Abstract
Suramin exerts antitumour effects by interfering with the biological activity of several growth factors. It is also known that growth factors, including epidermal growth factor, play a primary role in the protection of gastric mucosa and promotion of ulcer healing. In the present study, the penetration of suramin into the stomach as well as the influence exerted by this drug on ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage were investigated. Suramin was administered by the intraperitoneal route to male rats every other day for fourteen days. Animals were then used for:
-
1.
Assessment of suramin levels in plasma and tissues;
-
2.
Histomorphometric evaluation of ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage;
-
3.
Measurement of gastric acid secretion after pylorus ligation.
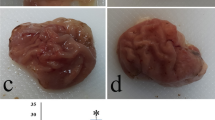
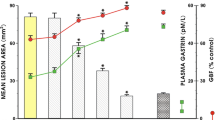
The concentrations of suramin in plasma, stomach and kidney were 158±18.8 μg/ml, 179.7±33.0 μg/g and 1480.9±85.8 μg/g (n=6), respectively. Suramin did not induce gastric mucosal damage under basal conditions. However, the drug markedly enhanced ethanol-induced necrotic damage at all times tested. In addition, suramin significantly enhanced gastric acid output induced by pylorus ligation in conscious rats. Suramin is characterized by an unusually long half-life and a remarkable accumulation in kidney, whereas, in the majority of other organs, the drug reaches levels that are 8–10 times lower than those found in renal tissue. The data obtained in the present study are consistent with this pharmacokinetic profile and suggest that suramin concentration achieved in gastric tissue, which is known to inhibit the proliferation of several cell lines in vitro, is high enough to induce an impairment of mucosal protective mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Voogd TE, Vansterkenburg ELM, Wilting J, Janssen LHM. Recent research on the biological activity of suramin. Pharmacol Rev. 1993;45:177–203.
La Rocca RV, Stein CA, Meyers CE. Suramin: prototype of a new generation of antitumor compounds. Cancer Cells. 1990;2:106–15.
Myers CE, Cooper M, Stein C et al. Suramin: a novel growth factor antagonist with activity in hormone-refractory metastatic prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1992;10:881–9.
Gansler T, Vaghmar N, Olson J, Graham S. Suramin inhibits growth factor binding and proliferation by urothelial carcinoma cell cultures. J Urol. 1992;148:910–14.
Aaronson SA. Growth factors and cancer. Science 1991;254:1146–53.
Lemoine NR, Leung HY, Gullick WJ. Growth factors in the gastrointestinal tract. Gut. 1992;33:1297–300.
Konturek SJ, Dembinski A, Warzecha Z, Brzozowski T, Gregory H. Role of epidermal growth factor in healing of chronic gastroduodenal ulcers in rats. Gastroenterology. 1988;94:1300–7.
Folkman J, Szabo S, Stovroff M, McNeil P, Li W, Shing Y. Duodenal ulcer. Discovery of a new mechanism and development of angiogenic therapy that accelerates healing. Ann Surg. 1991;214:414–27.
Dembinski A, Gregory H, Konturek SJ, Polanski M. Trophic action of epidermal growth factor in the pancreas and gastroduodenal mucosa in rats. J Physiol (London) 1982;325:35–42.
Koffman CG, Elder JB, Ganguli PC, Gregory H, Geary CG. Effect of urogastrone on gastric secretion and serum gastrin concentration in patients with duodenal ulceration. Gut. 1982;23:951–6.
Hui WM, Chen BW, Kung AWC, Cho CH, Luk CT, Lam SK. Effect of epidermal gastric blood flow in rats: possible role in mucosal protection. Gastroenterology. 1993;104:1605–10.
Hase S, Nakazawa S, Tsukamoto Y, Segawa K. Effects of prednisolone and human epidermal growth factor on angiogenesis in granulation tissue of gastric ulcer induced by acetic acid. Digestion. 1989;42:135–41.
La Rocca RV, Danesi R, Cooper MR et al. Effect of suramin on human prostate cancer cells in vitro. J Urol. 1991;145:393–8.
Blandizzi C, Gherardi G, Marveggio C, Natale G, Carignani D, Del Tacca M. Mechanisms of protection by omeprazole against experimental gastric mucosal damage in rats. Digestion. 1995;56:220–9.
Lacy ER, Ito S. Microscopic analysis of ethanol damage to rat gastric mucosa after treatment with a prostaglandin. Gastroenterology 1982;83:619–25.
Ito S, Lacy ER. Morphology of rat gastric mucosal damage, defense, and restitution in the presence of liminal ethanol. Gastroenterology. 1985;88:250–60.
Itoh M, Joh T, Imai S et al. Experimental and clinical studies on epidermal growth factor for gastric mucosal protection and healing of gastric ulcers. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1988;10(suppl. 1):S7-S12.
Olsen SP, Poulsen SS, Kikegaard P, Nexo E. Role of submandibular saliva and epidermal growth factor in gastric cytoprotection. Gastroenterology. 1984;87:103–8.
Tepperman BL, Soper DB, Morris GP. Effect of sialoadenectomy on adaptive cytoprotection in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1989;97:123–9.
Oates PJ, Hakkinen JP. Studies on the mechanism of ethanol-induced gastric damage in rats. Gastroenterology. 1988;94:10–21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blandizzi, C., Danesi, R., Gherardi, G. et al. Effect of suramin on ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury: Relationship between tissue distribution and severity of damage. Inflammopharmacology 4, 331–340 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02755786
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02755786