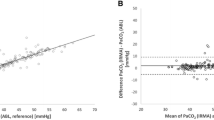
Conclusions
Transcutaneous CO2 monitoring is a useful non-invasive method of following PtcCO2 along with PtcO2 can be used to monitor pulmonary function, systemic circulation and local tissue perfusion. They are more sensitive in reflecting circulatory changes than conventional monitoring variables such as heart rate, EKG, arterial
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haab P. Factors influencing magnitude of the CO2 partial pressures in the body.Intensive Care Med 1981; 7: 250.
Eberhard P, Mindt W, Schafer R. Methodology: Calculated aspects of cutaneous PCO2 monitoring.Intensive Care Med 1981; 7:255–256.
Whitehead MD. Trancutaneous PO2 and PCO2 monitoring with a single electrochemical sensor; its clinical use and advantages in neonatal intensive care unit.Intensive Care Med 1981; 7: 256–257.
Ernly P, Messer J, Willard D. Cutaneous PCO2 monitoring and artificial ventilation in the newborn.Intensive Care Med 1981; 7: 252–253.
Keller HE, Fischer W, Willie L. Continuous cutaneous bedside monitoring of carbon dioxide tensions.Intensive Care Med 1981;7:253–254.
Rome ES, Stork EK, Carlo WA et al. Limitations of transcutaneous PO2 and PCO2 monitoring in infants with broncho pulmonary dysplasia.Pediatrics 1984; 74: 217–220.
Monaco F, Nickerson BG, McQuitty JC. Continuous transcutaneous oxygen and carbon dioxide monitoring in the pediatric ICU.Crit Care Med 1982; 10: 765–766.
Laptook A, Oh W. Transcutaneous Carbon dioxide monitoring in the newborn period.Crit Care Med 1981; 9: 759–760.
Monaco F, McQuitty JC. Transcutaneous measurements of carbon dioxide partial pressure in sick neonates.Crit Care Med 1981; 9: 756–758.
Hansen TN, Tooley WH. Skin surface carbon dioxide tension in sick infants.Pediatrics1919; 64:942–945.
Frey P, Ruh H, Ruk P. Continuous PCO2 monitoring by means of skin surface sensors: The influence of various sensor temperatures and first clinical experiences.Abstract, Intensive Care Med1981 ;7 :260.
Eletr S, Jimison H, Hill C et al. Cutaneous CO2 partial pressures of patients in respiratory intensive care units: A new monitoring procedure.Abstract, Intensive Care Med 1977; 3 : 124.
Versmold HT, Brunstler I, Enders A et al. Transcutaneous PCO2 monitoring of newborn infants in shock at electrode temperatures of 41 C to 44 C.Abstract, Inten sive Care Med 1981; 7: 251, & 1984; 12 : 276.
Palmisan BW, Severinghaus JW. Clinical Accuracy of combined transcutaneous PO2-PCO2 electrode.Abstract, Crit Care Med 1984; 3:124.
Bompard Y, Aufrant C, Mercier T. Cutaneous PCO2 monitoring in respiratory distress in infants and children.Abstract, Intensive Care Med 1981; 7: 255.
Schober JG, Stubiny K, Kuhwald R. Transcutaneous monitoring of PCO2 in infants and children after cardiac surgery.Abstract, Intensive Care Med 1981; 7: 261.
Vogel F, Heer S, Spannbrucker N. Comparative measurements of cutaneous and arterial PCO2 in patients with low cardiac output on an intensive care unit for internal medicine.Intensive Care Med1981; 7: 258–259.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ravindranath, T. Non-invasive monitoring in the pediatric ICU, part II: Transcutaneous Carbon dioxide monitoring (PtcCO2). Indian J Pediatr 57, 175–178 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02722081
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02722081