Abstract
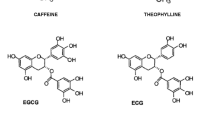
This paper involves a feasibility study on using molecular imprinted polymers as the sorbent materials in solid phase extraction for caffeine and theophylline from green tea. Two kinds of MIPs, with caffeine-theophylline mixture and pentoxifylline-theophylline mixture as the templates respectively, MAA as the monomer, EDMA as the crosslinker and ATBN as the initiator, were applied to this purpose. Mixture solution of caffeine and theophylline (1 Μg/ ml in acetonitrile) was applied to the solid extraction cartridges following a load, wash and elute procedure with acetonitrile, methanol, methanol-acetic acid (90/10, v/v) as the solvents, respectively. This solid phase extraction protocol was applied for extraction of caffeine and theophylline from green tea. Comparison between the results obtained with the MIPs cartridges and a traditional C18 reversed-phase cartridge was made. It showed that the MIP-based sorbent on the solid phase extraction was comparable with that of C18 material. HPLC analysis using a C18 column (5 Μm, 250× 4.6 mm from Rstech corporation), methanol: water (60 :40, v/v) as the mobile phase at a flow rate of 0.6 ml/min was applied for the quantitative determination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson, L. I., Paprica, A. and Arvidsson, T.,“A Highly Selective Solid Phase Extraction Sorbent for Pre-concentration of Sameridine Made by Molecular Imprinting”Chromatographia,46(2), 57 (1997).
Baggiani, C., Giovannoli, C., Anfossi, L. and Tozzi, C.,“Molecularly Imprinted Solid-phase Extraction Sorbent for the Clean-up of Chlorinated Phenoxyacids from Aqueous Sample”J. Chromatogr. A,938, 35 (2001).
Baggiani, C., Trotta, F., Giraudi, G., Giovannoli, C. and Vanni, A.,“Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Pesticide Bentazone,”Anal Comm.,36(7), 263 (1999).
Baggiani, C., Trotta, F., Giraudi, G., Moraglio, G. and Vanni, A.,“Chromatographie Characterization of a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Binding Theophylline in Aqueous Buffers”J. Chromatogr. A,786, 23 (1997).
Blomgre, A., Berggren, C., Holmberg, A., Larsson, F., Sellergre, B. and Ensing, K.,“Extraction of Clenbuterol from Calf Urine Using aMolecularly Imprinted Polymer Followed by Quantitation by High-performance Liquid Chromatography with UV Detection”J. Chromatogr. A,975, 157 (2002).
Chen, W., Liu, F., Zhang, X., Li, K. A. and Tong, S., “The Specificity of a Chlorphenamineimprinted Polymer and its Application”Talanta,55, 29 (2001).
Chi, H.,“Screening of Anticarcinogenic Ingredients in Tea Polyphenols,”Cancer Letters,114, 153 (1997).
Chiehming, J. C., Chiu, K.-L., Chen, Y.-L. and Chang, C.-Y,“Separation of Catechins from Green Tea Using Carbon Dioxide Extraction,”Food Chemistry,68, 109 (2000).
Dauwe, C. and Sellergen, B.,“Influence of Template Basicity and Hydrophobicity on the Molecular Recognition Properties of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers,”J. Chromatogr,753(2), 181 (1996).
Jodlbauer, J., Maier, N. M. and Lindner, W., “Towards Ochratoxin A Selective Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Solid-phase Extraction;”J. Chromatogr. A,945, 45 (2002).
Kang, J. H., Chung, S. T. and Row, K. H.,“Separation of Epigallocatechin Gallate from Korean Green Tea by RP-HPLC,”J. Liq. Chrom. & Rel. Technol,23(17), 2739 (2000).
Kobayashi, T., Murawaki, Y., Reddy, P. S., Abe, M. and Fujii, N.,“Molecular Imprinting of Caffeine and its Recognition Assay by Quartzcrystal Microbalance”Analytica Chimica Acta,435, 141 (2001).
Kugimiya, A. and Takeuchi, T.,“Application of Indoleacetic Acid-imprinted Polymer to Solid Phase Extraction”Analytica Chimica Acta,395, 251(1999).
Liebert, M., Licht, U., Bohm, V. and Bitsch, R.,“Antioxidant Properties and Total Phenolic Content of Green and Black Tea Under Different Brewing Conditions”Zeitschrifl fur Lebensmittel-Untersuchung und-Forschung,208, 217 (1999).
Martin, P., Wilson, I. D., Morgan, D. E., Jones, G. R. and Jones, K., “Evaluation of a Molecular Imprinted Polymer for Use in Solid Phase Extraction of Propranolol from Biological Fluids”Anal Comm.,34(2), 45 (1997).
Matsui, J., Fujiwara, K., Ugata, S. and Takeuchi, T.,“Solid Phase Extraction with a Dibutylmelamine-imprinted Polymer as Triazine Herbicide-selective Sortent,”J. Chromatogr. A,889(1-2), 25 (2000).
Melissa, K. J. and George, L.,“Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate and Quercetin on Oxidative Damage to Cellular DNA,”Mutation Research,459, 211 (2000).
Meng, Z.-H. and Liu, Q.,“Determination of Degradation Products of Nerve Agents in Human Serum by Solid Phase Extraction Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymer,”Analytica Chimica Acta,435, 121 (2001).
Mullett, W. M. and Lai, E. P. C,“Rapid Determination of Theophylline in Serum by Selective Extraction Using a Heated Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Micro-column with Differential Pulsed Elution”J. Pharm Biomed, Anal,21, 835 (1999).
Nicholls, I. A., Ramstrom, O. and Mosbach, K.,“Insights into the Role of the Hydrogen Bond and Hydrophobic Effect on Recognition in Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Synthetic Peptide Receptor Mimics,”J. Chromatogr. A,691, 349 (1995).
Olsen, J., Martin, P., Wilson, I. D. and Jones, G. R.,“Methodology for Assessing the Properties of Molecular Imprinted Polymers for Solid Phase Extraction,”Analyst,124(4), 467 (1999).
Owens, P. K., Karlsson, L., Lutz, E. S. M. and Andersson, L. I.,“Molecular Imprinting for Bio and Pharmaceutical Analysis,”Trends Anal. Chem.,18, 146 (1999).
Pan, X., Niu, G. and Liu, H.,“Microwave-assisted Extraction of Tea Polyphenols and Tea Caffeine from Green Tea Leaves,”Chemical Engineering and Processing,42, 129 (2003).
Pap, T., Horvath, V., Tolokan, A., Horvai, G. and Sellergre, B.,“Effect of Solvents on the Selectivity of Terbutylazine Imprinted Polymer Sorbents Used in Solid-phase Extraction,”J. Chromatogr. A,973, 1 (2002).
Pelillo, M., Biguzzi, B., Bendini, A., Gallina Toschi, T., Vanzini, M. and Lercker, G.,“Preliminary Investigation into Development of HPLC with UV and MS-electrospray Detection for the Analysis of Tea Catechins,”Food Chemistry,78, 369 (2002).
Rashid, B. A., Briggs, R. J., Hay, J. N. and Stevenson, D.,“Preliminary Evaluation of a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for the Solid Phase Extraction of Tamoxifen,”Anal. Comm.,34(10), 303 (1997).
Sajonz, P., Kele, M., Zhong, G., Sellergren, B. and Guiochon, G.,“Study of the Thermodynamics and Mass Transfer Kinetics of Two Enantiomers on a Polymeric Imprinted Stationary Phase,”J. Chromatogr. A,810, 1 (1998).
Theodoridis, G. and Manesiotis, P.,“Selective Solid-phase Extraction Sorbent for Caffeine Made by Molecular Imprinting,”J. Chromatogr. A,948, 163 (2002).
Wang, H. and Helliwell, K., “Determination of Flavonols in Green and Black Tea Leaves and Green Tea Infusions by High-performance Liquid Chromatography,”Food Research International,34, 223 (2001).
Xie, J., Zhu, L., Luo, H., Zhou, L., Li, C. and Xu, X.,“Direct Extraction of Specific Pharmacophoric Flavonoids from Gingko Leaves using a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Quercetin”J. Chromatogr. A,934, 1 (2001).
Zheng, N., Li, Y. Z., Chang, W.B., Wang, Z. M. and Li, T J.,“Sulfonamide Imprinted Polymers using Co-functional Monomers,”Analytica Chimica Acta,452, 277 (2002).
Zhou, J., He, X. and Li, Y.,“Binding Study on 5,5-Diphenylhydantoin Imprinted Polymer Constructed by Utilizing an Amide Functional Group,”Analytica Chimica Acta,394, 353 (1999).
Zuo, Y., Chen, H. and Deng, Y.,“Simultaneous Determination of Catechins, Caffeine and Gallic Acids in Green, Oolong, Black and puterh teas using HPLC with Photodiode Array Detector,”Talanta,57, 307 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Hong, S.P. & Row, K.H. Solid extraction of caffeine and theophylline from green tea by molecular imprinted polymers. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 21, 853–857 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705530
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705530