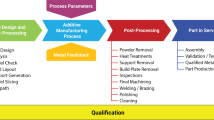
Abstract
New process design and control methods are needed for significantly improving productivity and reducing costs of thermomechanical processes such as hot metal forging. Current practices for accomplishing basic design tasks such as selecting the number of forming steps and specifying the processing conditions for each thermomechanical operation produce feasible solutions that are often far from optimal. Substantial improvements in effectiveness and efficiency can be realized through holistic approaches that optimize the whole system performance and not just individual subsystems such as workpiece material behavior, material flow in dies, and equipment responses. Recent progress in the application of dynamical modelling and process design techniques using ideal forming concepts and trajectory optimization are discussed. Monitoring methods for the on-line monitoring of the process and an intelligent forging system has been proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cebron D, Ashby M F 2000 Information systems for material and process selection.Adv. Mater. Proc. 157:44–48
Chung K, Richmond O 1993 A deformation theory of plasticity based upon minimum work paths.Int. J. Plasticity 9:907–920
Chung K, Richmond O 1994 The mechanics of ideal forming.Trans. ASME 61: 176–181
Frazier W G 1997 Modelling and simulation of metal forming equipment.J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 6: 153–156
Frazier W G, Malas J C, Medina E A, Venugopal S, Medeiros S C, Mullins W M, Choudhary A, Irwin R D 1998 Application of control theory principles to the optimization of grain size during hot extrusion.J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 14:25–31
Frost H J, Ashby M F 1982Deformation mechanism maps (New York: Pergamon) vol. 1
Gegel H L 1988 Synthesis of atomistic and continuum mechanics.Computer simulation in materials science (eds) R J Arsenaultet al (Metals Park, Ohio: ASM) pp 291–344
Gegel H L, Malas J C, Doraivelu S M, Shende V A 1988 Modelling techniques used in forging process design.Metals handbook, 9th edn (Metals Park, OH: ASM) vol. 14, pp 417–438
Gegel H L, Malas J C, Frazier W G, Venugopal S 2001Bulk workability and process modelling. (Metals Park, OH: ASM) (in press).
Khun H A, Lee P W, Erturk T 1973 A fracture criterion for cold forming.J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 213–218
Malas J C 1985A thermodynamic and continuum approach to the design and control of precision forging processes. M S thesis, Wright State University, Dayton, OH
Malas J C 1991Methodology for design and control of thermomechanical processes, Ph D dissertation, College of Engineering and Technology, Ohio University, Athens, OH, pp 77–83
Malas J C, Frazier W G 1999 Optimal design of thermomechanical processes using ideal forming concepts.The integration of material, processes and product design (eds) Zabaraset al (Rotterdam: Brookfield) pp 229–236
Malas J C, Seetharaman V 1992 Use of material behavior models in the development of process and control.J. Met. 8–13
Malas J C, Frazier W G, Medina E A, Seetharaman V, Venugopal S, Irwin R D, Mullins W M, Medeiros S C, Choudhary A, Srinivasan R 2001 “Optimization and control of microstructure development during hot metal working”. Invention of US Air Force, Patent Application No. 09-035,898 Applied for the Issue of US Patent
Mullins W M, Irwin R D, Malas J C, Venugopal S 1997 Examination on the use of acoustic emission for monitoring metal forging process: A study using simulation technique.Scr. Mater. 36: 967–974
Prasad Y V R K, Seshacharyulu T 1998 Modelling of hot deformation for microstructural control.Int. Mater. Rev. 43:243–258
Prasad Y V R K, Gegel H L, Doraivelu S M, Malas J C, Morgan J T, Lark K A, Barker D R 1984 Modelling of Dynamic Material Behavior in Hot Deformation: Forging of Ti-6242,Metall. Trans. A15: 1883–1891
Prasad Y V R K, Seshacharyulu T, Medeiros S C, Frazier W G, Morgan J T, Malas J C 2000 Titanium alloy processing.Adv. Mater. Proc. 157: 85–89
Raj R 1981 Development of processing maps of use in warm forming and hot forming processes.Metall. Trans. A12: 1089
Rodriguez P, Mannan S L, Venugopal S 2000 On the Workability of Austenitic stainless Steels,J. Materials Proce. Technol, (In Press)
Seybold P B 2001 Get inside the lives of your customers.Harvard Business Rev. 79 (5): 80–89
Skelton R E 1988Dynamic Systems Control (New York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc.) vol. 1
Stallkamp T 2001 Should suppliers be partners?Business Week June 4: 30B
Tamirisakandala S, Prasad Y V R K, Malas J C, Medeiros S C 2000 Strain-induced porosity during cogging of extra-low interstitial grade Ti-6Al-4V.J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 10: 125–130
Venugopal P 1981 Optimisation of workability and control of microstructures in deformation processing of austenitic stainless steels: Development and application of processing maps for stainless steels type AISI 304 and 316 L. Ph D thesis, Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai
Venugopal S 1993Optimization ofworkability and control of microstructure in deformation processing of austenitic stainless steels: Development and application of processing maps for stainless steels type AISI 304 and 316L Ph D thesis, University of Madras, Chennai
Venugopal S, Mannan S L 1998 Criteria for the stability of micro structure during deformation processing,Proc. of the 19th Int. Symp. on Materials Science: Modelling of structure and mechanics of materials from microscale to product (eds) J V Carstensen, T Leffers, T Lorentzen, O B Pedersen, B F Sorensen, G Winther (Roskilde: Riso National Lab.) pp 541–546
Venugopal S, Medina E A, Malas J C, Medeiros S C, Frazier W G, Mullins W M, Srinivasan R 1997 Optimization of microstructure during deformation processing using control theory principles.Scr. Mater. 36: 347–353
Wagoner R H, Chenot J L 2001Metal forming analysis (Cambridge: University Press) pp 206–255
Ziegler Z 1983 Progress in solid mechanics (New York: John Wiley and Son) p. 93
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Venugopal, S., Raj, B. A holistic approach to thermomechanical processing of alloys. Sadhana 28, 833–857 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02706462
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02706462