Abstract
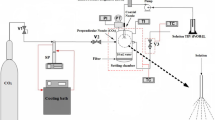
Fine particles of acetaminophen were produced by Aerosol Solvent Extraction System (ASES). The experiments were conducted to investigate the effects of various temperatures, pressures, solvents, solution concentrations and solution feed volume rates on particle size and morphology. The choice of solvent appears to be very important for getting specific particle shape and size. The result shows that when ethyl acetate is used as a solvent, the irregular and acicular morphology of raw material is recrystallized to be regular and monoclinic. The average particle size of recrystallized acetaminophen from ethyl acetate solution has been measured to be 3–4 Μm, which was about 1/20th of raw acetaminophen in size. The particle size distribution range also became narrow from 82 Μm to 4.9 Μm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chattopadhyay, P. and Guta, R. B., “Production of antibiotic nanoparticles using supercritical CO2 as antisolvent with enhanced mass transfer,”Ind. Eng. Chem. Res.,40, 3530 (2001).
Gilbert, D. J., Palakodaty, S., Slaan, R. and York, P., “Particle engineering for pharmaceutical application — a process scale up,” The 5th International Symposium on Supercritical Fluids, April, Atlanta (2000).
Hanna, M. and York, P., “Method and apparatus for the formation of particles,” WO 95/01221, International Publication Date 12, 01 (1995).
Jung, J. and Perrut, M., “Particle design using supercritical fluids: literature and patent survey,”J. Supercrit. Fluids,20, 179 (2001).
Lee, J.-H., “Preparation of polymeric fine particles with various morphologies using supercritical fluid,”Korean Chem. Eng. Res.,42, 202 (2004).
Lee, Y.-W., “Design of particles using supercritical fluids,”HWAHAK KONGHAK,41, 679 (2003).
Matson, D. W., Peterson, R. C. and Smith, R. D., “Production of powders and films from supercritical solutions,”J. Mater. Sci.,22, 1919 (1987).
Perez-Ruiz, T. and Martinez-Lozano, C., “Migration behavior and separation of acetaminophen and p-aminophenol in capillary zone electrophoresis: analysis of drugs based on acetaminophen,”J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal.,38, 87 (2005).
Reverchon, E. and Adami, R., “Nanomaterials and supercritical fluids,”J. Supercrit. Fluids,37, 1 (2006).
Reverchon, E., “Supercritical antisolvent precipitation of micro- and nano-particles,”J. Supercrit. Fluids,15, 1 (1999).
Wubbolts, F. E., Bruinsma, O. S. L. and Rosmalen, G. M., “Dry-spraying of ascorbic acid or acetaminophen solutions with supercritical carbon dioxide,”J. Crystal Growth,198/199, 767 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Chu, J., Song, ES. et al. Crystallization of acetaminophen micro-particle using supercritical carbon dioxide. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 23, 482–487 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02706753
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02706753