Abstract
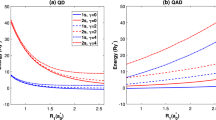
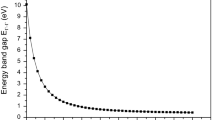
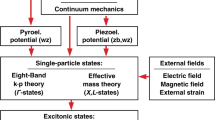
Research in semiconductor quantum dots (q-dots) has burgeoned in the past decade. The size (R) of these q-dots ranges from 1 to 100 nm. Based on the theoretical calculations, we propose energy and length scales which help in clarifying the physics of this mesoscopic system. Some of these length scales are: the Bohr exciton radius (αB*), the carrier de Broglie and diffusion length (λD andl D), the polaron radius (αp), and the reduction factor modulating the optical matrix element (M x).R<αB is an individual particle confinement regime, whereas the larger ones are exciton confinement regime wherein Coulomb interaction play an important role. Similarly a size-dependent dielectric constantε(R) should be used forR<αp<αB. An examination ofM x reveals that an indirect gap material q-dot behaves as a direct gap material in the limit of very small dot size. We have carried out effective mass theory (EMT) calculations to estimate the charge density on the surface of the quantum dot. We present tight binding (TB) calculation to show that the energy upshift scales as 1/R x, wherex is less than 2 and the exponent depends on the orientation of the crystallite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan G, Delerue C and Lannoo M 1997aPhys. Rev. Lett. 78 3161
Allan G, Delerue C and Lannoo M 1997bAppl. Phys. Lett. 71 1189
Ashoori R C 1996Nature 379 413
Bhattacharjee A and Guillaume C 1997Phys. Rev. B55 10613
Brus L E 1983J. Chem. Phys. 79 5566
Brus L E 1986J. Phys. Chem. 90 2555
Canham L T 1990Appl. Phys. Lett. 57 1046
Delerue C, Allan G and Lannoo M 1993Phys. Rev. B48 11024
Delerue C, Lannoo M and Allan G 1996Phys. Rev. Lett. 76 3038
Efros Al L and Efros A L 1982Sov. Phys. Semiconduct. 16 772
Filonov Aet al 1997Appl. Phys. Lett. 70 744
Hybertsen M S 1992Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 256 179
John G C and Singh V A 1995Phys. Rep. 263 93
Kayanuma Y 1988Phys. Rev. B38 9797
Khurgin J B, Forsythe E W, Tompa G S and Khan B A 1996Appl. Phys. Lett. 69 1241
Laheld U and Einevoll G 1997Phys. Rev. B55 12311
Lippens P E and Lannoo M 1989Phys. Rev. B39 10935
Menon M and Subbaswamy K 1997Phys. Rev. B55 9231
Nair S V and Takagahara T 1997Phys. Rev. B55 5153
Nair S V, Sinha S and Rustagi K C 1987Phys. Rev. B35 4098
Nomura S and Kobayashi T 1991Solid State Commun. 78 677
Ramaniah L and Nair S 1993Phys. Rev. B47 7132
Ranjan V and Singh V A 1998 inProc. of the ninth int. workshop on the physics of semiconductor devices (eds) V Kumar and S K Agrawal (London: Narosa) pp 98–101
Ranjan V, Singh Vijay A and John George C 1998Phys. Rev. B58 1158
Sawada S, Hamada N and Ookubo N 1994Phys. Rev. B49 5236
Takagahara T and Takeda K 1992Phys. Rev. B46 15578
Voos Met al 1992Appl. Phys. Lett. 61 1213
Wang Y and Herron N 1991J. Phys. Chem. 95 525
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, V.A., Ranjan, V. & Kapoor, M. Semiconductor quantum dots: Theory and phenomenology. Bull Mater Sci 22, 563–569 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02749969
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02749969