Abstract
Objective
The EBNA1 IgA antibody level of normal and NPC subjects in a high incidence area were analyzed for new diagnostic criteria to improve diagnosis.
Methods
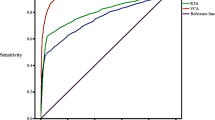
A total of 780 normal and 104 NPC sera were tested for EBNA1 IgA antibody levels by ELISA. Two diagnostic criteria were obtained from sensitivity and specificity data: 1) lower equivocal limit (rOD=1.10) where sensitivity = 95%; and 2) upper equivocal limit (rOD=1.85) where specificity = 95%.
Results
The range and distribution of EBNA1 IgA antibody levels are broad with those of normal subjects (0.093-4.726, mean = 0.850 ± 0.637) overlapping those from NPC subjects (0.235-3.721, mean = 2.241 ±0.875). However, NPC subjects did exhibit significantly higher antibody levels (t= 18.5, P<0.001). Based on the diagnostic criteria, 3 diagnostic categories were established: 1 Positive; 2 Suspected Positive; and 3) Negative. The percentage of NPC subjects falling into these 3 diagnostic categories were 75.13%, 17.44% and 7.44%, respectively and of normal subjects, 4.81%, 17.31%, 77.88% respectively.
Conclusion
Due to the broad distribution and overlapping of antibody levels between normal and NPC subjects in a high incidence area, it is important to have diagnostic criteria that will categorize those with equivocal results to minimize misdiagnosis. The 3 diagnostic categories established in this study will enhance detection and help physicians in their clinical diagnosis.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Shem ST, Wei W, Ng MH. Research on nasopharyngeal carcinoma in recent ten years by University of HongKong Medical College. Chin J Clin Oncol. 1997; 24:645–650.
Foong YT, Cheng HM, Sam CK, et al. Serum and Salivary IgA antibodies against a defined epitope of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear Aantigen (EBNA) are elevated in nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1990; 45:1061–1064.
Cao SM, Huang TB, Jian SW, et al. The Relationship between EB Virus ZEBRA IgG Change Regulation and Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Cancer Res Prev Treat. 1999; 20:115–117.
Liu MT, Lin LS, Yu Y, et al. Use of recombinant Epstein-Barr virus early antigen for detection of antibody in patients with nasopharynhgeal carcinoma. Chung Hua I Hsueh Tsa Chin (Taipei). 1996; 57:7–15.
Huang JY, Hu MH. Significance of ELISA detection of EBVIgG/EA antibody in serological diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chin J Immunol. 2002; 18:142.
Zheng YX, Li JZ, Jian SW, et al. Detectiom of salivary Epstein-Barr virus antibodies for early diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chin J Cancer. 2001; 20:235–238.
Cheng WM, Chen GX, Chen HL, et al. Assessment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma risk by EB virus antibody profile. Chin J Oncol. 2002; 24:561–563.
Gu YL, Zhang CQ, Ng Park, et al. Study on sero-diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma using a dual antibody test against recombinant Epstein-Barr virus antigens. Chin J Cancer. 2003; 22:903–906.
Cheng MT, Cheng WM, Ji MF, et al. Detection of serum Epstein-Barr virus antibody level by ELISA in normal populations and nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients in Zhongshan City of China. J First Mil Med Univ. 2002; 22: 817–818.
Cheng WM, Chen GX, Chen HL, et al. Assessing the risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma on the basis of EBV antibody spectrum. Intl J Cancer. 2002; 97:489–492.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, W., Ji, M., Zong, Y. et al. Establishment of diagnostic criteria using EBNA1 IgA antibody levels in a high-risk area for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chin. J. Clin. Oncol. 2, 637–640 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02739723
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02739723