Abstract
It is well known that corrosion can weaken structures over time, but because corrosion rates can differ significantly from location to location, it is difficult to predict the amount of weakening that can occur for a particular structure used outdoors in a given location. Over the years, salt fog testing has been used to help predict how a structure might degrade over time resulting from exposure. The most common tests are based upon MIL-STD 810 “Environmental Engineering Considerations and Laboratory Tests,” and ASTM B117 “Standard Practice for Operating Salt Spray (Fog) Apparatus.” Although these standards give guidelines on conducting accelerated tests, they provide no insight as to the real world exposure level corresponding to a test condition, i.e. an acceleration factor.
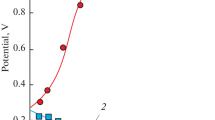
Small screw fasteners that had been exposed in service for two years in a marine environment were visually compared to similar fasteners exposed to varying lengths of time up to 22 days, under accelerated weathering conditions as specified in MIL-STD-810, and ASTM B117. A salt fog apparatus was used for the exposure testing. An acceleration factor for this service was determined, and found to be consistent with corrosion rate research conducted for other marine environments. Research of corrosion rates in other marine environments found that they can vary significantly, and are most strongly dependent on temperature, wind speed and direction, and rainfall.
Mechanical testing of the screws removed from service was compared to those subjected to the accelerated weathering conditions. Testing was conducted with a servo-hydraulic test machine fitted with custom grips designed to load the screws in their as-installed configuration. Both the screws returned from two years of service, and screws subjected to the salt fog for various amounts of time up to 22 days were tested in this fashion. In addition, standard single lap shear testing was conducted on several screws exposed to the salt fog for various amounts of time up to 22 days. The amount of time for the screw strength to drop below an acceptable level was determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
“Accelerated Corrosion Test,” GM9504P, General Motors Engineering Standards, July 1991
E.A. Baker and T.S. Lee: “Calibration of Atmospheric Corrosion Test Sites,” ASTM STP 767,Atmospheric Corrosion of Metals, S.W. Dean, Jr. and E.C. Rhea, Ed., American Society for Testing and Materials, 1982, p. 250–66
E.A. Baker: “Long-Term Corrosion Behavior of Materials in the Marine Atmosphere,” ASTM STP 965,Degradation of Metals in the Atmosphere, S.W. Dean, Jr. and T.S. Lee, Ed., American Society for Testing and Materials, 1988, p 125–144
B.C. Swain, S.K. Debroy, M.R. Panigrahi, and J.S. Murty: “Corrosion Behavior of Weather-Resistant Steels in Salt Spray and Humidity Chambers,”Mater. Perform. 31(51), 1992
S.P. Pednekar: “The Salt-Spray Tests as an Alternative to Long-Term Marine Exposure,”Proceedings of 1997 Tri-Service Conference on Corrosion (Wrightsville Beach, N.C.), Nov 1997
I.C. Handsy and M.T. Wolff: “Suitability of Prepainted (Coil Coated) Metal and Adhesive Assembly for Military Application”,Proceedings of Tri-Service Conference on Corrosion (Orlando, FL), June 1994, p 699
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duffner, D.H., Hopkins, S.W. & Pound, B.G. Strength reduction in screw fasteners resulting from outdoor exposure. Practical Failure Analysis 3, 57–64 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02715536
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02715536