Summary
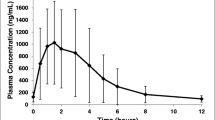
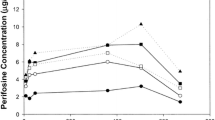
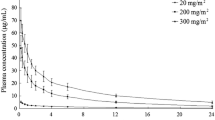
Thirty-six patients were entered on this study to determine the pharmacology, bioavailability, and toxicity of three different oral formulations of cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan®, Endoxan®, and an investigational direct compression tablet). Patients were randomized with respect to the order in which they received the different oral cyclophosphamide preparations, and received each one for two weeks followed by a two week washout period. Concurrent chemotherapy was allowed provided it remained constant across all 3 courses of cyclophosphamide. Plasma concentrations of cyclophosphamide and phosphoramide mustard were measured by gas chromatography with electron capture detection. Peak plasma cyclophosphamide concentrations and times to peak plasma cyclophosphamide and phosphoramide mustard preparations were significantly greater for Endoxan® than for Cytoxan® and the investigational direct compression tablet. Drug area under the concentration-time curve (AUC), bioavailability, and plasma elimination half-life could not be reliably calculated for Endoxan® but were similar for Cytoxan® and the investigational formulation. Based on AUC comparisons, bioavailability of parent compound (relative to an oral cyclophosphamide solution) was 85% for Cytoxan® and 69% for the investigational formulation. This difference was not significant. There were no significant differences between the 3 formulations with respect to any individual type of toxicity, although the investigational formulation tended to be associated with somewhat less overall toxicity (p=0.08).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shaw IC, Earl LK, Mruzek MN, Harper PG, McLean AEM, Souhami RL: Differences in bioavailability between two preparations of cyclophosphamide. Lancet i: 709 1983.
Holdiness MR, Morgan LR Jr: Electron-Capture-Gas Chromatographic Analysis of I ifosfamide in Human Plasma and Urine. J of Chromatogr 275 (2):432–435, 1983
Stewart DJ, Nundy D, Maroun JA, Tetreault L, Prior J: Bioavailability pharmacokinetics and clinical effects of an oral preparation of etoposide (VP-16-213, NSC 141540). Cancer Treat Rep 69:269–273 1985
Stewart DJ, Grewaal D, Green RM, Verma S, Maroun JA, Redmond D, Robillard L, Gupta S: Bioavailability and pharmacology of oral idarubicin. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 27:308–314 1991.
Grochow LB, Colvin M: Clinical pharmacokinetics of cyclophosphamide. Clin Pharmacokinet 4(5):380–394, 1979
Struck RF, Alberts DS, Horne K, Philips JG, Peng YM, Roe DJ: Plasma pharmacokinetics of cyclophosphamide and its cytotoxic metabolites after intravenous versus oral administration in a randomized, crossover trial. Cancer Res 47:2723–2726 1987.
Wilkinson PM, O’Neill VA, Thatcher N, Lucas SB: Pharmacokinetics of high-dose cyclophosphamide in patients with metastatic bronchogenic carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 11:196–199 1983.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stewart, D.J., Morgan, L.R., Verma, S. et al. Pharmacology, relative bioavailability, and toxicity of three different oral cyclophosphamide preparations in a randomized, cross-over study. Invest New Drugs 13, 99–107 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02614228
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02614228