Abstract
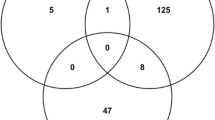
The ribosomal phosphoprotein P0 of the human malarial parasitePlasmodium falciparum (PfP0) has been identified as a protective surface protein. InDrosophila, P0 protein functions in the nucleus. The ribosomal function of P0 is mediated at the stalk of the large ribosomal subunit at the GTPase centre, where the elongation factor eEF2 binds. The multiple roles of the P0 protein presumably occur through interactions with other proteins. To identify such interacting protein domains, a yeast two-hybrid screen was carried out. Out of a set of sixty clones isolated, twelve clones that interacted strongly with both PfP0 and theSaccharomyces cerevisiae P0 (ScP0) protein were analysed. These belonged to three broad classes: namely (i) ribosomal proteins; (ii) proteins involved in nucleotide binding; and (iii) hypothetical integral membrane proteins. One of the strongest interactors (clone 67B) mapped to the gene YFL034W which codes for a hypothetical integral membrane protein, and is conserved amongst several eukaryotic organisms. The insert of clone 67B was expressed as a recombinant protein, and immunoprecipitaion (IP) reaction with anti-P0 antibodies pulled down this protein along with PfP0 as well as ScP0 protein. Using deletion constructions, the domain of ScP0, which interacted with clone 67B, was mapped to 60–148 amino acids. It is envisaged that the surface localization of P0 protein may be mediated through interactions with putative YFL034W-like proteins inP. falciparum
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GST:
-
glutathione-S transferase
- IP:
-
immunoprecipitation
- ORF:
-
open reading frame
- PfP0:
-
Plasmodium falciparum phosphoriboprotein P0
- ScP0:
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae phosphoriboprotein P0
References
Bocharov E V, Gudkov A T, Budovskaya E V and Arseniev A S 1998 Conformational independence of Nand C-domains in ribosomal protein L7/L12 and in the complex with the protein L10;FEBS Lett. 423 347–350
Brockstedt E, Rickers A, Kostka S, Laubersheimer A, Dorken B, Wittmann-Liebold B, Bommert K and Otto A 1998 A identification of apoptosis-associated proteins in a human Burkitt lymphoma cell line. Cleavage of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 by caspase 3;J. Biol. Chem. 273 28057–28064
Chatterjee S, Singh S, Sohoni R, Kattige V, Deshpande C, Chiplunkar S, Kumar N and Sharma S 2000a Characterization of domains of the phosphoriboprotein P0 ofPlasmodium falciparum;Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 107 143–154
Chatterjee S, Singh S, Sohoni R, Singh N J, Vaidya A, Long C and Sharma S 2000b Antibodies against the ribosomal phosphoprotein P0 ofPlasmodium falciparum protect mice against challenge withP. yoelii;Infect. Immun. 68 4312–4318
Craig T L and Denlinger D L 2000 Sequence and transcription patterns of 60S ribosomal protein P0, a diapause-regulated AP endonuclease in the flesh fly,Sarcophaga crassipalpis;Gene 255 381–388
Frolov M V and Birchler J A 1998 Mutation in P0, a dual function ribosomal protein/apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease, modifies gene expression and position effect variegation inDrosophila;Genetics 150 1487–1495
Goswami A, Chatterjee S and Sharma S 1996 Cloning of a ribosomal phosphoprotein P0 gene homologue fromPlasmodium falciparum;Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 82 117–120
Goswami A, Singh S, Redkar V D and Sharma S 1997 Characterization of P0, a ribosomal phosphoprotein ofPlasmodium falciparum;J. Biol. Chem. 272 12138–12143
Gyuris G J, Golemis E, Chertkov H and Roger Brent 1993 Cdi1, a human G1 and S phase protein phosphatase that associates with Cdk2;Cell 75 791–803
Hirohata S and Nakanishi K 2001 Antiribosomal P protein antibody in human systemic lupus erythematosus reacts specifically with activated T cells;Lupus 10 612–621
Ho Y, Gruhler A, Heilbut Aet al 2002 Systematic identification of protein complexes inSaccharomyces cerevisiae by mass spectrometry;Nature (London) 415 180–183
Joseph S 2003 After the ribosome structure: How does translocation work?;RNA 9 160–164
Justice M C, Ku T, Hsu M J, Carniol K, Schmatz D and Nielsen J 1999 Mutations in ribosomal L10e confer resistance to the fungal-specific eukaryotic elongation factor 2 inhibitor sordarin;J. Biol. Chem. 274 4869–4875
Koren E, Reichlin M W, Kosec M, Fugate R D and Reichlin M 1992 Autoantibodies to the ribosomal P proteins react with a plasma membrane-related target on human cells;J. Clin. Invest. 89 1236–1241
Koscec M, Koren E, Wolfson-Reichlin M, Fugate R D, Trieu E, Targoff I N and Reichlin M J 1997 Autoantibodies to ribosomal P proteins penetrate into live hepatocytes and cause cellular dysfunction in culture;J. Immunol. 159 2033–2041
Lalioti V S, Perez-Fernandez J, Remacha M and Ballesta JPG 2002 Characterization of interaction sites in theSaccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomal stalk components;Mol. Microbiol. 46 719–729
Liliensiek B, Rocha M, Umansky V, Benner A, Lin J, Ziegler Z, Nawroth P P and Schirrmacher V 1998 Identification of four genes in endothelial cells whose expression is affected by tumour cells and host immune status-a study in ex vivo-isolated endothelial cells;Blood 92 3394–3404
Maessen S, Wessling J G, Smits M A, Konings R N H and Schoenmakers J G G 1993 The gamma-tubulin gene of the malaria parasitePlasmodium falciparum;Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 60 27–36
Miller J H 1972Experiments in molecular genetics (New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press)
Mizuta K, Hashimoto T and Otaka E 1995 The evolutionary relationships between homologs of ribosomal YL8 and YL8-like proteins;Curr. Genet. 28 19–25
Rich B E and Steitz J A 1987 Human acidic ribosomal phosphoproteins P0, P1 and P2: Analysis of cDNA clones,in vitro synthesis and assembly;Mol. Cell Biol. 7 4065–4074
Rodriguez-Gabriel M A, Remacha M and Ballesta JPG 2000 The RNA-interacting domain but not the protein interacting domain is highly conserved in ribosomal protein P0;J. Biol. Chem. 275 2130–2136
Santos C and Ballesta JPG 1994 Ribosomal protein P0, contrary to phosphoproteins P1 and P2, is required for ribosome activity andSaccharomyces cerevisiae viability;J. Biol. Chem. 269 15689–15696
Santos C and Ballesta, JPG 1995 The highly conserved protein P0 Carboxyl end is essential for ribosome activity only in the absence of proteins P1 and P2;J. Biol. Chem. 270 20608–20614
Sehgal A, Kumar N, Carruthers V and Sharma S 2003 Translocation of ribosomal protein P0 onToxoplasma gondii tachyzoite surface;Int. J. Parasitol. 33 1589–1594
Shimmin L C, Ramirez G, Matheson A T and Dennis P P 1989 Sequence alignment and evolutionary comparison of the L10 equivalent ribosomal proteins from archaebacterial, eubacterial and eukaryotes;J. Mol. Evol. 29 448–462
Singh S, Sehgal A, Goswami A, Waghmare S, Chakrabarty T and Sharma S 2002 Surface expression of the conserved ribosomal protein P0 on parasite and other cells;Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 119 121–124
Sun K H, Liu W T, Tang S J, Tsai C Y, Hsieh S C, Wu T H, Han S H and Yu C 1996 The expression of acidic ribosomal phosphoproteins on the surface membrane of different tissues in autoimmune and normal mice which are the target molecules for anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies;Immunology 87 362–371
Tchorzewski M, Boldyreff B and Grankowski N 1999 Extraribosomal function of the acidic ribosomal P1-protein YP1 alpha fromSaccharomyces cerevisiae;Acta Biochim. Pol. 46 901–910
Uchiumi T and Kominami R 1992 Direct evidence for interaction of the conserved GTPase domain within 28S RNA with mammalian ribosomal acidic phosphoproteins and L12;J. Biol. Chem. 267 19179–19185
Uchiumi T, Wahha A J and Traut R R 1987 Topography and stoichiometry of acidic proteins in large ribosomal subunits fromArtemia salina as determined by cross linking;Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84 5580–5584
von Mikecz A, Neu E, Krawinkel U and Hemmerich P 1999 Human ribosomal protein L7 carries two nucleic acid-binding domains with distinct specificities;Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 258 530–536
Wool I G 1996 Extraribosomal functions of ribosomal proteins;Trends Biochem. Sci. 21 164–165
Yacoub A, Kelley M R and Deutsch WA 1996Drosophila ribosomal protein P0 contains apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease activity;Nucleic Acids Res. 24 4298–4303
Zampieri S, Degen W, Ghiradello A, Doria A, van Venrooij W J 2001 Dephosphorylation of autoantigenic ribosomal P proteins during Fas-L induced apoptosis: a possible trigger for the development of the autoimmune response in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus;Ann. Rheum. Dis. 60 72–76
Zurdo J, van den Berg A, Parada P, Nusspaumer G, Jimenez-Diaz, Remacha A and Ballesta JPG 2000 Assembly ofSaccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomal stalk: Binding of P1 protein is required for the interaction of P2 proteins;Biochemistry 39 8929–8934
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aruna, K., Chakraborty, T., Nambeesan, S. et al. Identification of a hypothetical membrane protein interactor of ribosomal phosphoprotein P0. J Biosci 29, 33–43 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02702559
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02702559