Abstract
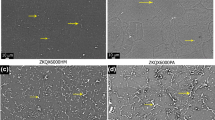
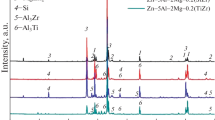
This paper is aimed at investigating the corrosion behaviour, microstructure and phase transitions of Zn-based alloys with different compositions. The corrosion tests are carried out both in acidic medium using 1 N HCl solution and in temperature dependence of thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). In the two different media, in particular, the corrosion behaviour of Zn-based alloys with respect to Al and Si contents is examined, and microstructure in acidic and TGA and phase transformations in TGA are also studied. Corrosion mechanism in TGA is also examined in terms of oxidation parameters and activation energies. The study reveals that corrosion behaviour of Zn-based alloys in acidic medium shows sometimes an increase and sometimes a decrease with time due to Al content which assists in delaying the corrosion by forming a oxide layer on the surface of Zn-based alloys. This property does not appear in temperature dependence of TGA. Further, Si content appears to remain in main matrix without being affected by acidic solution. On the other hand, it is observed that in microstructure, AlO(Al2O3), ZnO oxides and Zn-Cu phase precipitations are formed in main matrix, grain boundaries and partially inside the grains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aylor D M and Moran P J 1985J. Electrochem. Soc. 132 1277
Boyer H E and Gall T L (eds) 1992Metals handbook (Metals Park, Ohio: American Society for Metals) pp 6.64, 11.6 and 14.10
Colin S, Beche E, Berjoan R, Jolibois H and Chambaudet A 1999Corros. Sci. 41 1051
Dellis M A, Kaustermans J P, Delannay F and Wergra J 1991Mater. Sci. Eng. 135 253
Fontana M G 1987Corr. Eng. (New York: McGraw-Hill) 3rd ed., p. 236
Li Y 2001Corr. Sci. 43 1793
Pohlman S L 1978Corrosion 34 156
Prasad B K 2000aMater. Charact. 44 301
Prasad B K 2000bMater. Sci. Eng. A277 95
Rishel D M, Smee J D and Kammenzind B F 2002J. Nucl. Mater. 303 210
Seah K H W, Sharma S C and Girish B M 1997Corr. Sci. 39 1
Sharma S C, Seah K H W, Satish B M and Girish B M 1997Corr. Sci. 39 2143
Sharma S C, Somashekar D R and Satish B M 2001J. Mater. Process. Technol. 118 62
Showak W and Dunbar S R 1972Metals handbook: Atlas of microstructures of industrial alloys (ed) T Leyman (Metals Park, Ohio: American Society for Metals) pp 339–340
Toldin V A, Burykin A A and Kleschev G V 1981Phys. Met. Metall. 17 116
Zhu Y H and Islas J J 1997J. Mater. Process. Technol. 66 244
Zhu Y H, Murphy S and Yeung C 1999J. Mater. Process. Technol. 94 78
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yildiz, A.K., Kaplan, M. Corrosion behaviour, microstructure and phase transitions of Zn-based alloys. Bull Mater Sci 27, 341–345 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02704770
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02704770