Mkwbiol. Lett., 1983, vol. 17, pp. 311–315.
Dopson, M. and Lindstrom, E.B., Potential Role ofThiobacillus caldus in Arsenopyrite Bioleaching,Appl. Environ. MicrobioL, 1999, vol. 65, no. 1, pp. 36–40.
Clark, D.A. and Norris, P.R., Acidophilic Bacteria and Their Activity in Mineral Sulfide Oxidation,Microbial Mineral Recovery, Ehrlich, H.L. and Brierley, C.L., Eds., New York: McGraw-Hill, 1996, pp. 3–27.
Clark, D.A. and Norris, PR.,Acidimicrobium ferrooxidans gen. nov., sp. nov.: Mixed-Culture Ferrous Iron Oxidation withSulfobacillus Species,Microbiology (Reading, UK), 1996, vol. 142, pp. 785–790.
Johnson, D.B., Biodiversity and Ecology of Acidophilic Microorganisms,FEMS MicrobioL Ecol., 1998, vol. 27, pp. 307–317.
Karavaiko, G.J., Kovalenko, T.V., and Golovacheva, R.S., Microbiological Aspects of Leaching Copper from Ores,Proc. Int. Conf. on Use of Microorganisms in Hydrometallurgy, Pecs (Hung.), 1980, pp. 95–107.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsaplina, I.A., Krasil’nikova, E.N., Zakharchuk, L.M. et al. Carbon metabolism inSulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans subsp.asporogenes, strain 41. Microbiology 69, 271–276 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02756732
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02756732