Summary
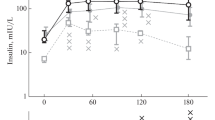
The aim of this study was to evaluate the relationships between blood lactate and plasma glucose, insulin (IRI) and C-peptide (IRCP) during the first hour of an oral glucose load (OGTT, 100 g). Twelve controls, sixteen non-insulin-dependent (NIDDM) and four insulin-dependent (IDDM) diabetic subjects were studied. A significant increase in blood lactate was observed at 15 min in normal subjects, whereas there was a delayed increase at 45 min in NIDDM subjects, in the presence of IRCP increments of 0.31 nmol/l. In order to have a minimum significant lactate increment, the threshold value of peripheral IRCP increment was about 0.30 nmol/l. In IDDM subjects, despite considerable hyperglycemia, blood lactate concentration remained unchanged throughout the test. In normal and NIDDM subjects there was a significant negative correlation between Δ lactate and Δ glucose (r=−0.89, p<0.001) and a significant positive correlation between Δ lactate and Δ IRCP (r=0.78, p<0.001). In conclusion, hyperglycemia itself and the lack of increase in insulin secretion do not affect blood lactate increase during OGTT; blood concentration of this metabolite depends mainly on an early insulin secretion apt to enhance tissue glucose uptake and to inhibit gluconeogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asplin C. M., Hartog M., Goldie D. J., Alberti K. G. M. M., Binder C., Faber O. K.: Diurnal profiles of serum insulin, C-peptide and blood intermediary metabolites in insulin treated diabetics, their relationship to the control of diabetes and the role of endogenous insulin secretion — Quart. J. Med.190, 343–360, 1979.
Bergman R. N., Beir J. R., Hourigan P. M.: Intraportal glucose infusion matched to oral glucose absorption. Lack of evidence for ‘Gut Factor’ involvement in hepatic glucose storage — Diabetes31, 27–35, 1982.
Bratusch-Marrain P. R., Waldhäusl W. K., Gasić S., Korn A., Nowotny P.: Oral glucose tolerance test: effect of different glucose loads on splanchnic carbohydrate and substrate metabolism in healthy man — Metabolism29, 289–295, 1980.
Chiasson J. L., Atkinson R. L., Cherrington A. D., Keller U., Sinclair-Smith B. C., Lacy W. W., Liljenquist J. E.: Effects of insulin at two dose levels on gluconeogenesis from alanine in fasting man — Metabolism29, 810–821, 1980.
Chiasson J. L., Liljenquist J. E., Finger F. E., Lacy W. W.: Differential sensitivity of glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis to insulin infusions in dogs — Diabetes25, 283–291, 1976.
Davidson M. B.: Autoregulation by glucose of hepatic glucose balance: permissive effect of insulin — Metabolism30, 279–284, 1981.
De Fronzo R. A., Jacot E., Jequier E., Maeder E., Wahren J., Felber J. P.: The effect of insulin on the disposal of intravenous glucose. Results from indirect calorimetry and hepatic and femoral venous catheterization — Diabetes30, 1000–1007, 1981.
Doar J. W. H., Cramp D. G., Maw D. S. J., Seed M., Wynn V.: Blood pyruvate and lactate levels during oral and intravenous glucose tolerance test in diabetes mellitus — Clin. Sci.39, 259–269, 1970.
Felig P., Wahrén J.: Influence of endogenous insulin secretion on splanchnic glucose and aminoacid metabolism in man — J. clin. Invest.50, 1702–1711, 1971.
Felig P., Wahrén J., Hendler R.: Influence of oral glucose ingestion on splanchnic glucose and gluconeogenic substrate metabolism in man — Diabetes24, 468–475, 1975.
Hohorst H. J.: L-(+) lactate. In:Bergmeyer H. V. (Ed.): Methods of enzymatic analysis. Academic Press, New York-London, 1974.
Horwitz D. L., Starr J. I., Mako M. E., Blackard W. G., Rubenstein A. H.: Proinsulin, insulin and C-peptide concentration in human portal and peripheral blood — J. clin. Invest.55, 1278–1283, 1975.
Katz J., McGarry J. D.: The glucose paradox. Is glucose a substrate for liver metabolism? — J. clin. Invest.74, 1901–1909, 1984.
Jackson R. A., Moloney M., Lowy C., Wright A. D., Hartog M., Pilkington T. R. E., Fraser T. R.: Differences between metabolic responses to fasting in obese diabetic and obese nondiabetic subjects — Diabetes20, 214–227, 1971.
Madsbad S., Faber O. K., Binder C., Alberti K. G. M. M., Lloyd B.: Diurnal profiles of intermediary metabolites in insulin-dependent diabetes and their relationship to different degrees of residual B-cell function — Acta diabetol. lat.18, 115–121, 1981.
Miller T. B. Jr.: Effects of diabetes on glucose regulation of enzymes involved in hepatic glycogen metabolism. — Amer. J. Physiol.234, E13-E19, 1978.
Miller T. B. Jr., Hazen R., Larner J.: An absolute requirement for insulin in the control of hepatic glycogenesis by glucose — Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun.53, 466–474, 1973.
National Diabetes Data Group: Classification and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and other categories of glucose intolerance — Diabetes28, 1039–1057, 1979.
Pozefsky T., Felig P., Tobin J. D., Soeldner J. S., Cahill G. F. Jr.: Amino acid balance across tissues of the forearm in postabsorptive man. Effect of insulin at two dose levels — J. clin. Invest.48, 2273–2282, 1969.
Rabinowitz D., Liljenquist J. E.: Glucose metabolism in intact man: the responsiveness of splanchnic and peripheral tissues to insulin — Metabolism27, (Suppl. 2), 1832–1838, 1978.
Rabinowitz D., Zierler K. L.: Forearm metablism in obesity and its response to intraarterial insulin. Characterization of insulin resistance and evidence for adaptive hyperinsulinism — J. clin. Invest.41, 2173–2181, 1962.
Radziuk J.: Sources of carbon in hepatic glycogen synthesis during absorption of an oral glucose load in humans — Fed. Proc.41, 110–116, 1982.
Radziuk J., Inculet R.: The effects of ingested and intravenous glucose on forearm uptake of glucose and glucogenic substrate in normal man — Diabetes32, 977–981, 1983.
Rizza R., Mandarino L., Gerich J.: Dose response characteristics for effects of insulin on production and utilization of glucose in man — Amer. J. Physiol.240, E630–639, 1981.
Saccà L., Cicala M., Trimarco B., Ungaro B., Vigorito C.: Differential effects of insulin on splanchnic and peripheral glucose disposal after an intravenous glucose load in man — J. clin. Invest.70, 117–126, 1982.
Saccà L., Hendler R., Sherwin R. S.: Hyperglycemia inhibits glucose production in man independent of changes in glucoregulatory hormones — J. clin. Endocrinol. Metabol.47, 1160–1163, 1978.
Saccà L., Vitale D., Cicala M., Trimarco B., Ungaro B.: The glucoregulatory response to intravenous glucose infusion in normal man: roles of insulin and glucose — Metabolism30, 457–461, 1981.
Shulman G. I., Lacy W. W., Liljenquist J. E., Keller U., Williams P. E., Cherrington A. D.: Effect of glucose independent of changes in insulin and glucagon secretion, on alanine metabolism in the conscious dog — J. clin. Invest.65, 496–505, 1980.
Trevisan R., Nosadini R., Avogaro A., Lippe G., Duner E., Fioretto P., Deana R., Tessari P., Tiengo A., Velussi M., Cernigoi A., Del Prato S., Crepaldi G.: Type I diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance not only with regard to glucose, but also to lipid and amino acid metabolism — J. clin. Endocrinol. Metabol.62, 1155–1162, 1986.
Waldhäusl W. K., Bratusch-Marrain P., Gasić S., Korn A., Nowotny P.: Insulin production rate, hepatic insulin retention and splanchnic carbohydrate metabolism after oral glucose ingestion in hyperinsulinaemic type 2 (non insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus — Diabetologia23, 6–15, 1982.
Wahrén J., Felig P., Cerasi E., Luft R.: Splanchnic and peripheral glucose and amino acid metabolism in diabetes mellitus — J. clin. Invest.51, 1870–1878, 1972.
Zierler K. L., Rabinowitz D.: Effect of very small concentrations of insulin on foream metabolism. Persistence of its action on potassium and free fatty acids without its effects on glucose — J. clin. Invest.43, 95–962, 1964.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prando, R., Cheli, V., Buzzo, P. et al. Blood lactate behavior after glucose load in diabetes mellitus. Acta diabet. lat 25, 247–256 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02624820
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02624820